Channel Tunnel
 Map of the Channel Tunnel | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Location | English Channel (Strait of Dover) |
| Coordinates | 51°00′45″N 1°30′15″E / 51.0125°N 1.5041°ECoordinates: 51°00′45″N 1°30′15″E / 51.0125°N 1.5041°E |
| Status | Active |
| Start |
Folkestone, Kent, England, United Kingdom (51°5′49.5″N 1°9′21″E / 51.097083°N 1.15583°E) |
| End |
Coquelles, Pas-de-Calais, Hauts-de-France, France (50°55′22″N 1°46′50.16″E / 50.92278°N 1.7806000°E) |
| Operation | |
| Opened |
|
| Owner | Eurotunnel |
| Operator |
|
| Character | Through-rail passenger and freight. Vehicle shuttle. |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 50.45 km (31.35 mi) |
| No. of tracks |
2 single track tunnels 1 service tunnel |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) (standard gauge) |
| Electrified | 25 kV AC OHLE, 5.87 m[1] |
| Operating speed | 160 kilometres per hour (99 mph) |
| Channel Tunnel / Eurotunnel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Mileages from Castle Hill Tunnel Portal Mileages to terminals measured around terminal loops | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Channel Tunnel (French: Le tunnel sous la Manche; also nicknamed Chunnel)[2][3] is a 50.45-kilometre (31.35 mi) rail tunnel linking Folkestone, Kent, in the United Kingdom, with Coquelles, Pas-de-Calais, near Calais in northern France, beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. At its lowest point, it is 75 m (250 ft) deep below the sea bed, and 115 m (380 ft) below sea level.[4][5][6] At 37.9 kilometres (23.5 mi), the tunnel has the longest undersea portion of any tunnel in the world, although the Seikan Tunnel in Japan is both longer overall at 53.85 kilometres (33.46 mi) and deeper at 240 metres (790 ft) below sea level. The speed limit for trains in the tunnel is 160 kilometres per hour (99 mph).[7]
The tunnel carries high-speed Eurostar passenger trains, the Eurotunnel Shuttle for road vehicles—the largest such transport in the world[8]—and international goods trains.[9] The tunnel connects end-to-end with the LGV Nord and High Speed 1 high-speed railway lines.
Ideas for a cross-Channel fixed link appeared as early as 1802,[10][11] but British political and press pressure over the compromising of national security stalled attempts to construct a tunnel.[12] An early attempt at building a Channel Tunnel was made in the late 19th century, on the English side "in the hope of forcing the hand of the English Government".[13] The eventual successful project, organised by Eurotunnel, began construction in 1988 and opened in 1994. At £5.5 billion (1985 prices),[14] it was at the time the most expensive construction project ever proposed. The cost finally came in at £9 billion ($21 billion), well over its predicted budget.[15][16]
Since its construction, the tunnel has faced a few mechanical problems. Both fires and cold weather have temporarily disrupted its operation.[17][18]
Illegal immigrants have attempted to use the tunnel to enter the UK since 1997, creating the ongoing issue of the Migrants around Calais on the French side, causing both diplomatic disagreement, as well as violence.[19][20][21][22]
Origins
Earlier proposals
- 1875: The Channel Tunnel Company Ltd[23] began preliminary trials
- 1882: The Abbot's Cliff heading had reached 897 yards (820 m) and that at Shakespeare Cliff was 2,040 yards (1,870 m) in length
- January 1975: A UK–France government-backed scheme, that started in 1974, was cancelled
- February 1986:The Treaty of Canterbury was signed, allowing the project to proceed
- June 1988: First tunnelling commenced in France
- December 1988: UK TBM commenced operation
- December 1990: Service tunnel broke through under the Channel
- May 1994: Tunnel formally opened by Queen Elizabeth II and President Mitterrand
- Mid-1994: Freight and passenger trains commenced operation
- November 1996: Fire in a lorry shuttle severely damaged the tunnel
- November 2007: High Speed 1, linking London to the tunnel, opened
- September 2008: Another fire in a lorry shuttle severely damaged the tunnel
- December 2009: Eurostar trains stranded in the tunnel due to melting snow affecting the trains' electrical hardware
- November 2011: First commercial freight service run on High Speed 1
In 1802, Albert Mathieu-Favier, a French mining engineer, put forward a proposal to tunnel under the English Channel, with illumination from oil lamps, horse-drawn coaches, and an artificial island positioned mid-Channel for changing horses.[10] Mathieu-Favier's design envisaged a bored two-level tunnel with the top tunnel used for transport and the bottom one for groundwater flows.[24]
In 1839, Aimé Thomé de Gamond, a Frenchman, performed the first geological and hydrographical surveys on the Channel, between Calais and Dover. Thomé de Gamond explored several schemes and, in 1856, he presented a proposal to Napoleon III for a mined railway tunnel from Cap Gris-Nez to Eastwater Point with a port/airshaft on the Varne sandbank[25] at a cost of 170 million francs, or less than £7 million.[26]
In 1865, a deputation led by George Ward Hunt proposed the idea of a tunnel to the Chancellor of the Exchequer of the day, William Ewart Gladstone.[27]
Around 1866, William Low and Sir John Hawkshaw promoted ideas,[28] but apart from preliminary geological studies[29] none were implemented. An official Anglo-French protocol was established in 1876 for a cross-Channel railway tunnel. In 1881, the British railway entrepreneur Sir Edward Watkin and Alexandre Lavalley, a French Suez Canal contractor, were in the Anglo-French Submarine Railway Company that conducted exploratory work on both sides of the Channel. On the English side a 2.13-metre (7 ft) diameter Beaumont-English boring machine dug a 1,893-metre (6,211 ft) pilot tunnel from Shakespeare Cliff. On the French side, a similar machine dug 1,669 m (5,476 ft) from Sangatte. The project was abandoned in May 1882, owing to British political and press campaigns asserting that a tunnel would compromise Britain's national defences.[12] These early works were encountered more than a century later during the TML project.
In 1919, during the Paris Peace Conference, the British prime minister, David Lloyd George, repeatedly brought up the idea of a Channel tunnel as a way of reassuring France about British willingness to defend against another German attack. The French did not take the idea seriously, and nothing came of Lloyd George's proposal.[30]
In the 1920s Winston Churchill was an advocate for the Channel Tunnel, using that exact nomenclature in an essay entitled "Should Strategists Veto The Tunnel?" The essay was published on 27 July 1924 in the Weekly Dispatch, and argued vehemently against those that believed the tunnel could be used by a Continental enemy in an invasion of Britain. Churchill extolled his enthusiasm for the project again in an article for the Daily Mail on 12 February 1936, "Why Not A Channel Tunnel?"[31]
There was another proposal in 1929, but nothing came of this discussion and the idea was shelved. Proponents estimated construction to be about US$150 million. The engineers had addressed the concerns of both nations' military leaders by designing two sumps—one near the coast of each country—that could be flooded at will to block the tunnel. This design feature did not override the concerns of both nations' military leaders, and other concerns about hordes of undesirable tourists who would disrupt English habits of living.[32] Military fears continued during the Second World War. After the fall of France, as Britain prepared for an expected German invasion, a Royal Navy officer in the Directorate of Miscellaneous Weapons Development calculated that Hitler could use slave labour to build two Channel tunnels in 18 months. The estimate caused rumours that Germany had already begun digging.[33]
A British film from Gaumont Studios, The Tunnel (also called TransAtlantic Tunnel), was released in 1935 as a futuristic science fiction project concerning the creation of a transatlantic tunnel. It referred briefly to its protagonist, a Mr. McAllan, as having completed a British Channel tunnel successfully in 1940, five years into the future of the film's release.
By 1955, defence arguments had become less relevant due to the dominance of air power, and both the British and French governments supported technical and geological surveys. In 1958 the 1881 workings were cleared in preparation for a £100,000 geological survey by the Channel Tunnel Study Group. 30% of the funding came from the Channel Tunnel Co Ltd, the largest shareholder of which was the British Transport Commission, as successor to the South Eastern Railway.[34] A detailed geological survey was carried out in 1964–65.[35]
Although the two countries agreed to build a tunnel in 1964, the phase 1 initial studies and signing of a second agreement to cover phase 2 took until 1973.[36] Construction work of this government-funded project to create two tunnels designed to accommodate car shuttle wagons on either side of a service tunnel started on both sides of the Channel in 1974.
On 20 January 1975, to the dismay of their French partners, the now-governing Labour Party in Britain cancelled the project due to uncertainty about EEC membership, doubling cost estimates and the general economic crisis at the time. By this time the British tunnel boring machine was ready and the Ministry of Transport was able to do a 300 m (980 ft) experimental drive.[12] This short tunnel was reused as the starting and access point for tunnelling operations from the British side. The cancellation costs were estimated to be £17 million.[36]
Opposition to the tunnel over the decades reflected the high value the British placed on their insularity, and their preference for imperial links that they controlled directly. Only after the British Empire collapsed in the 1950s, and air travel replaced sea travel, could they appreciate the desirability of closer ties to the continent.[37] With opposition fading, the government could more carefully consider the long-term economic and strategic value, and the new sense of a European identity. The British government's attitude toward a tunnel changed from hostility in 1948 to acceptance and promotion in 1964. This change reflected not only a more favourable view of being part of European unity, but also the calculation that the tunnel would provide economic advantages, especially if Britain ever joined the European Economic Community. By the 1960s, British attitudes toward the tunnel also reflected a realistic reappraisal of the country's international status: after Suez 1956 everyone realized the islands were no longer a super-power. Britain's prestige and security now seemed safest when tied closely to the continent.[38]
Initiation of project
In 1979, the "Mouse-hole Project" was suggested when the Conservatives came to power in Britain. The concept was a single-track rail tunnel with a service tunnel, but without shuttle terminals. The British government took no interest in funding the project, but Margaret Thatcher, the prime minister, said she had no objection to a privately funded project. In 1981 Thatcher and François Mitterrand, the French president, agreed to establish a working group to evaluate a privately funded project. In June 1982 the Franco-British study group favoured a twin tunnel to accommodate conventional trains and a vehicle shuttle service. In April 1985 promoters were invited to submit scheme proposals. Four submissions were shortlisted:
- a rail proposal based on the 1975 scheme presented by Channel Tunnel Group/France–Manche (CTG/F–M),
- Eurobridge: a 4.5 km (2.8 mi) span suspension bridge with a roadway in an enclosed tube
- Euroroute: a 21 km (13 mi) tunnel between artificial islands approached by bridges, and
- Channel Expressway: large diameter road tunnels with mid-channel ventilation towers.[12]
The cross-Channel ferry industry protested under the name "Flexilink". In 1975 there was no campaign protesting against a fixed link, with one of the largest ferry operators (Sealink) being state-owned. Flexilink continued rousing opposition throughout 1986 and 1987.[12] Public opinion strongly favoured a drive-through tunnel, but ventilation issues, concerns about accident management, and fear of driver mesmerisation led to the only shortlisted rail submission, CTG/F-M, being awarded the project in January 1986.[12] Among reasons given for the selection was that it caused least disruption to shipping in the Channel, least environmental disruption, was the best protected against terrorism, and was the most likely to attract sufficient private finance.[39]
Arrangement
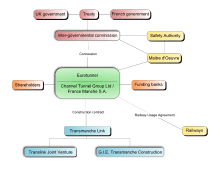
The British Channel Tunnel Group consisted of two banks and five construction companies, while their French counterparts, France–Manche, consisted of three banks and five construction companies. The role of the banks was to advise on financing and secure loan commitments. On 2 July 1985, the groups formed Channel Tunnel Group/France–Manche (CTG/F–M). Their submission to the British and French governments was drawn from the 1975 project, including 11 volumes and a substantial environmental impact statement.[12]
The design and construction was done by the ten construction companies in the CTG/F-M group. The French terminal and boring from Sangatte was undertaken by the five French construction companies in the joint venture group GIE Transmanche Construction. The English Terminal and boring from Shakespeare Cliff was undertaken by the five British construction companies in the Translink Joint Venture. The two partnerships were linked by TransManche Link (TML), a bi-national project organisation.[12] The Maître d'Oeuvre was a supervisory engineering body employed by Eurotunnel under the terms of the concession that monitored project activity and reported back to the governments and banks.[40]
In France, with its long tradition of infrastructure investment, the project garnered widespread approval. In April the French National Assembly gave unanimous support and, in June 1987, after a public inquiry, the Senate gave unanimous support. In Britain, select committees examined the proposal, making history by holding hearings away from Westminster, in Kent. In February 1987, the third reading of the Channel Tunnel Bill took place in the House of Commons, and was carried by 94 votes to 22. The Channel Tunnel Act gained Royal assent and passed into law in July.[12] Parliamentary support for the project came partly from provincial members of Parliament on the basis of promises of regional Eurostar through train services that never materialised; the promises were repeated in 1996 when the contract for construction of the Channel Tunnel Rail Link was awarded.[41]
The tunnel is a build-own-operate-transfer (BOOT) project with a concession.[42] TML would design and build the tunnel, but financing was through a separate legal entity, Eurotunnel. Eurotunnel absorbed CTG/F-M and signed a construction contract with TML, but the British and French governments controlled final engineering and safety decisions, now in the hands of the Channel Tunnel Safety Authority. The British and French governments gave Eurotunnel a 55-year operating concession (from 1987; extended by 10 years to 65 years in 1993)[39] to repay loans and pay dividends. A Railway Usage Agreement was signed between Eurotunnel, British Rail and SNCF guaranteeing future revenue in exchange for the railways obtaining half of the tunnel's capacity.
Private funding for such a complex infrastructure project was of unprecedented scale. An initial equity of £45 million was raised by CTG/F-M, increased by £206 million private institutional placement, £770 million was raised in a public share offer that included press and television advertisements, a syndicated bank loan and letter of credit arranged £5 billion.[12] Privately financed, the total investment costs at 1985 prices were £2600 million. At the 1994 completion actual costs were, in 1985 prices, £4650 million: an 80% cost overrun.[16] The cost overrun was partly due to enhanced safety, security, and environmental demands.[42] Financing costs were 140% higher than forecast.[43]
Construction
Working from both the English side and the French side of the Channel, eleven tunnel boring machines or TBMs cut through chalk marl to construct two rail tunnels and a service tunnel. The vehicle shuttle terminals are at Cheriton (part of Folkestone) and Coquelles, and are connected to the English M20 and French A16 motorways respectively.
Tunnelling commenced in 1988, and the tunnel began operating in 1994.[44] In 1985 prices, the total construction cost was £4.650 billion (equivalent to £13 billion in 2015), an 80% cost overrun. At the peak of construction 15,000 people were employed with daily expenditure over £3 million.[8] Ten workers, eight of them British, were killed during construction between 1987 and 1993, most in the first few months of boring.[45][46][47]
Completion

A two-inch (50-mm) diameter pilot hole allowed the service tunnel to break through without ceremony on 30 October 1990.[48] On 1 December 1990, Englishman Graham Fagg and Frenchman Phillippe Cozette broke through the service tunnel with the media watching.[49] Eurotunnel completed the tunnel on time,[42] and it was officially opened, one year later than originally planned, by Queen Elizabeth II and the French president, François Mitterrand, in a ceremony held in Calais on 6 May 1994. The Queen travelled through the tunnel to Calais on a Eurostar train, which stopped nose to nose with the train that carried President Mitterrand from Paris.[50] Following the ceremony President Mitterrand and the Queen travelled on Le Shuttle to a similar ceremony in Folkestone.[50] A full public service did not start for several months.
The Channel Tunnel Rail Link (CTRL), now called High Speed 1, runs 69 miles (111 km) from St Pancras railway station in London to the tunnel portal at Folkestone in Kent. It cost £5.8 billion. On 16 September 2003 the prime minister, Tony Blair, opened the first section of High Speed 1, from Folkestone to north Kent. On 6 November 2007 the Queen officially opened High Speed 1 and St Pancras International station,[51] replacing the original slower link to Waterloo International railway station. High Speed 1 trains travel at up to 300 km/h (186 mph), the journey from London to Paris taking 2 hours 15 minutes, to Brussels 1 hour 51 minutes.[52]
In 1994, the American Society of Civil Engineers elected the tunnel as one of the seven modern Wonders of the World.[53] In 1995, the American magazine Popular Mechanics published the results.[54]
Engineering

Surveying undertaken in the 20 years before construction confirmed earlier speculations that a tunnel could be bored through a chalk marl stratum. The chalk marl is conducive to tunnelling, with impermeability, ease of excavation and strength. The chalk marl runs along the entire length of the English side of the tunnel, but on the French side a length of 5 kilometres (3 mi) has variable and difficult geology. The tunnel consists of three bores: two 7.6-metre (25 ft) diameter rail tunnels, 30 metres (98 ft) apart, 50 kilometres (31 mi) in length with a 4.8-metre (16 ft) diameter service tunnel in between. The three bores are connected by cross-passages and piston relief ducts. The service tunnel was used as a pilot tunnel, boring ahead of the main tunnels to determine the conditions. English access was provided at Shakespeare Cliff, French access from a shaft at Sangatte. The French side used five tunnel boring machines (TBMs), the English side six. The service tunnel uses Service Tunnel Transport System (STTS) and Light Service Tunnel Vehicles (LADOGS). Fire safety was a critical design issue.
Between the portals at Beussingue and Castle Hill the tunnel is 50.5 kilometres (31 mi) long, with 3.3 kilometres (2 mi) under land on the French side and 9.3 kilometres (6 mi) on the UK side, and 37.9 kilometres (24 mi) under sea.[5] It is the third-longest rail tunnel in the world, behind the Gotthard Base Tunnel in Switzerland and the Seikan Tunnel in Japan, but with the longest under-sea section.[55] The average depth is 45 metres (148 ft) below the seabed.[56] On the UK side, of the expected 5 million cubic metres (6.5×106 cu yd) of spoil approximately 1 million cubic metres (1.3×106 cu yd) was used for fill at the terminal site, and the remainder was deposited at Lower Shakespeare Cliff behind a seawall, reclaiming 74 acres (30 ha)[8] of land.[57] This land was then made into the Samphire Hoe Country Park. Environmental impact assessment did not identify any major risks for the project, and further studies into safety, noise, and air pollution were overall positive. However, environmental objections were raised over a high-speed link to London.[58]
Geology

Successful tunnelling required a sound understanding of the topography and geology and the selection of the best rock strata through which to dig. The geology of this site generally consists of northeasterly dipping Cretaceous strata, part of the northern limb of the Wealden-Boulonnais dome. Characteristics include:
- Continuous chalk on the cliffs on either side of the Channel containing no major faulting, as observed by Verstegan in 1605.
- Four geological strata, marine sediments laid down 90–100 million years ago; pervious upper and middle chalk above slightly pervious lower chalk and finally impermeable Gault Clay. A sandy stratum, glauconitic marl (tortia), is in between the chalk marl and gault clay.
- A 25–30-metre (82–98 ft) layer of chalk marl (French: craie bleue) in the lower third of the lower chalk appeared to present the best tunnelling medium. The chalk has a clay content of 30–40% providing impermeability to groundwater yet relatively easy excavation with strength allowing minimal support. Ideally the tunnel would be bored in the bottom 15 metres (49 ft) of the chalk marl, allowing water inflow from fractures and joints to be minimised, but above the gault clay that would increase stress on the tunnel lining and swell and soften when wet.[59]
On the English side, the stratum dip is less than 5°; on the French side this increases to 20°. Jointing and faulting are present on both sides. On the English side, only minor faults of displacement less than 2 metres (7 ft) exist; on the French side, displacements of up to 15 metres (49 ft) are present owing to the Quenocs anticlinal fold. The faults are of limited width, filled with calcite, pyrite and remoulded clay. The increased dip and faulting restricted the selection of route on the French side. To avoid confusion, microfossil assemblages were used to classify the chalk marl. On the French side, particularly near the coast, the chalk was harder, more brittle and more fractured than on the English side. This led to the adoption of different tunnelling techniques on the two sides.[60]
The Quaternary undersea valley Fosse Dangaered, and Castle Hill landslip at the English portal, caused concerns. Identified by the 1964–65 geophysical survey, the Fosse Dangaered is an infilled valley system extending 80 metres (262 ft) below the seabed, 500 metres (1,640 ft) south of the tunnel route in mid-channel. A 1986 survey showed that a tributary crossed the path of the tunnel, and so the tunnel route was made as far north and deep as possible. The English terminal had to be located in the Castle Hill landslip, which consists of displaced and tipping blocks of lower chalk, glauconitic marl and gault debris. Thus the area was stabilised by buttressing and inserting drainage adits.[60] The service tunnel acted as a pilot preceding the main ones, so that the geology, areas of crushed rock, and zones of high water inflow could be predicted. Exploratory probing took place in the service tunnel, in the form of extensive forward probing, vertical downward probes and sideways probing.[60]
Surveying
Marine soundings and samplings by Thomé de Gamond were carried out during 1833–67, establishing the seabed depth at a maximum of 55 metres (180 ft) and the continuity of geological strata (layers). Surveying continued over many years, with 166 marine and 70 land-deep boreholes being drilled and over 4,000-line-kilometres of marine geophysical survey completed.[61] Surveys were undertaken in 1958–1959, 1964–1965, 1972–1974 and 1986–1988.
The surveying in 1958–59 catered for immersed tube and bridge designs as well as a bored tunnel, and thus a wide area was investigated. At this time, marine geophysics surveying for engineering projects was in its infancy, with poor positioning and resolution from seismic profiling. The 1964–65 surveys concentrated on a northerly route that left the English coast at Dover harbour; using 70 boreholes, an area of deeply weathered rock with high permeability was located just south of Dover harbour.[61]
Given the previous survey results and access constraints, a more southerly route was investigated in the 1972–73 survey, and the route was confirmed to be feasible. Information for the tunnelling project also came from work before the 1975 cancellation. On the French side at Sangatte, a deep shaft with adits was made. On the English side at Shakespeare Cliff, the government allowed 250 metres (820 ft) of 4.5-metre (15 ft) diameter tunnel to be driven. The actual tunnel alignment, method of excavation and support were essentially the same as the 1975 attempt. In the 1986–87 survey, previous findings were reinforced, and the characteristics of the gault clay and the tunnelling medium (chalk marl that made up 85% of the route) were investigated. Geophysical techniques from the oil industry were employed.[61]
Tunnelling
.svg.png)
Tunnelling was a major engineering challenge, with the only precedent being the undersea Seikan Tunnel in Japan. A serious risk with underwater tunnels is major water inflow due to the pressure from the sea above, under weak ground conditions. The tunnel also had the challenge of time: being privately funded, early financial return was paramount.
The objective was to construct two 7.6-metre-diameter (25 ft) rail tunnels, 30 metres (98 ft) apart, 50 kilometres (31 mi) in length; a 4.8-metre-diameter (16 ft) service tunnel between the two main ones; pairs of 3.3-metre-diameter (11 ft) cross-passages linking the rail tunnels to the service one at 375-metre (1,230 ft) spacing; piston relief ducts 2 metres (7 ft) in diameter connecting the rail tunnels 250 metres (820 ft) apart; two undersea crossover caverns to connect the rail tunnels,[62] with the service tunnel always preceding the main ones by at least 1 kilometre (0.6 mi) to ascertain the ground conditions. There was plenty of experience with excavating through chalk in the mining industry, while the undersea crossover caverns were a complex engineering problem. The French one was based on the Mount Baker Ridge freeway tunnel in Seattle; the UK cavern was dug from the service tunnel ahead of the main ones, to avoid delay.
Precast segmental linings in the main TBM drives were used, but two different solutions were used. On the French side, neoprene and grout sealed bolted linings made of cast iron or high-strength reinforced concrete were used; on the English side, the main requirement was for speed so bolting of cast-iron lining segments was only carried out in areas of poor geology. In the UK rail tunnels, eight lining segments plus a key segment were used; in the French side, five segments plus a key.[63] On the French side, a 55-metre (180 ft) diameter 75-metre (246 ft) deep grout-curtained shaft at Sangatte was used for access. On the English side, a marshalling area was 140 metres (459 ft) below the top of Shakespeare Cliff, the New Austrian Tunnelling method (NATM) was first applied in the chalk marl here. On the English side, the land tunnels were driven from Shakespeare Cliff - same place as the marine tunnels - not from Folkestone. The platform at the base of the cliff was not large enough for all of the drives and, despite environmental objections, tunnel spoil was placed behind a reinforced concrete seawall, on condition of placing the chalk in an enclosed lagoon, to avoid wide dispersal of chalk fines. Owing to limited space, the precast lining factory was on the Isle of Grain in the Thames estuary,[62] which used Scottish granite aggregate delivered by ship from the Foster Yeoman coastal super quarry at Glensanda in Loch Linnhe on the west coast of Scotland.
On the French side, owing to the greater permeability to water, earth pressure balance TBMs with open and closed modes were used. The TBMs were of a closed nature during the initial 5 kilometres (3 mi), but then operated as open, boring through the chalk marl stratum.[62] This minimised the impact to the ground, allowed high water pressures to be withstood and it also alleviated the need to grout ahead of the tunnel. The French effort required five TBMs: two main marine machines, one main land machine (the short land drives of 3 km (2 mi) allowed one TBM to complete the first drive then reverse direction and complete the other), and two service tunnel machines. On the English side, the simpler geology allowed faster open-faced TBMs.[64] Six machines were used, all commenced digging from Shakespeare Cliff, three marine-bound and three for the land tunnels.[62] Towards the completion of the undersea drives, the UK TBMs were driven steeply downwards and buried clear of the tunnel. These buried TBMs were then used to provide an electrical earth. The French TBMs then completed the tunnel and were dismantled.[65] A 900 mm (35 in) gauge railway was used on the English side during construction.[66]
In contrast to the English machines, which were given alphanumeric names, the French tunnelling machines were all named after women: Brigitte, Europa, Catherine, Virginie, Pascaline, Séverine.[67]
At the end of the tunnelling, one machine was on display at the side of the M20 motorway in Folkestone until Eurotunnel sold it on eBay for £39,999 to a scrap metal merchant.[68] Another machine (T4 "Virginie") still survives on the French side, adjacent to Junction 41 on the A16, in the middle of the D243E3/D243E4 roundabout. On it are the words "hommage aux batisseurs du tunnel", meaning "tribute to the builders of the tunnel".
Railway design

Communications
There are three communication systems: concession radio (CR) for mobile vehicles and personnel within Eurotunnel's Concession (terminals, tunnels, coastal shafts); track-to-train radio (TTR) for secure speech and data between trains and the railway control centre; Shuttle internal radio (SIR) for communication between shuttle crew and to passengers over car radios.[69] This service was discontinued within one year of opening because of drivers' difficulty setting their radios to the correct frequency (88.8 MHz).
Power supply
Power is delivered to the locomotives via an overhead line (catenary)[70] at 25 kV 50 Hz.[71] All tunnel services run on electricity, shared equally from English and French sources. There are two sub-stations fed at 400 kV at each terminal, but in an emergency the tunnel's lighting (about 20,000 light fittings) and plant can be powered solely from either England or France.[72]
The traditional railway south of London uses a 750 V DC third rail to deliver electricity, but since the opening of High Speed 1 there is no longer any need for tunnel trains to use the third rail system. High Speed 1, the tunnel and the LGV Nord all have power provided via overhead catenary at 25 kV 50 Hz. The railways on "classic" lines in Belgium are also electrified by overhead wires, but at 3000 V DC.[71]
Signalling
A cab signalling system gives information directly to train drivers on a display. There is a train protection system that stops the train if the speed exceeds that indicated on the in-cab display. TVM430, as used on LGV Nord and High Speed 1, is used in the tunnel.[73] The TVM signalling is interconnected with the signalling on the high-speed lines either side, allowing trains to enter and exit the tunnel system without stopping. The maximum speed is 160 km/h.[74]
Signalling in the tunnel is coordinated from two control centres: The main control centre at the Folkestone terminal, and a backup at the Calais terminal, which is staffed at all times and can take over all operations in the event of a breakdown or emergency.
Track system
Conventional ballasted tunnel-track was ruled out owing to the difficulty of maintenance and lack of stability and precision. The Sonneville International Corporation's track system was chosen based on reliability and cost-effectiveness based on good performance in Swiss tunnels and worldwide. The type of track used is known as Low Vibration Track (LVT). Like ballasted track the LVT is of the free floating type, held in place by gravity and friction. Reinforced concrete blocks of 100 kg support the rails every 60 cm and are held by 12 mm thick closed cell polymer foam pads placed at the bottom of rubber boots. The latter separate the blocks' mass movements from the lean encasement concrete. Ballastless track provides extra overhead clearance necessary for the passage of larger trains.[75] The corrugated rubber walls of the boots add a degree of isolation of horizontal wheel-rail vibrations, and are insulators of the track signal circuit in the humid tunnel environment. UIC60 (60 kg/m) rails of 900A grade rest on 6 mm (0.2 in) rail pads, which fit the RN/Sonneville bolted dual leaf-springs. The rails, LVT-blocks and their boots with pads were assembled outside the tunnel, in a fully automated process developed by the LVT inventor, Mr. Roger Sonneville. About 334,000 Sonneville blocks were made on the Sangatte site.
Maintenance activities are less than projected. Initially the rails were ground on a yearly basis or after approximately 100MGT of traffic. Ride quality continues to be noticeably smooth and of low noise. Maintenance is facilitated by the existence of two tunnel junctions or crossover facilities, allowing for two-way operation in each of the six tunnel segments thereby created, and thus providing safe access for maintenance of one isolated tunnel segment at a time. The two crossovers are the largest artificial undersea caverns ever built; 150 m long, 10 m high and 18 m wide. The English crossover is 8 km (5 mi) from Shakespeare Cliff, and the French crossover is 12 km (7 mi) from Sangatte.[76]
Ventilation, cooling and drainage
The ventilation system maintains the air pressure in the service tunnel higher than in the rail tunnels, so that in the event of a fire, smoke does not enter the service tunnel from the rail tunnels. Two cooling water pipes in each rail tunnel circulate chilled water to remove heat generated by the rail traffic. Pumping stations remove water in the tunnels from rain, seepage, and so on.[77]
Rolling stock

Eurotunnel Shuttle
Initially 38 Le Shuttle locomotives were commissioned, with one at each end of a shuttle train. The shuttles have two separate halves: single and double deck. Each half has two loading/unloading wagons and 12 carrier wagons. Eurotunnel's original order was for nine tourist shuttles.
Heavy goods vehicle (HGV) shuttles also have two halves, with each half containing one loading wagon, one unloading wagon and 14 carrier wagons. There is a club car behind the leading locomotive. Eurotunnel originally ordered six HGV shuttle rakes.
Freight locomotives
Forty-six Class 92 locomotives for hauling freight trains and overnight passenger trains (the Nightstar project, which was abandoned) were commissioned, running on both overhead AC and third-rail DC power. However, RFF does not let these run on French railways, so there are plans to certify Alstom Prima II locomotives for use in the tunnel.[78]
International passenger
Thirty-one Eurostar trains, based on the French TGV, built to UK loading gauge with many modifications for safety within the tunnel, were commissioned, with ownership split between British Rail, French national railways (SNCF) and Belgian national railways (SNCB). British Rail ordered seven more for services north of London.[79] Around 2010, Eurostar ordered ten trains from Siemens based on its Velaro product.
Germany (DB) has since around 2005 tried to get permission to run train services to London. At the end of 2009, extensive fire-proofing requirements were dropped and DB received permission to run German Intercity-Express (ICE) test trains through the tunnel. In June 2013 DB was granted access to the tunnel.[80] In June 2014 the plans were shelved, because there are special safety rules that requires custom made trains (DB calls them Class 407).[81]
Service locomotives
Diesel locomotives for rescue and shunting work are Eurotunnel Class 0001 and Eurotunnel Class 0031.
Operation
The following chart presents the estimated number of passengers and tonnes of freight, respectively, annually transported through the Channel Tunnel since 1994, in millions:

| Million passengers |
Million tonnes of freight |
Usage and services


Transport services offered by the tunnel are as follows:
- Eurotunnel Le Shuttle roll-on roll-off shuttle service for road vehicles and their drivers and passengers,
- Eurostar passenger trains,
- through freight trains.[9]
Both the freight and passenger traffic forecasts that led to the construction of the tunnel were overestimated; in particular, Eurotunnel's commissioned forecasts were over-predictions.[82] Although the captured share of Channel crossings was forecast correctly, high competition (especially from budget airlines which expanded rapidly in the 1990s and 2000s) and reduced tariffs led to low revenue. Overall cross-Channel traffic was overestimated.[83][84]
With the EU's liberalisation of international rail services, the tunnel and High Speed 1 have been open to competition since 2010. There have been a number of operators interested in running trains through the tunnel and along High Speed 1 to London. In June 2013, after several years, DB obtained a licence to operate Frankfurt – London trains, not expected to run before 2016 because of delivery delays of the custom-made trains.[85]
Passenger traffic volumes
Cross-tunnel passenger traffic volumes peaked at 18.4 million in 1998, dropped to 14.9 million in 2003, then rose to 21.0 million in 2014.[86]
At the time of the decision about building the tunnel, 15.9 million passengers were predicted for Eurostar trains in the opening year. In 1995, the first full year, actual numbers were a little over 2.9 million, growing to 7.1 million in 2000, then dropping to 6.3 million in 2003. Eurostar was initially limited by the lack of a high-speed connection on the British side. After the completion of High Speed 1 in two stages in 2003 and 2007, traffic increased. In 2008, Eurostar carried 9,113,371 passengers, a 10% increase over the previous year, despite traffic limitations due to the 2008 Channel Tunnel fire.[87] Eurostar passenger numbers continued to increase, reaching 10,397,894 in 2014.[88]
| Year | Passengers transported... | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| by Eurostar[A][89][90] (actual ticket sales) | by Eurotunnel Passenger Shuttles[83][89] (estimated, millions) | Total (estimated, millions) | |
| 1994 | ~100,000[83] | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| 1995 | 2,920,309 | 4.4 | 7.3 |
| 1996 | 4,995,010 | 7.9 | 12.9 |
| 1997 | 6,004,268 | 8.6 | 14.6 |
| 1998 | 6,307,849 | 12.1 | 18.4 |
| 1999 | 6,593,247 | 11.0 | 17.6 |
| 2000 | 7,130,417 | 9.9 | 17.0 |
| 2001 | 6,947,135 | 9.4 | 16.3 |
| 2002 | 6,602,817 | 8.6 | 15.2 |
| 2003 | 6,314,795 | 8.6 | 14.9 |
| 2004 | 7,276,675 | 7.8 | 15.1 |
| 2005 | 7,454,497 | 8.2 | 15.7 |
| 2006 | 7,858,337 | 7.8 | 15.7 |
| 2007 | 8,260,980 | 7.9 | 16.2 |
| 2008 | 9,113,371 | 7.0 | 16.1 |
| 2009 | 9,220,233 | 6.9 | 16.1 |
| 2010 | 9,528,558 | 7.5 | 17.0 |
| 2011 | 9,679,764 | 9.3 | 19.0 |
| 2012 | 9,911,649 | 10.0 | 19.9 |
| 2013[86] | 10,132,691 | 10.3 | 20.4 |
| 2014[86] | 10,397,894 | 10.6 | 21.0 |
| 2015[86] | 10,399,267 | 10.5 | 20.9 |
| 2016[91] | 10,011,337 | 10.7 | 20.7 |
|
A only passengers taking Eurostar to cross the Channel | |||
Freight traffic volumes
Freight volumes have been erratic, with a major decrease during 1997 due to a closure caused by a fire in a freight shuttle. Freight crossings increased over the period, indicating the substitutability of the tunnel by sea crossings. The tunnel has achieved a market share close to or above Eurotunnel's 1980s predictions but Eurotunnel's 1990 and 1994 predictions were overestimates.
For through freight trains, the first year prediction was 7.2 million gross tonnes; the actual 1995 figure was 1.3M gross tonnes.[82] Through freight volumes peaked in 1998 at 3.1M tonnes. This fell back to 1.21M tonnes in 2007, increasing slightly to 1.24M tonnes in 2008.[87] Together with that carried on freight shuttles, freight growth has occurred since opening, with 6.4M tonnes carried in 1995, 18.4M tonnes recorded in 2003[83] and 19.6M tonnes in 2007.[89] Numbers fell back in the wake of the 2008 fire.
| Year | Freight Transported (tonnes) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| through freight trains[90] | Eurotunnel Truck Shuttles (est.)[83][89] | Total (est.) | |
| 1994 | 0 | 800,000[83] | 800,000 |
| 1995 | 1,349,802 | 5,100,000 | 6,400,000 |
| 1996 | 2,783,774 | 6,700,000 | 9,500,000 |
| 1997 | 2,925,171 | 3,300,000 | 6,200,000 |
| 1998 | 3,141,438 | 9,200,000 | 12,300,000 |
| 1999 | 2,865,251 | 10,900,000 | 13,800,000 |
| 2000 | 2,947,385 | 14,700,000 | 17,600,000 |
| 2001 | 2,447,432 | 15,600,000 | 18,000,000 |
| 2002 | 1,463,580 | 15,600,000 | 17,100,000 |
| 2003 | 1,743,686[92] | 16,700,000 | 18,400,000 |
| 2004 | 1,889,175[93] | 16,600,000 | 18,500,000 |
| 2005 | 1,587,790[93] | 17,000,000 | 18,600,000 |
| 2006 | 1,569,429[94] | 16,900,000 | 18,500,000 |
| 2007 | 1,213,647[94] | 18,400,000 | 19,600,000 |
| 2008 | 1,239,445[95] | 14,200,000 | 15,400,000 |
| 2009 | 1,181,089[95] | 10,000,000 | 11,200,000 |
| 2010[86] | 1,128,079[88] | 14,200,000 | 15,300,000 |
| 2011[96] | 1,324,673 | 16,400,000[86] | 17,700,000 |
| 2012 | 1,227,139[97] | 19,000,000[86] | 20,200,000 |
| 2013 | 1,363,834[98] | 17,700,000[86] | 19,100,000 |
| 2014 | 1,648,047[99] | 18,700,000[86] | 20,350,000 |
| 2015 | 1,420,000[86] | 19,300,000[86] | 20,720,000 |
| 2016[91] | 1,040,000 | 21,300,000 | 22,340,000 |
Eurotunnel's freight subsidiary is Europorte 2.[100] In September 2006 EWS, the UK's largest rail freight operator, announced that owing to cessation of UK-French government subsidies of £52 million per annum to cover the tunnel "Minimum User Charge" (a subsidy of around £13,000 per train, at a traffic level of 4,000 trains per annum), freight trains would stop running after 30 November.[101]
Economic performance
Shares in Eurotunnel were issued at £3.50 per share on 9 December 1987. By mid-1989 the price had risen to £11.00. Delays and cost overruns led to the price dropping; during demonstration runs in October 1994 it reached an all-time low. Eurotunnel suspended payment on its debt in September 1995 to avoid bankruptcy.[102] In December 1997 the British and French governments extended Eurotunnel's operating concession by 34 years, to 2086. Financial restructuring of Eurotunnel occurred in mid-1998, reducing debt and financial charges. Despite the restructuring, The Economist reported in 1998 that to break even Eurotunnel would have to increase fares, traffic and market share for sustainability.[103] A cost benefit analysis of the tunnel indicated that there were few impacts on the wider economy and few developments associated with the project, and that the British economy would have been better off if it had not been constructed.[83][104]
Under the terms of the Concession, Eurotunnel was obliged to investigate a cross-Channel road tunnel. In December 1999 road and rail tunnel proposals were presented to the British and French governments, but it was stressed that there was not enough demand for a second tunnel.[105] A three-way treaty between the United Kingdom, France and Belgium governs border controls, with the establishment of control zones wherein the officers of the other nation may exercise limited customs and law enforcement powers. For most purposes these are at either end of the tunnel, with the French border controls on the UK side of the tunnel and vice versa. For some city-to-city trains, the train is a control zone.[106] A binational emergency plan coordinates UK and French emergency activities.[107]
In 1999 Eurostar posted its first net profit, having made a loss of £925m in 1995.[44] In 2005 Eurotunnel was described as being in a serious situation.[108] In 2013, operating profits rose 4 per cent from 2012, to £54 million.[109]
Security
There is a need for full passport controls, since this is the border between the Schengen Area and the Common Travel Area. There are juxtaposed controls, meaning that passports are checked before boarding first by officials belonging to departing country and then officials of the destination country. These are only placed at the main Eurostar stations: French officials operate at London St Pancras, Ebbsfleet International and Ashford International, while British officials operate at Calais-Fréthun, Lille-Europe, Brussels-South and Paris-Gare du Nord. There are security checks before boarding as well. For the shuttle road-vehicle trains, there are juxtaposed passport controls before boarding the trains.
For Eurostar trains travelling from places south of Paris, there is no passport and security check before departure, and those trains must stop in Lille at least 30 minutes to allow all passengers to be checked. No checks are done on board. There have been plans for services from Amsterdam, Frankfurt and Cologne to London, but a major reason to cancel them was the need for a stop in Lille.
The reason for juxtaposed controls is a wish to prevent illegal immigration before reaching British soil, and because a check of all passengers on a train can take 30 minutes, which creates long queues if done at arrival.
Terminals

The terminals' sites are at Cheriton (near Folkestone in the United Kingdom) and Coquelles (near Calais in France). The terminals are designed to transfer vehicles from the motorway onto trains at a rate of 700 cars and 113 heavy vehicles per hour. The UK site uses the M20 motorway for access. The terminals are organised with the frontier controls juxtaposed with the entry to the system to allow travellers to go onto the motorway at the destination country immediately after leaving the shuttle. The area of the UK site was severely constrained and the design was challenging. The French layout was achieved more easily. To achieve design output, the shuttles accept cars on double-deck wagons; for flexibility, ramps were placed inside the shuttles to provide access to the top decks.[110] At Folkestone there are 20 kilometres (12 mi) of main-line track, 45 turnouts and eight platforms. At Calais there are 30 kilometres (19 mi) of track and 44 turnouts. At the terminals the shuttle trains traverse a figure eight to reduce uneven wear on the wheels.[111] There is a freight marshalling yard west of Cheriton at Dollands Moor Freight Yard.
Regional impact
A 1996 report from the European Commission predicted that Kent and Nord-Pas de Calais had to face increased traffic volumes due to general growth of cross-Channel traffic and traffic attracted by the tunnel. In Kent, a high-speed rail line to London would transfer traffic from road to rail.[112] Kent's regional development would benefit from the tunnel, but being so close to London restricts the benefits. Gains are in the traditional industries and are largely dependent on the development of Ashford International passenger station, without which Kent would be totally dependent on London's expansion. Nord-Pas-de-Calais enjoys a strong internal symbolic effect of the Tunnel which results in significant gains in manufacturing.[113]
The removal of a bottleneck by means like the tunnel does not necessarily induce economic gains in all adjacent regions. The image of a region being connected to the European high-speed transport and active political response are more important for regional economic development. Some small-medium enterprises located in the immediate vicinity of the terminal have used the opportunity to re-brand the profile of their business with positive effect, such as The New Inn at Etchinghill which was able to commercially exploit its unique selling point as being 'the closest pub to the Channel Tunnel'. Tunnel-induced regional development is small compared to general economic growth.[114] The South East of England is likely to benefit developmentally and socially from faster and cheaper transport to continental Europe, but the benefits are unlikely to be equally distributed throughout the region. The overall environmental impact is almost certainly negative.[115]
Since the opening of the tunnel, small positive impacts on the wider economy have been felt, but it is difficult to identify major economic successes directly attributed to the tunnel.[116] The Eurotunnel does operate profitably, offering an alternative transportation mode unaffected by poor weather.[117] High costs of construction did delay profitability, however, and companies involved in the tunnel's construction and operation early in operation relied on government aid to deal with debts amounted.[118][119][120]
Unauthorized immigration
Illegal Immigrants and would-be asylum seekers have used the tunnel to attempt to enter Britain. By 1997, the problem had attracted international press attention, and by 1999, the French Red Cross opened the first migrant centre at Sangatte, using a warehouse once used for tunnel construction; by 2002, it housed up to 1,500 people at a time, most of them trying to get to the UK.[121] In 2001, most came from Afghanistan, Iraq, and Iran, but African and Eastern European countries were also represented.[122]
Eurotunnel, the company that operates the crossing, said that it has intercepted more than 37,000 migrants between January and July 2015.[123] According to the official count in July 2015, about 3,000 migrants, mainly from Ethiopia, Eritrea, Sudan and Afghanistan, were living in the makeshift camps in Calais. It is estimated that about 5,000 migrants are waiting in the harbour town Calais to find a chance to get to England.
Britain and France operate a system of Juxtaposed controls on immigration and customs, where investigations happen before travel. France is part of the Schengen Agreement, which border checks between member nations have largely been abolished, but the United Kingdom is not.
Most illegal immigrants and would-be asylum seekers who got into Britain found some way to ride a freight train. Trucks are loaded onto freight trains. In a few instances, groups of migrants were able to stowaway in the cargo area of a tanker truck carrying liquid chocolate and managed to survive, though they did not enter the UK in one attempt.[124] Although the facilities were fenced, airtight security was deemed impossible; migrants would even jump from bridges onto moving trains. In several incidents people were injured during the crossing; others tampered with railway equipment, causing delays and requiring repairs.[125] Eurotunnel said it was losing £5m per month because of the problem.[126]
In 2001 and 2002, several riots broke out at Sangatte, and groups of migrants (up to 550 in a December 2001 incident) stormed the fences and attempted to enter en masse.[127]
Other migrants use the Eurostar passenger train. They arrive as legitimate Eurostar passengers, but without proper entry papers.[128]
Diplomatic efforts
Local authorities in both France and the UK called for the closure of the Sangatte migrant camp, and Eurotunnel twice sought an injunction against the centre.[121] The United Kingdom blamed France for allowing Sangatte to open, and France blamed both the UK for its lax asylum rules, and the EU for not having a uniform immigration policy.[126] The cause célèbre nature of the problem even included journalists detained as they followed migrants onto railway property.[129]
In 2002, after the European Commission told France that it was in breach of European Union rules on the free transfer of goods because of the delays and closures as a result of its poor security, a double fence was built at a cost of £5 million, reducing the numbers of migrants detected each week reaching Britain on goods trains from 250 to almost none.[130] Other measures included CCTV cameras and increased police patrols.[131] At the end of 2002, the Sangatte centre was closed after the UK agreed to absorb some migrants.[132][133]
On 23 and 30 June 2015,[134] striking workers associated with MyFerryLink damaged the sections of track by burning car tires, leading to all trains being cancelled and a backlog of vehicles. Hundreds seeking to reach Britain made use of the situation to attempt to stowaway inside and underneath transport trucks destined for the United Kingdom. Extra security measures including: £2-million upgrade of detection technology; £1 million extra for dog searches; £12 million (over three years) towards a joint fund with France for security surrounding the Port of Calais.
Deaths
Migrants take great risks to evade security precautions. By 2002, a dozen migrants have died in crossing attempts.[121] In the two months from June to July 2015, ten migrants died near the French tunnel terminal, during a period when 1,500 attempts to evade security precautions were being made each day.[135][136]
On 6 July 2015, a migrant died while attempting to climb onto a freight train while trying to reach Britain from the French side of the Channel.[137] The previous month an Eritrean man was killed under similar circumstances.[138]
During the night of 28 July 2015, one person aged 25–30, was found dead, after a night in which 1,500–2,000 migrants had attempted to enter the Eurotunnel terminal.[139]
On 4 August 2015, a Sudanese migrant walked nearly the entire length of one of the tunnels. He was arrested close to the British side, after having walked about 30 miles (48 km) through the tunnel.[140]
On 20 June 2017, a lorry driver was killed when migrants stopped vehicles on the A16 autoroute with a tree trunk, in order to stowaway in the cargo area.[22] A van registered in Poland hit the lorry, and burst into fire, killing the van driver.[141] Nine migrants from Eritrea have been arrested in connection with this incident.[22]
Mechanical incidents
Fires
There have been three fires in the tunnel, all on the heavy goods vehicle (HGV) shuttles, that were significant enough to close the tunnel, as well as other more minor incidents.
On 9 December 1994, during an "invitation only" testing phase, a fire broke out in a Ford Escort car whilst its owner was loading it onto the upper deck of a tourist shuttle. The fire started at about 10:00, with the shuttle train stationary in the Folkestone terminal and was put out about 40 minutes later with no passenger injuries.[142]
On 18 November 1996, a fire broke out on an HGV shuttle wagon in the tunnel, but nobody was seriously hurt. The exact cause is unknown,[143] although it was neither a Eurotunnel equipment nor rolling stock problem; it may have been due to arson of a heavy goods vehicle. It is estimated that the heart of the fire reached 1,000 °C (1,800 °F), with the tunnel severely damaged over 46 metres (151 ft), with some 500 metres (1,640 ft) affected to some extent. Full operation recommenced six months after the fire.[144]
On 21 August 2006, the tunnel was closed for several hours when a truck on an HGV shuttle train caught fire.[145][146]
On 11 September 2008, a fire occurred in the Channel Tunnel at 13:57 GMT. The incident started on an HGV shuttle train travelling towards France.[147] The event occurred 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) from the French entrance to the tunnel. No one was killed but several people were taken to hospitals suffering from smoke inhalation, and minor cuts and bruises. The tunnel was closed to all traffic, with the undamaged South Tunnel reopening for limited services two days later.[148] Full service resumed on 9 February 2009[149] after repairs costing €60 million.
On 29 November 2012, the tunnel was closed for several hours after a truck on an HGV shuttle caught fire.[150]
On 17 January 2015, both tunnels were closed following a lorry fire which filled the midsection of Running Tunnel North with smoke. Eurostar cancelled all services.[151] The shuttle train had been heading from Folkestone to Coquelles and stopped adjacent to cross-passage CP 4418 just before 12:30 UTC. Thirty-eight passengers and four members of Eurotunnel staff were evacuated into the service tunnel, and then transported to France using special STTS road vehicles in the Service Tunnel. The passengers and crew were taken to the Eurotunnel Fire/Emergency Management Centre close to the French portal.[152]
Train failures
On the night of 19/20 February 1996, about 1,000 passengers became trapped in the Channel Tunnel when Eurostar trains from London broke down owing to failures of electronic circuits caused by snow and ice being deposited and then melting on the circuit boards.[153]
On 3 August 2007, an electrical failure lasting six hours caused passengers to be trapped in the tunnel on a shuttle.[154]
On the evening of 18 December 2009, during the December 2009 European snowfall, five London-bound Eurostar trains failed inside the tunnel, trapping 2,000 passengers for approximately 16 hours, during the coldest temperatures in eight years.[155] A Eurotunnel spokesperson explained that snow had evaded the train's winterisation shields,[156] and the transition from cold air outside to the tunnel's warm atmosphere had melted the snow, resulting in electrical failures.[157][158][159][160] One train was turned back before reaching the tunnel; two trains were hauled out of the tunnel by Eurotunnel Class 0001 diesel locomotives. The blocking of the tunnel led to the implementation of Operation Stack, the transformation of the M20 motorway into a linear car park.[161]
The occasion was the first time that a Eurostar train was evacuated inside the tunnel; the failing of four at once was described as "unprecedented".[162] The Channel Tunnel reopened the following morning.[163] Nirj Deva, Member of the European Parliament for South East England, had called for Eurostar chief executive Richard Brown to resign over the incidents.[164] An independent report by Christopher Garnett (former CEO of Great North Eastern Railway) and Claude Gressier (a French transport expert) on the 18/19 December 2009 incidents was issued in February 2010, making 21 recommendations.[165][166]
On 7 January 2010, a Brussels–London Eurostar broke down in the tunnel. The train had 236 passengers on board and was towed to Ashford; other trains that had not yet reached the tunnel were turned back.[167][168]
Safety
The Channel Tunnel Safety Authority is responsible for some aspects of safety regulation in the tunnel; it reports to the IGC.[169]
| Channel Tunnel safety | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The service tunnel is used for access to technical equipment in cross-passages and equipment rooms, to provide fresh-air ventilation and for emergency evacuation. The Service Tunnel Transport System (STTS) allows fast access to all areas of the tunnel. The service vehicles are rubber-tyred with a buried wire guidance system. The 24 STTS vehicles are used mainly for maintenance but also for firefighting and in emergencies. "Pods" with different purposes, up to a payload of 2.5–5 t (2.8–5.5 tons), are inserted into the side of the vehicles. The vehicles cannot turn around within the tunnel, and are driven from either end. The maximum speed is 80 km/h (50 mph) when the steering is locked. A fleet of 15 Light Service Tunnel Vehicles (LADOGS) was introduced to supplement the STTSs. The LADOGS have a short wheelbase with a 3.4 m (11 ft) turning circle, allowing two-point turns within the service tunnel. Steering cannot be locked like the STTS vehicles, and maximum speed is 50 km/h (31 mph). Pods up to 1 tonne can be loaded onto the rear of the vehicles. Drivers in the tunnel sit on the right, and the vehicles drive on the left. Owing to the risk of French personnel driving on their native right side of the road, sensors in the vehicles alert the driver if the vehicle strays to the right side.[170]
The three tunnels contain 6,000 tonnes (6,600 tons) of air that needs to be conditioned for comfort and safety. Air is supplied from ventilation buildings at Shakespeare Cliff and Sangatte, with each building capable of providing 100% standby capacity. Supplementary ventilation also exists on either side of the tunnel. In the event of a fire, ventilation is used to keep smoke out of the service tunnel and move smoke in one direction in the main tunnel to give passengers clean air. The tunnel was the first main-line railway tunnel to have special cooling equipment. Heat is generated from traction equipment and drag. The design limit was set at 30 °C (86 °F), using a mechanical cooling system with refrigeration plants on both sides that run chilled water circulating in pipes within the tunnel.[171]
Trains travelling at high speed create piston-effect pressure changes that can affect passenger comfort, ventilation systems, tunnel doors, fans and the structure of the trains, and which drag on the trains.[171] Piston relief ducts of 2-metre (7 ft) diameter were chosen to solve the problem, with 4 ducts per kilometre to give close to optimum results. Unfortunately this design led to unacceptable lateral forces on the trains so a reduction in train speed was required and restrictors were installed in the ducts.[172]
The safety issue of a possible fire on a passenger-vehicle shuttle garnered much attention, with Eurotunnel noting that fire was the risk attracting the most attention in a 1994 safety case for three reasons: the opposition of ferry companies to passengers being allowed to remain with their cars; Home Office statistics indicating that car fires had doubled in ten years; and the long length of the tunnel. Eurotunnel commissioned the UK Fire Research Station - now part of the Building Research Establishment - to give reports of vehicle fires, and liaised with Kent Fire Brigade to gather vehicle fire statistics over one year. Fire tests took place at the French Mines Research Establishment with a mock wagon used to investigate how cars burned.[173] The wagon door systems are designed to withstand fire inside the wagon for 30 minutes, longer than the transit time of 27 minutes. Wagon air conditioning units help to purge dangerous fumes from inside the wagon before travel. Each wagon has a fire detection and extinguishing system, with sensing of ions or ultraviolet radiation, smoke and gases that can trigger halon gas to quench a fire. Since the HGV wagons are not covered, fire sensors are located on the loading wagon and in the tunnel. A 10-inch (250 mm) water main in the service tunnel provides water to the main tunnels at 125-metre (410 ft) intervals.[174] The ventilation system can control smoke movement. Special arrival sidings accept a train that is on fire, as the train is not allowed to stop whilst on fire in the tunnel, unless continuing its journey would lead to a worse outcome. Eurotunnel has banned a wide range of hazardous goods from travelling in the tunnel. Two STTS (Service Tunnel Transportation System)[175] vehicles with firefighting pods are on duty at all times, with a maximum delay of 10 minutes before they reach a burning train.[144]
Unusual traffic
In 2009, former F1 racing champion John Surtees drove a Ginetta G50 EV electric sports car prototype from England to France, using the service tunnel, as part of a charity event. He was required to keep to the 50-kilometre-per-hour (30 mph) speed limit.[176] To celebrate the 2014 Tour de France's transfer from its opening stages in Britain to France in July of that year, Chris Froome of Team Sky rode a bicycle through the service tunnel, becoming the first solo rider to do so.[177][178] The Crossing took under an hour, reaching speeds of 40 mph–faster than most cross-channel ferries.[179]
Mobile network coverage
Since 2012, French operators Bouygues Telecom, Orange and SFR have covered Running Tunnel South, the tunnel bore normally used for travel from France to Britain.
In January 2014, UK operators EE and Vodafone signed ten-year contracts with Eurotunnel for Running Tunnel North. The agreements will enable both operators' subscribers to use 2G and 3G services. Both EE and Vodafone plan to offer LTE services on the route; EE said it expected to cover the route with LTE connectivity by summer 2014. EE and Vodafone will offer Channel Tunnel network coverage for travellers from the UK to France. Eurotunnel said it also held talks with Three UK but has yet to reach an agreement with the operator.[180]
On 6 May 2014, Eurotunnel announced that they had installed equipment from Alcatel-Lucent to cover Running Tunnel North and simultaneously to provide mobile service (GSM 900/1800 MHz and UMTS 2100 MHz) by EE, O2 and Vodafone. The service of EE and Vodafone commenced on the same date as the announcement. O2 service was expected to be available soon afterwards.[181]
On 21 November 2014, EE announced that it had previously switched on LTE earlier in September 2014.[182] O2 turned on 2G, 3G and 4G services in November 2014. Whilst Vodafone's 4G was due to go live later.[183]
Other (non-transport) services
Another usage of the Channel Tunnel is the 1,000 MW high voltage direct current ElecLink connecting the electrical grids of the two countries, scheduled for 2019 at a cost of €580m.[184][185][186] The foundation stone of the Folkestone Converter Station was laid in February 2017, by Jesse Norman, Minister for Industry and Energy.[187]
Channel Tunnel in popular culture
In A Diplomatic Incident, the eleventh episode of the British sitcom Yes, Prime Minister, first screened in 1987, Jim Hacker decides who is to negotiate with the French government over questions such as whether French or English should come first on signs and menus, and where the legal boundary between France and England should be in the tunnel.
See also
- British Rail Class 373
- Irish Sea tunnel
- Japan-Korea Undersea Tunnel
- List of rail megaprojects
- Marmaray
- Samphire Hoe
- Strait of Gibraltar crossing
References
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers (Great Britain) (1995). The Channel Tunnel: Transport systems, Volume 4. 108. Thomas Telford. p. 22. ISBN 9780727720245.
- ↑ Oxford Dictionary of English (2nd ed.). OUP Oxford. 11 August 2005. ISBN 3-411-02144-6.
- ↑ Janet Stobart (20 December 2009). "Rail passengers spend a cold, dark night stranded in Chunnel". L.A. Times. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ↑ "Folkestone Eurotunnel Trains". Transworld Leisure Limited. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- 1 2 Institute of Civil Engineers p. 95
- ↑ Jeff Wise (1 October 2009). "Turkey Building the World's Deepest Immersed Tube Tunnel". Popular Mechanics. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014.
- ↑ Dumitrache, Alina (24 March 2010). "The Channel Tunnel - Traveling Under the Sea". AutoEvolution. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Anderson, pp. xvi–xvii
- 1 2 Chisholm, Michael (1995). Britain on the edge of Europe. London: Routledge. p. 151. ISBN 0-415-11921-9.
- 1 2 Whiteside p. 17
- ↑ "The Channel Tunnel". library.thinkquest.org. Archived from the original on 12 December 2007. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Wilson pp. 14–21
- ↑ Paddy at Home ("Chez Paddy") (2nd ed.). Chapman & Hall Covent Garden, London. 1887.
- ↑ Leslie Allen Veditz. "The Channel Tunnel - A Case Study" (PDF). Fort McNair, Washington, DC, U.S.: The Industrial College of the Armed Forces, National Defense University. p. 8. Retrieved 9 December 2016.
- ↑ "How the Channel Tunnel was Built". Folkstone, England / Coquelles Cedex France: Eurotunnel Group. Retrieved 9 December 2016.
It was at the time the most expensive construction project ever proposed and the cost finally came in at £9 billion.
- 1 2 Flyvbjerg et al. p. 12
- ↑ "Channel tunnel fire worst in service's history". The Guardian. 12 September 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ↑ "Thousands freed from Channel Tunnel after trains fail". BBC News. 19 December 2009. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ↑ "Four men caught in Channel Tunnel". BBC News. 4 January 2008. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ "Sangatte refugee camp". The Guardian. UK. 23 May 2002. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ "French Channel Tunnel train drivers 'haunted' by migrant deaths". The Daily Telegraph. 1 October 2015. Retrieved 18 January 2017.
- 1 2 3 Henry Samuel (20 June 2017). "Van driver killed in fireball crash after migrants block Calais road with tree trunks". The Telegraph. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- ↑ "Subterranea Britannica: Channel Tunnel – 1880 attempt". subbrit.org. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ "Channel Tunnel History". Eurotunnel. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ↑ Whiteside pp. 18–23
- ↑ "The Proposed Tunnel Between England and France" (PDF). The New York Times. 7 August 1866. Retrieved 3 January 2008.
- ↑ Gladstone, William (1902). "The Channel Tunnel". In A. W. Hutton & H. J. Cohen. The Speeches of the Right Hon. W. E. Gladstone on Home Rule, Criminal Law, Welsh And Irish Nationality, National Debt and the Queen's Reign. The Speeches And Public Addresses of the Right Hon. W. E. Gladstone, M.P. X. London: Methuen And Company.
- ↑ Beaumont, Martin (2015). Sir John Hawkshaw 1811-1891. The Lancashire & Yorkshire Railway Society www.lyrs.org.uk. pp. 126–129. ISBN 978-0-9559467-7-6.
- ↑ "Things Worth Recording about Steam Navigation". The Mercury (Hobart, Tas. : 1860 – 1954). Hobart, Tas.: National Library of Australia. 9 October 1866. p. 3. Retrieved 26 April 2014.
- ↑ MacMillan, Margaret. "Paris 1919". Random House, 2002, p. 174, 194
- ↑ Churchill, Winston (1976). The Collected Essays of Sir Winston Churchill, Vol I, Churchill at War (Centenary Edition ed.). Library of Imperial History. pp. 260–264 and 357–359. ISBN 0903988429.
- ↑ "New Plan for Channel Tunnel" Popular Mechanics, May 1929, pp. 767–768
- ↑ Breuer, William B. (2003). The Spy Who Spent the War in Bed: And Other Bizarre Tales from World War II. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley. p. 40. ISBN 0-471-26739-2.
- ↑ Railway Magazine November 1958 p. 805
- ↑ "Channel Tunnel Site Investigation – 1964 – Halcrow Group". Halcrow Group. 13 July 2011. Archived from the original on 1 October 2011. Retrieved 26 July 2011. Online presentation of a 1964–65 film documentary of a geological survey of the Channel, with a brief summary.
- 1 2 "Illustrated London News". 1975.
- ↑ Duncan Redford, "Opposition to the Channel Tunnel, 1882–1975: Identity, Island Status and Security." History 99.334 (2014): 100-120.
- ↑ Richard S. Grayson, "The British Government, the Channel Tunnel and European Unity, 1948-64." European History Quarterly 26.3 (1996): 415-436.
- 1 2 Foreign & Commonwealth Office 1994, p. 5.
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 10–11
- ↑ "Parliamentary note on the Channel Tunnel Rail Link" (PDF). House of Commons Library. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- 1 2 3 Flyvbjerg et al. pp. 96–97
- ↑ Flyvbjerg et al. p. 3
- 1 2 "On this day: Tunnel links UK and Europe". BBC News. 1 December 1990. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ Harlow, John (2 April 1995). "Phantom Trains Wreak Havoc in Channel Tunnel". The Times. UK.
- ↑ "ingenious: Navvies". ingenious. 11 March 2008. Archived from the original on 27 July 2009. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ "Thirteen workers die as safety standards are ignored in race to build Olympic sites". The Independent. UK. 3 April 2004. Retrieved 26 September 2008.
- ↑ Glenn Frankel (31 October 1990). "Britain and France Link Up-at Last". The Washington Post.
- ↑ "Chunnel birthday". Evening Mail. Birmingham Post & Mail Ltd. 2 December 2000.
- 1 2 "On This Day – 1994: President and Queen open Chunnel". BBC News. 6 May 1994. Retrieved 12 January 2008.
- ↑ Woodman, Peter (14 November 2007). "High-speed Rail Link Finally Completed". Press Association National Newswire.
- ↑ "New high-speed rail line opens to link Britain to Europe". Channel NewsAsia. MediaCorp News. 15 November 2007.
- ↑ "Seven Wonders". American Society of Civil Engineers. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- ↑ Pope, Gregory T. (December 1995). "The seven wonders of the modern world". Popular Mechanics. pp. 48–56
- ↑ Gilbert, Jane (1 December 2006). "'Chunnel' workers link France and Britain". The Daily Post (New Zealand). APN New Zealand Ltd.
- ↑ Kirkland p. 13
- ↑ Institute of Civil Engineers p. 208
- ↑ Flyvbjerg et al. p. 51
- ↑ Harris, C.S.; et al., eds. (1996). Engineering Geology of the Channel Tunnel. London: Thomas Telford. p. 57. ISBN 0-7277-2045-7.
- 1 2 3 Kirkland pp. 21–50
- 1 2 3 Kirkland pp. 22–26
- 1 2 3 4 Kirkland pp. 63–128
- ↑ Wilson p. 38
- ↑ Kirkland p. 29
- ↑ Wilson p. 44
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 117–128
- ↑ Pierre-Jean Pompee. "Channel Tunnel: Tunnel's Construction" (PDF). pagesperso-orange.fr. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ https://www.eurotunnel.com/build/
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 129–132
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 134–148
- 1 2 Article: Railway electric traction 9 August 2009
- ↑ Foreign & Commonwealth Office 1994, p. 9.
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 149–155
- ↑ Article-de: Eurotunnel#Betrieb 9 August 2009
- ↑ Bonnett 2005, p. 78
- ↑ Foreign & Commonwealth Office 1994, p. 14.
- ↑ Foreign & Commonwealth Office 1994, p. 8.
- ↑ "Prima II tested in the Channel Tunnel". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 175–211
- ↑ "IGC grants Deutsche Bahn access to Channel Tunnel", www.railwaygazette.com, 13 June 2013
- ↑ DB puts London - Frankfurt plans on ice, 19 February 2014
- 1 2 Flyvbjerg et al. p. 22
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Ricard Anguera (May 2006). "The Channel Tunnel—an ex post economic evaluation". Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice. 40 (4): 291–315. doi:10.1016/j.tra.2005.08.009.
- ↑ Sen, Soutetsu (February 2004). "The Channel Tunnel and its impact on Tourism in the United Kingdom" (PDF). Geographical Paper No. 172.
- ↑ DVV Media UK. "IGC grants Deutsche Bahn access to Channel Tunnel". Railway Gazette.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Traffic figures". Eurotunnel. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- 1 2 "Eurotunnel 2008 traffic and revenue figures". Eurotunnel. 15 January 2009. Retrieved 15 January 2009.
- 1 2 "Eurotunnel 2010 traffic and revenue figures" (PDF). Eurotunnel. 18 January 2011. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 "Traffic figures". Eurotunnel. Retrieved 15 January 2009.
- 1 2 "Study Report Annex 2". southeast-ra.gov.uk. South East England Regional Assembly. June 2004. pp. Table 11. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 21 January 2009.
- 1 2 Eurotunnel. "Traffic figures". www.eurotunnelgroup.com. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel 2003 Revenue & Traffic". Eurotunnel. 20 January 2004. Retrieved 21 January 2009.
- 1 2 "Eurotunnel: 2005 Traffic and revenue figures.". Eurotunnel. 16 January 2006. Retrieved 21 January 2009.
- 1 2 "Eurotunnel 2007 Traffic and Revenue figures: a remarkable year". Eurotunnel. 15 January 2008. Retrieved 21 January 2009.
- 1 2 "Eurotunnel 2009 traffic and revenue figures". Eurotunnel. 10 January 2010. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- ↑ "Traffic and Revenue 2011" (PDF). Eurotunnel. Retrieved 21 December 2012.
- ↑ "2012 revenue and traffic figures for the Eurotunnel Group" (PDF). Eurotunnel. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ↑ "Groupe Eurotunnel SA: traffic and revenue for 2013". Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel Group 2014 Traffic and Revenue". Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel gets backing for freight service". AFX. Agence France Presse. 28 October 2004.
- ↑ Dominic O'Connell (3 September 2006). "Chunnel cash row threatens freight trains". The Times. UK. Retrieved 3 September 2006.
- ↑ "Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition" (PDF). josephcoates.com. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ Flyvbjerg et al. pp. 32–34
- ↑ Flyvbjerg, B. Buzelius; N. Rothengatter, W (2003). Megaprojects and Risk. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 68–69. ISBN 0-521-00946-4.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel unveils plans for second link". Birmingham Post. 6 January 2000.
- ↑ "The CPS: Channel Tunnel". Crown Prosecution Service. Archived from the original on 20 February 2008. Retrieved 11 March 2008.
- ↑ Kirkland p. 331
- ↑ "Facts and figures Eurotunnel 2000-2004/Forecast 2005: Commentry and a suggestion". Adacte.com. June 2005. Archived from the original on 31 July 2009. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- ↑ "Eurostar hails 'record-breaking' year as profits jump". The Independent (UK). 5 March 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 255–270
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 157–174
- ↑ European Commission pp. 220–222
- ↑ European Commission pp. 248–252
- ↑ Fayman, Sonia; Metge, Pierre (September 1995). "The regional impact of the Channel Tunnel: Qualitative and quantitative analysis". European Planning Studies. 3 (3): 333. doi:10.1080/09654319508720310.
- ↑ Button, Kenneth (July 1990). "The Channel Tunnel: The Economic Implications for the South East of England". The Geographical Journal. Blackwell Publishing. 156 (2): 187–199. JSTOR 635327. doi:10.2307/635327.
- ↑ Flyvbjerg et al. p. 68–69
- ↑ "Eurotunnel revenues boosted by shuttle demand". BBC. UK. 18 January 2011. Retrieved 18 January 2011.
- ↑ Harrison, Michael (10 February 2004). "Eurotunnel calls for government support after record £1.3bn loss". The Independent. UK. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel has £4bn too much debt". The Telegraph. London. 12 January 2005. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- ↑ Clark, Andrew (21 February 2006). "Debt-laden Channel tunnel rail link is 'nationalised'". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- 1 2 3 Pierre Kremer (February 2002). "Sangatte: A place of hope and despair". The Magazine of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- ↑ Caryl Phillips (17 November 2001). "Strangers in a strange land". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- ↑ "Britain and France Scramble as Channel Becomes Choke Point in Migration Crisis". The New York Times. 29 July 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ↑ Daniel Silas Adamson; Mamdouh Akbiek (31 March 2015). "I nearly drowned in chocolate". BBC World Service.
- ↑ Avril Stephens (31 July 2007). "Desperate journeys fraught with danger". CNN. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- 1 2 "Europe's most notorious refugee camp". BBC News. 12 July 2002. Retrieved 5 August 2006.
- ↑ Paul Webster (27 December 2007). "Police braced for new tunnel raid". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- ↑ "UK/Ireland: Asylum (news digest)". Migration News. May 1998. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ "2001 World Press Freedom Review: France". International Press Institute. Archived from the original on 24 October 2007. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- ↑ "Sangatte asylum talks due". BBC News. 26 September 2002. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- ↑ "Tunnel security to be tightened". BBC News. 31 May 2002. Retrieved 4 August 2006.
- ↑ Philip Delves Broughton; Andrew Sparrow (27 September 2002). "Blunkett reaches deal to shut Sangatte camp". Daily Telegraph. UK. Retrieved 25 February 2009.
- ↑ "Calais mayor threatens to block port if UK fails to help deal with migrants". The Guardian. AFP. 2 September 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ "Cross-Channel transport improving after Calais migrant chaos". BBC News. 24 June 2014. Retrieved 3 July 2015.
- ↑ "Calais: Polizei kesselt Hunderte Flüchtlinge am Eurotunnel ein". spiegel (in German). 31 July 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ↑ "Calais: man killed as migrants make 1,500 attempts to enter Eurotunnel site". The Guardian. 29 July 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ↑ "Migrant dies on UK-bound freight train near Calais". The Guardian. 7 July 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ "Migrant reportedly dies trying to board Channel tunnel freight train". The Guardian. 26 June 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ "Calais in Frankreich: 2000 Flüchtlinge in einer Nacht am Eurotunnel". spiegel. 29 July 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ↑ Bilefsky, Dan (7 August 2015). "Sudanese Migrant Tries to Reach England by Walking Length of Channel Tunnel". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- ↑ "Van driver dies as he crashes into tail-back after migrants set up roadblock near Calais". Russia Today. 20 June 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- ↑ Wolmar, Christian (10 December 1994). "Fire raises Channel Tunnel fears". The Independent. London. Retrieved 25 December 2009.
- ↑ "Inquiry into the fire on Heavy Goods Vehicle Shuttle 7539 on 18 November 1996" (PDF). Channel Tunnel Safety Authority. May 1997. ISBN 0-11-551931-9. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- 1 2 C. J. Kirkland (2002). "The fire in the Channel Tunnel" (PDF). Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology. 17 (2): 129–132. doi:10.1016/S0886-7798(02)00014-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2010.
- ↑ "Lorry fire closes Channel Tunnel". BBC News. 21 August 2006. Retrieved 21 August 2006.
- ↑ Rail Accident Investigation Branch (October 2007). Fire on HGV shuttle in the Channel Tunnel 21 August 2006 (PDF) (Report). Rail Accident Report. Department for Transport.
- ↑ Robert Wright (12 September 2008). "Channel tunnel fire causes further cancellations". Financial Times. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- ↑ "Channel Tunnel Fire Evacuation". Sky News. 11 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2009.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel fully open to traffic". Eurotunnel.com. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- ↑ "Fire in the Channel Tunnel". ITV. 29 November 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2013.
- ↑ "Channel Tunnel closed and services hit after lorry fire". BBC. 17 January 2015. Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ↑ RAIB (28 January 2015). "Fire on board a freight shuttle in the Channel Tunnel" (press release). Gov.uk. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
shuttle 7340 made a controlled stop in the tunnel at cross-passage 4418
- ↑ Wolmar, Christian (22 February 1996). "Wrong kind of snow in tunnel...". The Independent. UK. Retrieved 21 December 2009.
- ↑ "Delays after Channel Tunnel fault". BBC News. 3 August 2007. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- ↑ "Severe Weather Brings Eurostar to a Halt". Sky News. 19 December 2009. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ↑ Bird, Steve; Lindsay, Robert (21 December 2009). "Eurostar blames 'fluffy' snow for weekend chaos". The Times. London. Retrieved 21 December 2009.
- ↑ Gray, Melissa (19 December 2009). "Eurostar services cancelled as snow brings havoc". CNN. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ↑ Randall, David; Lakhani, Nina (20 December 2009). "Thousands stranded in Eurostar chaos". The Independent. London. Retrieved 20 December 2009.
- ↑ "Passengers trapped on Eurostar trains relive ordeal". BBC News. 20 December 2009. Retrieved 20 December 2009.
- ↑ Cole, Rob (18 December 2009). "'Nightmare' Over For Stranded Passengers". Sky News. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ↑ "Passengers home after trapped in Channel Tunnel". The Press Association. 19 December 2009. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ↑ "Chaos in Eurotunnel as several trains break down". Amsterdam News.Net. 19 December 2009. Archived from the original on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
"Four Eurostars broken down at one time – it's absolutely unprecedented", John Keefe of Eurotunnel ... "There's never actually been an evacuation of a Eurostar train in the fifteen years that the tunnel has been opened and last night we evacuated two whole trains to get people off",
- ↑ "Eurotunnel rescues Eurostar" (PDF). Eurotunnel Press Release. 19 December 2009. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ↑ "Eurostar transports 500 vulnerable passengers to France". BBC News. 20 December 2009. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- ↑ Woodman, Peter (12 February 2010). "Eurostar rapped over Channel Tunnel breakdown – News & Advice, Travel". The Independent. UK. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Garnett, Christopher; Gressier, M. Claude (12 February 2010). "Eurostar Independent Review" (PDF report). Eurostar. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- ↑ "Eurostar disrupted after new breakdown in Channel tunnel". The Independent. London. 7 January 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- ↑ "Stricken Eurostar train towed out of Channel Tunnel". Uk.reuters.com. 7 January 2010. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- ↑ "The Channel Tunnel Safety Authority". Channel Tunnel Intergovernmental Commission. 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 247–254
- 1 2 Kirkland pp. 212–230
- ↑ The Channel Tunnel Experience Lessons for the Future pp. 19–23
- ↑ Kirkland pp. 231–240
- ↑ McFarlane, Andrew (12 September 2008). "Focus turns to cause of tunnel blaze". BBC News. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- ↑ "Glossary".
- ↑ "Formula One: Surtees drives through Channel Tunnel". The Independent. 17 November 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- ↑ "Chris Froome cycles through the Channel Tunnel". The Daily Telegraph. 7 July 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ Chris Froome, Team Sky and Jaguar: 'Cycling Under The Sea' on YouTube
- ↑ "Are you sure this is the right way Chris? Tour de France favourite Froome becomes the first person ever to cycle UNDER the sea from England to France in channel tunnel". Daily Mail. 7 July 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ Dawinderpal Sahota (9 January 2014). "EE and Vodafone offer Channel Tunnel network coverage". Telecoms.com. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ↑ "Eurotunnel completes mobile telephone and internet connections in Channel Tunnel" (PDF). Eurotunnel. 6 May 2014. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- ↑ "4G From EE Live in the Channel Tunnel". EE. 21 November 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ↑ Michael Garwood (21 November 2014). "EE and O2 now providing full 2G, 3G, and 4G access in Eurotunnel". Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ↑ "ElecLink". Eleclink. ElecLink. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- ↑ "Foundation laid for UK-France link". reNEWS - Renewable Energy News. 23 February 2017. Retrieved 26 February 2017.
- ↑ "Contracts awarded for ElecLink interconnector". 4c Offshore. Retrieved 26 February 2017.
- ↑ "Eurorunnel Press Release 23 Feb 2017" (PDF). eleclink. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
Sources
- Anderson, Graham; Roskrow, Ben (1994). The Channel Tunnel Story. London: E & F N Spon. ISBN 0-419-19620-X.
- Bonavia, Michael R (1987). The Channel Tunnel Story. Newton Abbot: David & Charles. ISBN 0-7153-8964-5.
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Regional Policy and Cohesion. (1996). The regional impact of the Channel Tunnel throughout the Community. Luxembourg: European Commission. ISBN 92-826-8804-6.
- Flyvbjerg, B.; Buzelius N.; Rothengatter, W. (2003). Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-00946-4.
- Foreign & Commonwealth Office (1994). The Channel Tunnel Story: The world's longest undersea tunnel system. London: Foreign & Commonwealth Office.
- Grayson, Richard S. (1996). "The British Government, the Channel Tunnel and European Unity, 1948-64". European History Quarterly. 26 (3): 415–436.
- Institution of Civil Engineers (1989). The Channel Tunnel. London: Thomas Telford. ISBN 0-7277-1546-1.
- Kirkland, Colin J., ed. (1995). Engineering the Channel Tunnel. London: Chapman and Hall. ISBN 0-419-17920-8.
- Redford, Duncan (2014). "Opposition to the Channel Tunnel, 1882–1975: Identity, Island Status and Security". History. 99 (334): 100–120.
- Whiteside, Thomas (1962). The Tunnel under the Channel. Rupert Hart-Davis. ISBN 0-684-83243-7.
- Wilson, Jeremy; Spick, Jerome (1994). Eurotunnel – The Illustrated Journey. HarperCollins. ISBN 0-00-255539-5.
Further reading
- Dupont, Christophe (1990). "The Channel Tunnel Negotiations, 1984–1986: Some aspects of the process and its outcome". Negotiation Journal. 6 (1): 71–80.
- Forbes, Horace Courtenay Gammell (1883). Shall we have a Channel tunnel?. Aberdeen: A. Brown & Co.
- Holliday, Ian (1992). "The politics of the Channel Tunnel". Parliamentary Affairs. 45 (.2): 188–204.
- "Main tunnel dig starts". RAIL. No. 93. EMAP National Publications. 6–19 April 1989. p. 6. ISSN 0953-4563. OCLC 49953699.
- Moore, Gary & Sutton, Philip (30 November – 13 December 1989). "Eurotunnel competes service tunnel". RAIL. EMAP National Publications (110): 7. ISSN 0953-4563. OCLC 49953699.
- "New Plan For Channel Tunnel". Popular Mechanics. May 1929. Article on a post-WW1 plan for a tunnel that was scrapped by the Great Depression. A total cost figure of 150 million was given in 1929
- Stokes, Sir John. "Chapter 14: Chunnel". fortunecity.com. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009. Autobiography of Sir John Stokes regarding 1882 deliberations
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eurotunnel. |
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Official website
- Tribute website at chunnel.com
- "Chunnel Tunnel 1880 Attempt". ubbrit.org.uk.
- Channel Tunnel on OpenStreetMap wiki
- "Channel Tunnel". Structurae.