Clemmensen reduction
| Clemmensen reduction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Erik Christian Clemmensen |
| Reaction type | Organic redox reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | clemmensen-reduction |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000038 |
Clemmensen reduction is a chemical reaction described as a reduction of ketones (or aldehydes) to alkanes using zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.[1][2][3] This reaction is named after Erik Christian Clemmensen, a Danish chemist.[4]
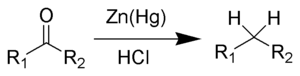
The Clemmensen reduction is particularly effective at reducing aryl-alkyl ketones,[5][6] such as those formed in a Friedel-Crafts acylation. With aliphatic or cyclic ketones, zinc metal reduction is much more effective.[7]
The substrate must be unreactive to the strongly acidic conditions of the Clemmensen reduction. Acid-sensitive substrates should be reacted in the Wolff-Kishner reduction, which utilizes strongly basic conditions; a further, milder method is the Mozingo reduction. The oxygen atom is lost in the form of one molecule of water.
However, the reaction is not suitable for substances sensitive to acids. Also, carboxylic acid groups cannot be reduced by this method, although they can be reduced by treating with soda lime and then heating.
In spite of the antiquity of this reaction, the mechanism of the Clemmensen reduction remains obscure. Due to the heterogeneous nature of the reaction, mechanistic studies are difficult, and only a handful of studies have been disclosed.[8][9] Proposal mechanisms invoke organozinc intermediates, possibly zinc carbenoids, either as discrete species or with the organic fragment bound to the metal surface. However, the corresponding alcohol is not believed to be an intermediate, since subjection of alcohols to Clemmensen conditions generally does not afford the alkane product.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Clemmensen, E. (1913). "Reduktion von Ketonen und Aldehyden zu den entsprechenden Kohlenwasserstoffen unter Anwendung von amalgamiertem Zink und Salzsäure". Chemische Berichte. 46: 1837–1843. doi:10.1002/cber.19130460292.
- ↑ Clemmensen, E. (1914). "Über eine allgemeine Methode zur Reduktion der Carbonylgruppe in Aldehyden und Ketonen zur Methylengruppe". Chemische Berichte. 47: 51–63. doi:10.1002/cber.19140470108.
- ↑ Clemmensen, E. (1914). "Über eine allgemeine Methode zur Reduktion der Carbonylgruppe in Aldehyden und Ketonen zur Methylengruppe. (III. Mitteilung.)". Chemische Berichte. 47: 681–687. doi:10.1002/cber.191404701107.
- ↑ Biographies of Chemists, accessed 6 Feb 2007
- ↑ "γ-Phenylbutyric acid". Org. Synth. 2: 499. 1943.; Vol. 15, p.64 (1935)
- ↑ "Creosol". Org. Synth. 4: 203. 1963.; Vol. 33, p.17 (1953).
- ↑ "Modified Clemmensen Reduction: Cholestane". Org. Synth. 6: 289. 1988.; Vol. 53, p.86 (1973).
- ↑ Brewster, James H. (2002-05-01). "Reductions at Metal Surfaces. II. A Mechanism for the Clemmensen Reduction 1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (24): 6364–6368. doi:10.1021/ja01653a035.
- ↑ Nakabayashi, Tadaaki (2002-05-01). "Studies on the Mechanism of Clemmensen Reduction. I. The Kinetics of Clemmensen Reduction of p-Hydroxyacetophenone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 82 (15): 3900–3906. doi:10.1021/ja01500a029.
- ↑ Martin, Elmore L. (2004-01-01). The Clemmensen Reduction. John Wiley & Sons,Inc. ISBN 9780471264187. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or001.07.
Reviews
- Martin, E. L. (1942). "The Clemmensen reduction". Org. React. 1: 155.
- Buchanan, J. G. St. C.; Woodgate, P. D. (1969). "The Clemmensen reduction of difunctional ketones". Quarterly Reviews, Chemical Society. 23: 522. doi:10.1039/QR9692300522.
- Vedejs, E. (1975). "Clemmensen reduction of ketones in anhydrous organic solvents". Org. React. 22: 401–422.
- Yamamura, S.; Nishiyama, S. (1991). "1.13.2.2 Clemmensen reduction". Comprehensive Organic Synthesis. 8: 309–313.