Chadic languages
| Chadic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Nigeria, Niger, Chad, Central African Republic, Cameroon |
| Linguistic classification |
|
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-5 | cdc |
| Glottolog | chad1250[1] |
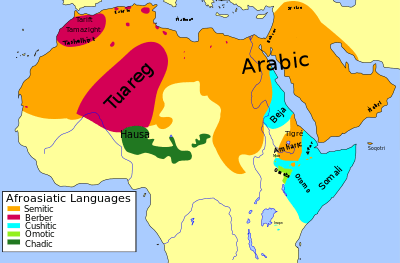 | |
The Chadic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family that is spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 150 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, Central African Republic and northern Cameroon. The most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a lingua franca of much of inland West Africa.
Composition
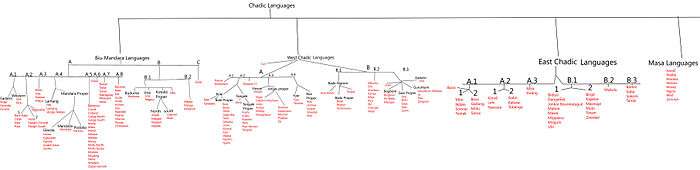
Newman (1977) classified the languages into the four groups which have been accepted in all subsequent literature. Further subbranching, however, has not been as robust; Blench (2006), for example, only accepts the A/B bifurcation of East Chadic.[2]
- West Chadic. Two branches, which include
- (A) the Hausa, Ron, Bole, and Angas languages; and
- (B) the Bade, Warji, and Zaar languages.
- Biu–Mandara (Central Chadic). Three branches, which include
- (A) the Bura, Kamwe, and Bata languages, among other groups;
- (B) the Buduma and Musgu languages; and
- (C) Gidar
- East Chadic. Two branches, which include
Origin


Several modern genetic studies of Chadic speaking groups in the northern Cameroon region have observed high frequencies of the Y-Chromosome Haplogroup R1b in these populations (specifically, of R1b's R-V88 variant). This paternal marker is common in parts of West Eurasia, but otherwise rare in Africa. Cruciani et al. (2010) thus propose that the Proto-Chadic speakers during the mid-Holocene (~7,000 years ago) migrated from the Levant to the Central Sahara, and from there settled in the Lake Chad Basin.[3]
Bibliography
- Lukas, Johannes (1936) 'The linguistic situation in the Lake Chad area in Central Africa.' Africa, 9, 332–349.
- Lukas, Johannes. Zentralsudanische Studien, Hamburg 1937;
- Newman, Paul and Ma, Roxana (1966) 'Comparative Chadic: phonology and lexicon.' Journal of African Languages, 5, 218–251.
- Newman, Paul (1977) 'Chadic classification and reconstructions.' Afroasiatic Linguistics 5, 1, 1–42.
- Newman, Paul (1978) 'Chado-Hamitic 'adieu': new thoughts on Chadic language classification', in Fronzaroli, Pelio (ed.), Atti del Secondo Congresso Internazionale di Linguistica Camito-Semitica. Florence: Instituto de Linguistica e di Lingue Orientali, Università di Firenze, 389–397.
- Newman, Paul (1980) The Classification of Chadic within Afroasiatic. Leiden: Universitaire Pers Leiden.
- Herrmann Jungraithmayr, Kiyoshi Shimizu: Chadic lexical roots. Reimer, Berlin 1981.
- Herrmann Jungraithmayr, Dymitr Ibriszimow: Chadic lexical roots. 2 volumes. Reimer, Berlin 1994
- Schuh, Russell (2003) 'Chadic overview', in M. Lionel Bender, Gabor Takacs, and David L. Appleyard (eds.), Selected Comparative-Historical Afrasian Linguistic Studies in Memory of Igor M. Diakonoff, LINCOM Europa, 55–60.
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Chadic". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Blench, 2006. The Afro-Asiatic Languages: Classification and Reference List (ms)
- ↑ Cruciani, F; Trombetta, B; Sellitto, D; Massaia, A; Destro-Bisol, G; Watson, E; Beraud Colomb, E; Dugoujon, JM; Moral, P; Scozzari, R (2010). "Human Y chromosome haplogroup R-V88: a paternal genetic record of early mid Holocene trans-Saharan connections and the spread of Chadic languages". European Journal of Human Genetics. 18 (7): 800–7. PMC 2987365
 . PMID 20051990. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2009.231.
. PMID 20051990. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2009.231.