Chesapeake Bay impact crater
|
Location of impact site in relation to the United States | |
| Impact crater/structure | |
|---|---|
| Confidence | Confirmed |
| Diameter | 85 kilometres (53 mi) |
| Depth | 1.3 kilometres (0.81 mi) |
| Age | 35.5 ± 0.3 million |
| Exposed | No |
| Drilled | Yes |
| Location | |
| Location | Chesapeake Bay |
| Coordinates | 37°17′N 76°1′W / 37.283°N 76.017°WCoordinates: 37°17′N 76°1′W / 37.283°N 76.017°W[1] |
| Country | United States |
| State | Virginia |
| Municipality | Cape Charles |
 Impact location Location of impact site in Virginia | |
| Access | U.S. Route 13 to S.R. 184 |
The Chesapeake Bay impact crater was formed by a bolide that impacted the eastern shore of North America about 35.5 ± 0.3 million years ago, in the late Eocene epoch. It is one of the best-preserved "wet-target" or marine impact craters, and the largest known impact crater in the U.S.
Continued slumping of sediments over the rubble of the crater has helped shape the Chesapeake Bay.
Formation and aftermath
During the warm late Eocene, sea levels were high, and the Tidewater region of Virginia lay in the coastal shallows. The shore of eastern North America, about where Richmond, Virginia, is today, was covered with dense tropical rainforest, and the waters of the gently sloping continental shelf were rich with marine life that was depositing dense layers of lime from their microscopic shells.
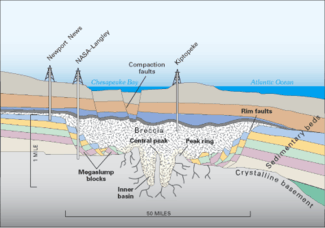
The bolide made impact at a speed of many kilometers per second, punching a deep hole through the sediments and into the granite continental basement rock. The bolide itself was completely vaporized, with the basement rock being fractured to depths of 8 km (5.0 mi), and a peak ring being raised around it. The deep crater, 38 km (24 mi) across, is surrounded by a flat-floored terrace-like ring trough with an outer edge of collapsed blocks forming ring faults.
The entire circular crater is about 85 km (53 mi) in diameter and 1.3 km (0.81 mi) deep, an area twice the size of Rhode Island, and nearly as deep as the Grand Canyon. However, numerical modeling techniques by Collins et al. indicate that the post-impact diameter was likely to have been around 40 km (25 mi), rather than the observed 85 km (53 mi).[2]
The surrounding region suffered massive devastation. USGS scientist David Powars, one of the impact crater's discoverers, has described the immediate aftermath: "Within minutes, millions of tons of water, sediment, and shattered rock were cast high into the atmosphere for hundreds of miles along the East Coast." An enormous tsunami engulfed the land and possibly even reached the Blue Ridge Mountains.[3] The sedimentary walls of the crater progressively slumped in, widened the crater, and formed a layer of huge blocks on the floor of the ring-like trough. The slump blocks were then covered with the rubble or breccia. The entire bolide event, from initial impact to the termination of breccia deposition, lasted only a few hours or days. In the perspective of geological time, the 1.2 km (0.75 mi) breccia is an instantaneous deposit. The crater was then buried by additional sedimentary beds that have accumulated during the 35 million years following the impact.
The impact has been identified as the source of the North American tektite field, namely the Georgiaite and Bediasite fields.[4]
Discovery
Until 1983, no one suspected the existence of a large impact crater buried beneath the lower part of the Chesapeake Bay and its surrounding peninsulas. The first hint was a 20 cm (8 in)-thick layer of ejecta that turned up in a drilling core taken off Atlantic City, New Jersey, far to the north. The layer contained the fused glass beads called tektites and shocked quartz grains that are unmistakable signs of a bolide impact.
In 1993, data from oil exploration revealed the extent of the crater.[5]
Effects on local rivers
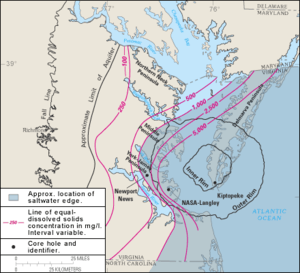
The continual slumping of the rubble within the crater has affected the flow of the rivers and shaped the Chesapeake Bay. The impact crater created a long-lasting topographic depression which helped predetermine the course of local rivers and the eventual location of Chesapeake Bay. Most important for present-day inhabitants of the area, the impact disrupted aquifers. The present freshwater aquifers lie above a deep salty brine, remnants of 100–145 million year old Early Cretaceous North Atlantic seawater, making the entire lower Chesapeake Bay area susceptible to groundwater contamination.[6]
The crater is also one of three factors contributing to the sinking of land near the Chesapeake Bay. For example, Hampton Roads is gradually sinking at a rate between 15 and 23 centimeters (5 and 7.5 inches) per century. This is occurring because of the slippage of the coast into the crater, the reverse effects of isostatic rebound of the crust of the earth from the weight of long absent glaciers north of Maryland, and groundwater removal.[7]
See also
- Toms Canyon structure probable impact crater 322 km (200 mi) to the northeast.
- Popigai crater of similar age
- Grande Coupure
References
- ↑ "Chesapeake Bay". Earth Impact Database. University of New Brunswick. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
- ↑ Collins, Gareth S.; Wünnemann, Kai (2005). "How big was the Chesapeake Bay impact? Insight from numerical modeling". Geology. 33 (12): 925–928. doi:10.1130/G21854.1.
- ↑ Dell'Amore, Christine (21 Nov 2013). ""Mind-Blowing" Discovery: Oldest Body of Seawater Found in Giant Crater". National Geographic. National Geographic Society. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ↑ Koeberl, C.; Poag, C. W.; Reimold, W. U.; Brandt, D. (1 March 1996). "Impact Origin of the Chesapeake Bay Structure and the Source of the North American Tektites". Science. 271 (5253): 1263–1266. doi:10.1126/science.271.5253.1263.
- ↑ Poag, C. Wylie; Koeberl, Christian; Reimold, Wolf Uwe (1 January 2004). "The Chesapeake Bay crater: geology and geophysics of a Late Eocene submarine impact structure". Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag: 69–93,. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-18900-5. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
- ↑ Sanford, Ward E.; Doughten, Michael W.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Hunt, Andrew G.; Bullen, Thomas D. (13 November 2013). "Evidence for high salinity of Early Cretaceous sea water from the Chesapeake Bay crater". Nature. 503 (7475): 252–256. PMID 24226889. doi:10.1038/nature12714.
- ↑ James V. Koch (2010). "Costs of Defending Against Rising Sea Levels and Flooding in Mid-Atlantic Metropolitan Coastal Areas: The Basic Issues" (PDF). The Journal of Regional Analysis & Policy. 40 (1): 53–60. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
Bibliography
- Poag, C. Wiley. Chesapeake Invader: Discovering America's Giant Meteorite Crater. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1999. ISBN 0-691-00919-8
- Post-impact Effects of the Eocene Chesapeake Bay Impact, Lower York-James Peninsula, Virginia, 31st Annual Meeting, Virginia Geological Field Conference, Williamsburg, Virginia, Oct. 19 and 20, 2001, G.H. Johnson et al. (fieldtrip guidebook)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chesapeake Bay impact crater. |
- 'Isostatic Rebound and its effects on the Chesapeake Bay'
- A brief introduction to the Chesapeake Bay Impact Crater.
- USGS, 'Investigating the Chesapeake Bay Impact Crater.'
- USGS, 'The Chesapeake meteorite: message from the past.'
- 'The Chesapeake Bay bolide: modern consequences of an ancient cataclysm.'
- Earth Impact Database
- Satellite image of the region (from Google Maps)
- Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure Deep Drilling Project
- 'North American Plate, mid-Atlantic Inversion a result of the Chesapeake Invader?' www.impacttectonics.org


