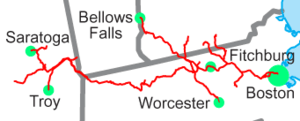
Fitchburg Railroad
 | |
| Locale | Boston to Fitchburg, Massachusetts and beyond into Vermont and New York |
|---|---|
| Dates of operation | 1840–1919 |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
The Fitchburg Railroad is a former railroad company, which built a railroad line across northern Massachusetts, United States, leading to and through the Hoosac Tunnel. The Fitchburg was leased to the Boston and Maine Railroad in 1900. The main line from Boston to Fitchburg is now operated as the MBTA Fitchburg Line; Pan Am Railways runs freight service on some other portions.
History

The Charlestown Branch Railroad was incorporated April 4, 1835, as a short branch from the Boston and Lowell Railroad to Sweet's Wharf in Charlestown, opening in January 1840. The Fitchburg Railroad was incorporated March 3, 1842, to run from Boston to Fitchburg, and bought land next to the Charlestown Branch in May 1843. Construction began on May 20, and the first section to Waltham opened on December 20, 1843, operated by the Charlestown Branch until May 1, 1844. Further sections opened to Concord June 17, 1844, Acton October 1, 1844, Shirley December 30, 1844, and Fitchburg March 5, 1845. The new track next to the Charlestown Branch opened in August 1844; the Fitchburg Railroad leased the Charlestown Branch itself on September 1, 1845, and outright bought the branch on January 31, 1846. In 1848 a new bridge opened, carrying the line from Charlestown to downtown Boston.
The original Charlestown terminal was southwest of City Square, west of the Warren Bridge (42°22′12″N 71°03′47″W / 42.370°N 71.063°W). The downtown Boston terminal was on the north side of Causeway Street between Haverhill Street and Beverly Street until the North Station union station opened in 1893.
In 1854 Henry David Thoreau wrote in his work Walden about his skepticism of the Fitchburg Railroad near Walden Pond.[1]
The Boston and Maine Railroad leased the Fitchburg for 99 years from July 1, 1900 as its Fitchburg Division. The two companies merged to form a new B&M December 1, 1919. The MBTA bought the line from Boston to Fitchburg, along with many other lines, from the B&M on December 27, 1976. Guilford Transportation took over the former B&M in June 1983.
Passenger service ran only to Fitchburg after 1960. On January 18, 1965, service was cut back to West Concord, but was restored to Ayer on June 28, 1965. On March 1, 1975, it was cut back to South Acton, but was restored to Fitchburg and beyond to Gardner on January 13, 1980. Gardner service was ended on January 1, 1987, when Amtrak took over the MBTA contract, due to a dispute between Amtrak and Guilford; the MBTA only owned the trackage to Fitchburg.
The Fitchburg Line west of the old Stony Brook Railroad, which now junctions east of the old Ayer Junction, now serves as part of Pan Am Railways' main line between Mattawamkeag, Maine, and Mechanicville, New York.
Branches
Harvard
The Harvard Branch Railroad was incorporated and opened in 1849, splitting from the Fitchburg in Somerville and running to Harvard Square. It was never leased or owned by the Fitchburg, and was never successful, closing in 1855.
Lexington
The Lexington and West Cambridge Railroad was chartered in 1845 and opened in 1846 as a branch from the Fitchburg near the present-day Alewife Brook Reservation area (now considered part of North Cambridge) to Lexington. The Fitchburg operated it from opening, leasing it from 1847 to 1859. In 1868 it was reorganized as the Lexington and Arlington Railroad and bought by the Boston and Lowell Railroad in 1870. The connection to the Fitchburg was cut (but reopened in 1927). Passenger service ceased in January 1977 due to a blizzard, never to resume. Freight operation ended in 1981, and the line was formally abandoned in 1991 to make way for the Minuteman Commuter Bike Trail.[2]
Watertown
The Watertown Branch Railroad was incorporated 1847, first as an independent short line RR, but was quickly taken over by the Fitchburg. It ran from the main line in Cambridge through Watertown to Waltham. It opened in 1851 and was soon the main passenger line between Boston and Waltham and one of the few branch lines to be double tracked. Passenger service on the line ended in 1938. The middle section of the line in the Watertown Square area was abandoned in 1960. This split the branch in two. The west side of the branch was mostly abandoned in 2000. The east side of the branch contained only one customer, Newly Weds Foods. The last delivery made was in early 2007, with the last move occurring on the line in early 2008. The entire branch is now either abandoned or out of service.
Marlborough
The Lancaster and Sterling Railroad was incorporated in 1846 and immediately merged with the Fitchburg Railroad. It was built from a junction at South Acton roughly southwest to Hudson, opening in 1850. The Marlborough Branch Railroad was incorporated in 1852 and opened in 1855, continuing the line from Hudson south to Marlborough. It was leased by the Fitchburg in 1853 and bought outright in 1863. This branch made South Acton a major junction and service point on the Fitchburg Route. A turntable and engine house existed in South Acton to service trains well into the 20th century. Passenger service from Marlborough ceased in 1932, and the section between Maynard and Hudson was abandoned in 1943. The section between Hudson saw its last passenger traffic via the Central Massachusetts Railroad in 1939, but it was not abandoned until 1980. Passenger service to Maynard via the Fitchburg mainline in South Acton ceased in 1958. The line was formally abandoned in 1979.[3] It is in the process of being converted into the Assabet River Rail Trail.
Peterborough and Shirley
The Peterborough and Shirley Railroad was incorporated in 1845 and opened as a branch from the Fitchburg in Ayer to West Townsend in 1848, continuing to Mason, New Hampshire, in 1849 or 1850. The Fitchburg Railroad leased it in 1847 and bought it in 1860, with an extension to Greenville opening at some point.
Milford
The Brookline and Milford Railroad was incorporated and built in 1892 from the Peterborough and Shirley at Squannacook Junction north to the Wilton Railroad in Milford, New Hampshire. It was merged into the Fitchburg in 1895.
Vermont and Massachusetts Railroad
The Vermont and Massachusetts Railroad was chartered in 1844 and immediately merged the Brattleborough and Fitchburg Railroad of Vermont into itself. The first section, from Fitchburg to Baldwinville, opened in 1847 and was operated by the Fitchburg Railroad until 1849. Further extensions opened to Athol and Miller's Falls in 1848, and to Brattleboro, Vermont, in 1850. Later in 1850, a branch from Grout's Corner west to Greenfield opened. A short branch to Turner's Falls opened in 1870 or 1871.
The original main line north from Miller's Falls was leased to the Rutland Railroad in 1870, which leased itself to the Vermont Central Railroad in 1871, which became the Central Vermont Railroad in 1872. This was a continuation of the New London Northern Railroad, built south from Miller's Falls in 1867 and also leased to the Vermont Central in 1871.
In 1874 the Fitchburg Railroad leased the rest of the V&M, extending its line west to Greenfield (and beyond via the Troy and Greenfield Railroad - see below).
- Ashburnham
The Ashburnham Railroad was chartered in 1871 and opened in 1874 from the V&M at South Ashburnham to Ashburnham. The Fitchburg bought it in 1885.
- Turners Falls
The Turners Falls Branch connected the main line at Turners Falls Junction to Turners Falls. It opened in 1871.
Cheshire
The Cheshire Railroad was chartered in New Hampshire in 1844, consolidating with the Winchendon Railroad of Massachusetts (chartered 1845) in 1845. The first section opened in 1847, from the Vermont and Massachusetts Railroad at South Ashburnham to Winchendon; an extension to Troy, New Hampshire, also opened in 1847. Extensions to Keene, New Hampshire, and Bellows Falls, Vermont, opened in 1848 and 1849, forming a connection between the Fitchburg Railroad and the Vermont Central Railroad (via trackage rights over the V&M east of South Ashburnham).
The Cheshire Railroad was merged into the Fitchburg in 1890, becoming the Cheshire Branch. Passenger service ended in 1958, and the line was abandoned in sections, Winchendon north in 1970 (after the bankruptcy of the Rutland RR) and in 1984 for the rest.[4]
- Monadnock
The Monadnock Railroad was incorporated in 1848, but did not open from Winchendon to Jaffrey, New Hampshire, until December 1870 and to Peterborough in 1871, from which the Peterborough and Hillsborough Railroad continued the line north after 1878. The Boston, Barre and Gardner Railroad, running south from Winchendon, leased the Monadnock in 1874, but transferred the lease to the Cheshire Railroad in 1880 to keep it out of the hands of the Boston and Albany. The Fitchburg took control of the Monadnock in 1890.
- Boston, Barre and Gardner
The Barre and Worcester Railroad was chartered in 1847 and reorganized in 1857 as the Boston, Barre and Gardner Railroad. It opened in 1871 between the Worcester and Nashua Railroad at Barber (from which it ran to Worcester via trackage rights) and the V&M in Gardner. An extension in 1874 took it to the Cheshire Railroad at Winchendon.
The BB&G leased the Monadnock Railroad in 1874, but reassigned the lease to the Cheshire in 1880. The BB&G was merged into the Fitchburg in 1885.
Troy and Greenfield
The Troy and Greenfield Railroad was incorporated and chartered in 1848, with a planned line from the Vermont border in Williamstown east through the Hoosac Tunnel to Greenfield. The first section opened from the state line to the west end of the tunnel at North Adams in 1859. The tunnel itself opened in 1875, before which the Troy and Boston Railroad leased the T&G. The T&G was consolidated into the Fitchburg Railroad in 1887.
The Southern Vermont Railroad was chartered in 1848 to connect the T&G across the southwest corner of Vermont to the New York state line. It opened in 1859 and was leased by the Troy and Boston Railroad, but in 1860 the T&G bought it. The Fitchburg bought the Southern Vermont directly in 1891.
The Troy and Boston Railroad was chartered in 1849 to continue the line west to Troy, New York. It was consolidated into the Fitchburg in 1887. The Troy and Bennington Railroad was organized in 1851 to build a branch from the Troy and Boston at Hoosick Junction to the Vermont state line towards Bennington. It opened in 1852, continuing as the Western Vermont Railroad (leased by the Troy and Boston from 1857 until it was reorganized into the Bennington and Rutland Railway in 1865).
- Hoosac Tunnel and Wilmington
The Deerfield River Railroad opened in 1885 as a private narrow gauge railroad connecting the V&M at the Hoosac Tunnel to the Deerfield Company saw mills at Readsboro, Vermont. It was taken over by the Hoosac Tunnel and Wilmington Railroad in 1886 and later extended to Wilmington, Vermont. The line was never owned by the Fitchburg or Boston and Maine Railroad, and was abandoned from Readsboro to Wilmington in 1937. The remainder of the line from the connection with the Boston & Maine at Hoosac Tunnel to Readsboro was abandoned in 1971.
Boston, Hoosac Tunnel and Western
The Boston, Hoosac Tunnel and Western Railway was organized in 1877 and opened in 1879 on a line from the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad at Rotterdam Junction, west of Schenectady, east to Mechanicville and beyond, closely paralleling the Troy and Boston into southwestern Vermont. The Fitchburg bought the BHT&W in 1887.
The Hoosac Tunnel and Saratoga Railway was chartered in 1880, and was leased by the BHT&W in 1882. In 1886 it merged with the Saratoga Lake Railway (also chartered 1880 and leased to the BHT&W in 1882) to form the Troy, Saratoga and Northern Railroad. The combined line was built in 1886 and 1887,[5] with a main line from Mechanicville (never built south to Troy) north and west to Saratoga Springs, and a branch east to Schuylerville. The Fitchburg Railroad leased it in 1887.
Station and junction listing
This list shows all stations and junctions that have existed on the original Fitchburg Railroad between Boston and Fitchburg. A list of current stations is also available.
| Milepost | City | Station / Junction | Opening date | Connections and notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | Boston | Orange Line, Green Line and all north side Commuter Rail lines Amtrak Downeaster | ||
| Boston Engine Terminal | A flag stop with a wooden platform for MBTA employees only | |||
| MBTA Commuter Rail Lowell Line, Haverhill/Reading Line and Newburyport/Rockport Line split | ||||
| Somerville | Union Square | 1835[6] | closed | |
| Somerville | closed (Park Street) | |||
| 3.37 | Cambridge | 1843–45 | Red Line, originally Porter's | |
| 4.16 | West Cambridge (station) | 1886 | closed (137 Sherman Street), originally Brickyards | |
| 4.28 | West Cambridge (junction) | split with (abandoned) Watertown Branch Railroad loop (east of New Street) | ||
| 4.53 | split with (abandoned) Lexington and West Cambridge Railroad (just east of Alewife Brook Parkway) | |||
| 5.35 | join with (abandoned) Fitchburg Cutoff | |||
| 5.52 | Belmont | Hill's Crossing | closed (near Brighton Street, Belmont/Blanchard Road, Cambridge) | |
| 6.43 | Belmont Center | 74/75 bus, temporarily closed 1958, reopened March 4, 1974 | ||
| 7.39 | Waverley | 73 trolleybus, temporarily closed 1958, reopened March 4, 1974. | ||
| 8.31 | Waltham | Clematis Brook | closed June 1978. Was located off Clematis Ave. in Waltham. Track connection to the (abandoned) Central Massachusetts Railroad. | |
| 9.26 | Beaver Brook | closed June 1978. Was located on Rose Hill Way in Waltham. | ||
| join with (abandoned) Watertown Branch Railroad loop | ||||
| 9.86 | 70, 70A, 505, 553, 554, 556, 558 buses | |||
| 10.55 | Riverview | closed January 17, 1965 | ||
| 11.49 | originally Roberts | |||
| 12.23 | Weston | Stony Brook | closed | |
| 13.16 | Kendal Green | |||
| 13.72 | Hastings | limited service, five inbound trains and six outbound trains on weekdays. | ||
| 14.71 | Silver Hill | limited service, two inbound trains and three outbound trains on weekdays. | ||
| 16.66 | Lincoln | Lincoln | originally South Lincoln | |
| 17.76 | Baker Bridge | closed | ||
| 20.05 | Concord | Concord | ||
| 21.89 | ||||
| 25.06 | Acton | Clock Tower Shuttle; temporarily closed January 17, 1965, reopened June 28, 1965. | ||
| 26.77 | West Acton | closed January 17, 1965, reopened June 28, 1965, closed April 30, 1975. The station building has been torn down and currently houses New London Pizza. | ||
| 28.93 | Boxborough | Boxboro | closed. The station stop was located on Depot Road. | |
| 30.16 | Littleton | 1980 | opened January 13, 1980, as a replacement for the former Littleton station; terminal station for some trains. It is located near the intersection of Route 2 and Interstate 495, on Foster St. | |
| 31.47 | Littleton | Opened 1879, temporarily closed January 17, 1965, reopened June 28, 1965, closed April 30, 1975. Replaced by Littleton/Route 495. The former station building, Harwood depot, still stands at the intersection of Taylor Street and King Street. | ||
| 33.72 | Ayer | Willows | Closed; it was located between Littleton and Ayer (at Willow and Westford Roads) and served both communities. | |
| 36.07 | Ayer | temporarily closed January 17, 1965, reopened June 28, 1965, temporarily closed April 30, 1975, reopened January 13, 1980 | ||
| 39.43 319.43 |
Shirley | Shirley | temporarily closed January 17, 1965, reopened May 1981 | |
| 42.14 322.14 |
Lunenburg | Lunenburg | closed | |
| 45.34 325.34 |
Leominster | temporarily closed January 17, 1965, reopened January 13, 1980 | ||
| 49.55 329.55 |
Fitchburg | MRTA Buses to Gardner, temporarily closed January 17, 1965, reopened January 13, 1980 | ||
References
- ↑ https://www.wired.com/2010/08/0809thoreau-walden-published/
- ↑ Dale Karr, Ronald (1989). Lost Railroads of New England. Branch Line Press. p. 137. ISBN 0-942147-04-9.
- ↑ Karr, Ronald, Lost Railroads of New England, 2nd edition. pp. 107, 137, 139
- ↑ Lost Railroads of New England 2nd edition, by Ronald Karr
- ↑ "History of Saratoga Springs, NY". The Boston History Company. 1899. Retrieved 2008-03-14.
- ↑ "Union Square/Boynton Yards - Somerville Strategic Planning and Community Development". Retrieved 2010-08-04.
See also
- File:Middlesex Canal (Massachusetts) map, 1852.jpg, map showing branches in Boston area