Central Solomon languages
| Central Solomons | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Solomon Islands |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | None |
|
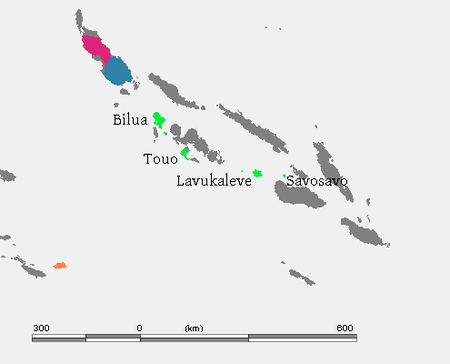
Language families of the Solomon Islands. Central Solomons | |
The Central Solomon languages are the four Papuan languages spoken in the Solomon Islands. They were identified as a family by Wilhelm Schmidt in 1908 and were classified as East Papuan languages by Wurm, but this does not now seem tenable, and was abandoned in Ethnologue (2009). Although some studies have tried to find if these languages are genetically related, no conclusive proof has been found by now.[1]
The four languages are,
- Bilua of Vella Lavella and Ghizo Islands,
- Touo (also known as Baniata) of Rendova Island,
- Lavukaleve of the Russell Islands, and
- Savosavo of Savo Island.
Pronouns reconstructions
Ross (2001) reconstructs pronouns and pronominal object suffixes (represented with hyphens) for proto-Central Solomons as follows:
| Person | Singular | Dual | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 exclusive | *ŋa, *a | *-la | *ge | *ŋe, *ve |
| 1 inclusive | ? | *mai | ||
| 2 | *ŋo, *nu | ? | *be | *me |
| 3 masculine | ? | *-la | *la(/*lo) | *ma, *mu |
| 3 feminine | *vo, ko | *-ma | ||
Pedrós (2015) argues for the existence of the family through comparison of pronouns and other gender, person and number morphemes and based on the existence of a common syncretism between 2nd person nonsingular and inclusive. He performs an internal reconstruction for the pronominal morphemes of each language and then proposes a reconstruction of some of the pronouns of the claimed family. The reconstructions are the following:
| 1 singular | 2 singular | inclusive/ 2 singular | 1 exclusive | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Savosavo | *a-ɲi | *no | *me | a- |
| Pre-Touo | e̤ | noe | *me | e̤- |
| Pre-Lavukaleve | *ŋai | *ŋo | *me | e |
| Pre-Bilua | *ani/*aŋai | *ŋo | me | e- |
| Proto-Central Solomons | *ani/*aŋai | *ŋo | *me | *e |
See also
References
- ↑ Terrill, Angela, 2006. "Central Solomon Languages". In Encyclopedia of language and linguistics, ed. by Keith Brown: 279–281.
- Ross, Malcolm, 2001. "Is there an East Papuan phylum? Evidence from pronouns", in The boy from Bundaberg. Studies in Melanesian linguistics in honour of Tom Dutton, ed. by Andrew Pawley, Malcolm Ross and Darrell Tryon: 301-322. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- Structural Phylogenetics and the Reconstruction of Ancient Language History. Michael Dunn, Angela Terrill, Ger Reesink, Robert A. Foley, Stephen C. Levinson. Science magazine, 23 Sept. 2005, vol. 309, p 2072.
- Ross, Malcolm, 2005. "Pronouns as a preliminary diagnostic for grouping Papuan languages", in Papuan pasts: cultural, linguistic and biological histories of Papuan speaking peoples, ed. by Andrew Pawley, Robert Attenborough, Robin Hide and Jack Golson: 15-65. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- Pedrós, Toni, 2015. "New arguments for a Central Solomons family based on evidence from pronominal morphemes". Oceanic Linguistics, vol. 54, no. 2 (358-395).