Chlornaphazine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
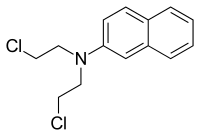
| IUPAC name
N,N-bis(2-Chloroethyl)naphthalen-2-amine | |
| Other names
Chlornapazine; 2-Naphthylbis(chloroethyl)amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.078 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H15Cl2N | |
| Molar mass | 268.18 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chlornaphazine, a derivative of 2-naphthylamine, is a nitrogen mustard that was developed in the 1950s for the treatment of polycythemia and Hodgkin's disease.[1] However, a high incidence of bladder cancers in patients receiving treatment with chlornaphthazine led to use of the drug being discontinued.[2]
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has listed chlornaphazine as a human carcinogen.[3]
References
- ↑ Videbaek, A.; Kaae, S. (1954). "2-Naphthylbis(chloroethyl)amine in the treatment of malignant diseases, particularly Hodgkin's disease". Acta Medica Scandinavica. 149 (5): 361–368. PMID 13180246. doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1954.tb11446.x.
- ↑ Benedicte Laursen (1970). "Cancer of the Bladder in Patients Treated with Chlornaphazine". Br Med J. 3 (5724): 684–685. PMC 1701774
 . PMID 5470116. doi:10.1136/bmj.3.5724.684.
. PMID 5470116. doi:10.1136/bmj.3.5724.684. - ↑ N,N-Bis(2-Chloroethyl)-2-Naphthylamine (Chlornaphazine), International Agency for Research on Cancer
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.