Cercocarpus betuloides
| Cercocarpus betuloides | |
|---|---|
| | |
| var. blancheae in fruit | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Genus: | Cercocarpus |
| Species: | C. betuloides |
| Binomial name | |
| Cercocarpus betuloides Nutt. 1840 | |
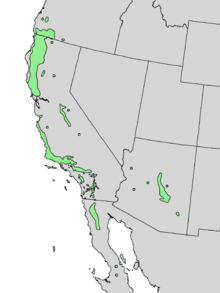 | |
| Natural range of Cercocarpus betuloides | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Cercocarpus montanus var. glaber (S. Watson) F.L. Martin | |
Cercocarpus betuloides is a shrub or small tree in the (rose family).[2] Its common names include mountain mahogany and birch leaf mountain mahogany[2][3] The common name "mahogany" comes from the hardness and color of the wood, although the genus is not a true mahogany.[2]
Range and habitat
The plant is native to California, Baja California, Oregon, Arizona, and northwestern New Mexico.[4] It typically grows in summer dry areas of the foothills and mountains of California, often in chaparral communities.[2]
Description
Growth pattern
Cercocarpus betuloides is a shrub or small tree growing from 3 feet (0.91 m) to 30 feet (9.1 m).[2][5] Its branches are incised and muscular in appearance from the side. In cross section they appear lobed.
Common shrub associates within the chaparral community include toyon.[6]
Leaves and stems
The leaves are distinctive in that they have smooth edges from the base to about half way up, then are wavy or toothed to the rounded tip.[2]
Betula is the birch genus, and the species name refers to the birch-like leaves.[2]
Inflorescence and fruit
The white flowers are small, clustered, and mildly scented, similar to acacia.[2]
The fruit is a tubular achene with the long, plumelike flower style still attached.
The genus name comes from the Greek kerkos ("tail"), referring to the tail-like appearance of the fruit; and carpus ("fruit"), thus, "fruit with tail".
Taxonomy
- Varieties
There are three varieties:[7][8]
- Cercocarpus betuloides var. betuloides, rangewide
- Cercocarpus betuloides var. blancheae – Catalina mahogany, island mountain mahogany, limited to California, especially the Channel Islands[9][10]
- Cercocarpus betuloides var. macrourus – few flowered mountain mahogany, California and Oregon[11][12]
Cercocarpus betuloides is sometimes treated as a part of Cercocarpus montanus,[13] var. glaber in particular.[14]
Uses
The reddish wood of the shrub is very hard and was traditionally used by the indigenous peoples of California to make arrow tips, fishing spears, and digging sticks.[2]
Cercocarpus betuloides is cultivated as an ornamental plant by specialty nurseries for planting in native plant, drought tolerant, and wildlife gardens; and in designed natural landscaping projects and habitat restoration programs.[15][16]
See also
References
- ↑ The Plant List, Cercocarpus montanus var. glaber (S.Watson) F.L.Martin
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Flowering Plants of the Santa Monica Mountains, Nancy Dale,2nd Ed, 2000, p. 170
- ↑ Calflora taxon report, University of California, Cercocarpus betuloides Torrey & A. GrayMountain mahogany, birch leaf mountain mahogany . accessed 2.28.2015
- ↑ Biota of North America Program 2014 county distribution map
- ↑ Abrams, L. (1951). Illustrated Flora of the Pacific States. Stanford University Press. 874 pages ISBN 0-8047-0004-4
- ↑ Hogan, C. M. (2008). Toyon (Heteromeles arbutifolia). Archived July 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. GlobalTwitcher, ed. N. Stromberg.
- ↑ Cercocarpus betuloides. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN).
- ↑ Cercocarpus betuloides. CalFlora.
- ↑ Cercocarpus betuloides var. blancheae. The Jepson Manual, 2012.
- ↑ Cercocarpus betuloides var. blancheae. CalFlora.
- ↑ Cercocarpus betuloides var. macrourus. The Jepson Manual, 2012.
- ↑ Cercocarpus betuloides var. macrourus. CalFlora.
- ↑ Cercocarpus montanus. NatureServe. 2012.
- ↑ Cercocarpus montanus var. glaber. USDA PLANTS . accessed 2.28.2015
- ↑ Las Pilitas Horticulture Database: Cercocarpus betuloides (Mountain Mahogany) . accessed 2.28.2015
- ↑ Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center Native Plant Information Network−NPIN: Cercocarpus montanus var. glaber (Smooth mountain mahogany) . accessed 2.28.2015
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cercocarpus betuloides. |
- Jepson Manual Treatment — Cercocarpus betuloides
- Calflora taxon report, University of California: Cercocarpus betuloides (Mountain mahogany, birch leaf mountain mahogany)
- United States Department of Agriculture Plants Profile for Cercocarpus montanus var. glaber (birchleaf mountain mahogany)
- Cercocarpus betuloides — Calphotos Photo gallery, University of California