Ciladopa
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
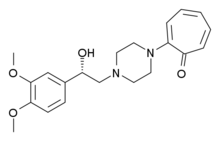
| Formula | C21H26N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 370.44 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Ciladopa (AY-27,110) is a dopamine agonist with a similar chemical structure to dopamine.[1] It was under investigation as an antiparkinsonian agent but was discontinued due to concerns of tumorogenesis in rodents.[2][3][4][5]
References
- ↑ Voith K (1985). "The comparative long-term effects of ciladopa (AY-27,110), a chemically novel dopaminergic agonist, in 6-OHDA-lesioned and intact rats". Psychopharmacology. 85 (4): 405–9. PMID 3927334. doi:10.1007/BF00429654.
- ↑ Koller WC, Fields JZ, Gordon JH, Perlow MJ (September 1986). "Evaluation of ciladopa hydrochloride as a potential anti-Parkinson drug". Neuropharmacology. 25 (9): 973–9. PMID 3774130. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(86)90190-5.
- ↑ Weiner WJ, Factor SA, Sanchez-Ramos J, Berger J (1987). "A double-blind evaluation of ciladopa in Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders : Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society. 2 (3): 211–7. PMID 3332914. doi:10.1002/mds.870020308.
- ↑ Lieberman A, Gopinathan G, Neophytides A, Pasternack P, Goldstein M (May 1987). "Advanced Parkinson's disease: use of partial dopamine agonist, ciladopa". Neurology. 37 (5): 863–5. PMID 3574692. doi:10.1212/wnl.37.5.863.
- ↑ Lang AE (August 1987). "Update on dopamine agonists in Parkinson's disease: "beyond bromocriptine"". The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. Le Journal Canadien Des Sciences Neurologiques. 14 (3 Suppl): 474–82. PMID 3315148.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.