Ceinture fléchée


The ceinture fléchée [sɛ̃tyʁ fleʃe] (French for "arrowed sash"; English: L'Assomption sash or "arrow sash") is a type of colorful sash, a traditional piece of French-Canadian clothing of the 19th century (of the Lower Canada, Canada East and early confederation eras). The Métis also made ceintures fléchées and use them as part of their national costume. While the traditional view is that the ceintures fléchées is a French-Canadian invention, others propose a different view on its origin. According to Dorothy K. Burnham who prepared an exhibit on textiles at the National Gallery of Canada in 1981, and published an accompanying catalogue raisonné, this type of finger weaving was learned by the residents of New France from the indigenous peoples.[1]
History
In Quebec, this wool sash was used by men to tie jackets around their waists to prevent the cold from creeping in. It was a both practical and fashionable accessory, worn by both the bourgeois and the habitant classes. The width of a traditional belt can be 15 centimetres to 25 centimetres, and its length can easily be more than 2 metres. The ceinture also had a practical use: it helped prevent back injuries or hernias amongst the fur traders of the time.[2]
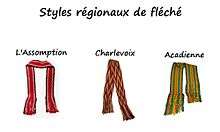
It is adorned by an arrowed pattern and was worn around the winter coats of the time. It is also a symbol of the Lower Canada Rebellion and the Quebec Winter Carnival, as it is worn by the festival mascot, Bonhomme Carnaval. Imitations are sold and seen throughout the carnival. The belt is represented in a number of artistic creations, such as the illustration Le Vieux de '37 by Henri Julien, the painting L'Assemblée des six-comtés by Charles Alexander Smith and the song Mon Pays, suivi du Reel des Aristocrates from néo-trad musical band Les Cowboys Fringants.
The arrow sash was part of the traditional costume of the Lower Canada habitant at least from 1776 on. Although at that time the British visitors and the German mercenaries who noticed its presence called it a "coloured sash". That is what Thomas Anbury called it when he wrote his account of travel after his visit to Charlesbourg and Beauport in 1776.[3] In 1777, Charlotte Luise de Riedesel, arriving from Germany to rejoin her husband, Major-General Frederick, related that when she met him in Chambly, he was wearing a red and blue sash with fringes[4] over the traditional Canadian costume to keep him warm as he was still suffering from influenza. That same year, a German mercenery lodged at Sainte-Anne related how people in their home were weaving the colored sashes using their domestic wool.[5] In 1778, E.V. Germann made a drawing showing clearly a Canadian peasant wearing his sash, the design was a chevron.[6] That drawing is a proof of what is written by others. Elisabeth Simcoe who lived in Quebec city in 1792 for more than a year wrote about the Canadians, "(…) their coats are tied round with a coloured sash."[7]
When in 1798, the corpse of a drowned voyageur was found along the St. Lawrence River, in Verchères, Labadie wrote in his personal diary that the voyageur was wearing "…une jolie cinture à flesche"[8] Also in 1798, the inventory after death of Mrs Chaboillez, whose husband, Charles, was one of the founders of the Beaver Club, numbered "deux cintures à flesches"[9] In 1806, the British John Lambert after having visited many villages wrote that five habitants out of six wore a colored sash. He even specified that sometimes the sash was decorated with beads. The sash was changing in its design, but this cannot be attributed to anyone in particular.[10]:158-159
The coloured sash was brought to western Canada by the men working for the North West Company. These voyageurs wore their sashes when leaving Lower Canada and travelling for the fur company. Their sashes attracted the attention of several nations with whom they exchanged goods and soon these people wished to possess such sashes. The company then had many sashes woven in Montreal and area with the fine worsted wool it imported from England. Beside the NWC, the Hudson's Bay Company also became interested in that barter article. One of its agents made a request to satisfy that wish. He wrote : "…worsted of colour to make sashes of the latter I have got sample of from my neighbour which will send home". His neighbour was Charles Boyer of the NWC.[11] The sashes adopted by the Indians and the Métis, sons of the voyageurs, are still favoured. They even name it their identity symbol. However, quite often the so-called Métis sashes are not the authentic hand-woven sashes but the kind woven on loom in England probably to meet the requests at lower cost. This can be read in the HBC archives.
The design of the sash continued to be modified and finally became a standard type that was mainly produced in L'Assomption region around 1835, according to the historian Mason Wade.[12] The HBC agents who came to collect them at Fort Assomption named these sashes lassomption or l’Assomption sash in the accounting books.
Despite its great popularity in Lower Canada as well as in the West, there was a slow-down in its production. That was probably due to the decline of the fur trade in 1870[13]:52 and in part to the suggestion of the parish priest Tancrède Viger to the weavers, to stop producing, considering them very badly paid for their work.
Sashes were worn by snow-shoers and by retired fur traders who took residence in Montreal and area. Many artists left drawings, paintings and sketches confirming the popularity of the sash. A few women continued weaving sashes and ensured the handing-down of the craft to other generations and the current one.
Marius Barbeau was very interested in ceinture fléchée trying to find its origin. He did not, but left many clues to learn more of its presence, popularity if not its origin.[14] E.Z. Massicotte, archivist at Montreal City Hall and folklorist, continued Barbeau's research and concluded: "la ceinture fléchée un chef d’œuvre de l’industrie domestique du Canada".[15] Yet no such type of diagonal weaving is known elsewhere in the world, let alone in France.[16] It seems that Native Americans were quick to improve their techniques upon the discovery of brightly coloured yarns that they did not have access to previous to contact, and often took apart fabrics to reuse the yarn for sashes, and a photo of an example is shown in Burnham's book.[17] Since 1968 many persons learned to hand weave ceintures fléchées though not all kept weaving sashes, many taught the craft and are spreading its knowledge.[18] Many popular singers, folklore dancers and especially Bonhomme Carnaval are contributing to make it known to visitors and in various countries.
Fabric-making process
Many steps are required in the creation of a ceinture fléchée. First, the craftmaker picks the wool threads that they need. The threads have to be long enough so that the person who will wear the sash can pass it twice around the waist. The craftmaker needs to add the length of the fringes at each end of the belt. The fringes are used to tie the arrow sash.
After that, the craftmaker organizes the threads and weaves them to create designs of lightning bolts (zigzags), flames (lozenges) and arrow heads (uusually in the middle of the sash). Finally, to make the fringes, the craftmaker finishes the belt by making twists or braids with the length of thread that remains.
In the creation of a perfect ceinture fléchée or the intricate beadwork designs that would adorn various artifacts a hard callus develops on the tips of the finger. This is referred to as a "needle finger". It was considered a "rite of passage" for young girls and is acknowledged by the matriarchs in the family.
Notes and references
- ↑ Dorothy K. Burnham. L'Art des étoffes, le filage et le tissage traditionnels au Canada, Galerie nationale du Canada, Musées nationaux du Canada, 198, p. 36
- ↑ Jean Provencher (2003). Le Carnaval de Québec: La grande fête de l'hiver. Éditions MultiMondes. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-2-89544-047-5. Retrieved 30 October 2012.
- ↑ Anbury, Thomas, Voyage dans les parties intérieures de l’Amérique , pendant le cours de la dernière guerre. Paris, Briand, 1790, 2 vol.
- ↑ Riedesel, Charlotte Luise de, « Letters in Memoirs » Die Berufsreise nach Amerika. Briefe von Frederick Riedesel. Berlin, Haude and Spenersche, 1827, version anglaise, New York, 1925, 348 p.
- ↑ Ein Canadischer Bauer, de Frederich von Germann, aquarelle, 1778, Photo :(New York Public Library) image reproduite dans « Une jolie cinture à flesche » Les Presses de l’Université Laval, 2003, p. 69
- ↑ Journal anonyme
- ↑ Simcoe, Elizabeth (1965). Innis, Mary Quayle, ed. Mrs. Simcoe's diary. Macmillan of Canada. p. 45.
- ↑ Louis Généreux de Labadie, « Journal de 1794-1817 », Archives du Petit Séminaire de Québec, M.G.-23 G3-18, p. 153
- ↑ Inventaire après décès de madame Chaboillez, 1798. (greffe du notaire J.G.Beek, 24 décembre 1798, ANQ.)
- ↑ Lambert, John (1814). Travels through Canada, and the United States of North America, in the years 1806, 1807, & 1808 : to which are added biographical notices and anecdotes of some of the leading characters in the United States. London. Retrieved 19 September 2016.
- ↑ HBCA,B-105A, 1796-1797, p. 8 (doer)
- ↑ Mason Wade, L’encyclopédie du Canada français à nos jours 1760-1967. Traduit par Adrien Venne avec le concours de Francis Lubeyrie, Montréal, 1963, 3 vol.
- ↑ Neering, Rosemary (1974). Fur trade. Toronto: Fitzhenry & Whiteside. ISBN 9780889021792.
- ↑ Marius Barbeau, Ceintures fléchées, Montréal, Éditions Paysana, 1945, 110p.
- ↑ E.Z.Massicotte, Mémoires de la Société royale du Canada, Montréal, section 1, série 111, vol. xviii, mai 1924
- ↑ Burnham, "L'art des étoffes", p. 36.
- ↑ "25. Ceinture vers 1780",Burnham, p. 37
- ↑ "Assomption Sash". Encyclopedia of French Cultural Heritage in North America. Retrieved 2014-02-23.
See also
- Culture of Quebec
- Folk costume
- Lower Canada Rebellion
- Metis people (Canada)
- Quebec Winter Carnival
- Festival du Voyageur
References
In English
- James, Carol (2008). Fingerweaving Untangled. An illustrated beginner's guide including detailed patterns and common mistakes, Altona, Manitoba: Friesens Printing, 64 p. ISBN 978-0-9784695-0-4
- Gottfred, J. "Ceinture Fléchée : Finger Weaving a Voyageur Sash", in Northwest Journal, Vol. VI, pp. 1–5.
- Beauvais, Michelle (2007). Braided Assomption Sash: so called "ceintured fléchée" or "arrowhead-design sash" pp. 37–42 in Space, Time and Braid published by Texte. Inc. Author Makiko Tada and Hiroyuki Hamada, printed in Japan (ISBN 978-4-925252-21-8).
- Bourdeau-Picard, Michelle (2004). An Alluring Symbol: The Arrow Sash in Canadian Art. Catalogue of an exhibition held at the Musée d'art de Joliette, Québec. May 21 to Aug. 22, 78 p. (ISBN 2-921801-28-0).
- Austin,Robert J. (2000). A manual of Fingerweaving56 p. A well ilustruted and colorful "How to do" sashes. Editor: Earl C. Fenner, published by Crazy Crow Trading Post Printed in Canada (ISBN NO.1-9929572-00-X)
- Speiser, Noémi (1983). "The Manual of Braiding" published by the author (Basel) Switzerland. Reedited in1988,1991,1997. Noémi Speiser is an international authority on Braids having researched the subject for over 35 years.
- Burnham, Dorothy,K. (1981). The Comfortable Art: spinning and weaving in Canada. Chater 2: Indian and French Braiding, published by National Museum of Canada. She join the staff of the Royal Ontario Museum in 1929 as a "second assistant draftsman" and became its first curator of textiles in 1939.
- Burnham, Dorothy K. (1976).Braided "Arrow" sash of Quebec. Irene Emery Roundtable at the Textile Museum Washington D.C. (Noemi Speiser was there).
- Turner, Altar A. (1973). Finger Weaving: Indian braiding, by Sterling Publishing, New York N.Y. (ISBN 0-8069-5264-4). Reprinted 1989 by Cherokee Publications NC 28719
- Barbeau Marius (1937). Assomption Sash, Ottawa: Dept. of Mines, National Museum of Canada. [Bulletin No. 93, Anthropological Series No. 24], 51 p. (online)
In French
- Beauvais, Michelle (2007). Le tressage au-delà du trois brins' avec révision (ressources électronique)Granby, M. Beauvais 167 pages (ISBN 978-2-9809125-1-1)
- Beauvais, Michelle (2006). Le tressage au-delà du trois brins, Granby: M. Beauvais, 137 p. (ISBN 2-9809125-0-6)
- Association des artisans de ceinture fléchées de Lanaudière inc. (1994). Histoire et origines de la ceinture fléchée traditionnelle dite de L'Assomption, collaboration avec le département d'ethnologie de l'université Laval à Québec. 125 p. Édition du Septentrion: Sillery, Québec. (ISBN 2-89448-002-4) (preview).
- Bourdeau-Picard, Michelle (2004). Un symbole de taille: la ceinture fléchée dans l'art canadien. Catalogue d'une exposition tenue du 21 mars au 22 août au Musée d'art de Joliette, Québec. 78p. (ISBN 2-921801-28-0).
- Genest Leblanc, Monique (2003). Une jolie cinture à flesche. sa présence au Bas Canada, son cheminement vers l'Ouest, son introduction chez les Amérindiens. Les Presses de l'Université Laval, Québec QC. Science humaine et sociale. 178 p. (ISBN 2-7637-7858-5).
- Verdeau-Hemlin, Denise (1990). Évolution des motifs de fléché, Montréal: Association des artisans de ceinture fléchée du Québec, 26 p. (ISBN 2980118915)
- Hamelin, Véronique L. (1983). Le Fléché authentique du Québec par la méthode renouvelée, Outremont: Léméac, 256 p. (ISBN 276095353X)
- Brousseau, Hélène Varin (1980). Le fléché traditionnel et contemporain, Montréal: La Presse, 133 p. (ISBN 2890430464)
- LeBlanc, Monique (1977). Parle-moi de la ceinture fléchée!, Montréal: Fides, 107 p. (ISBN 0775506613)
- LeBlanc, Monique (1974). J'apprends à flécher, Montréal: R. Ferron Éditeur, 127 p.
- Bourret, Françoise, Lucie Lavigne (1973). Le fléché : l'art du tissage au doigt, Montréal: Éditions de l'Homme, 222 p. (ISBN 077590399X)
- Barbeau Marius (1945). Ceinture fléchée, Montréal: Editions Paysana, 110 p. (ISBN 0885150341)
Specialized references in textiles
- Emery, Irene,(1966). The Primary Structures of Fabrics, The Textile Museum Washington, D.C.
- Burnham, Dorothy, K., (1976). Braided "Arrow" sashes of Quebec. Emery Roundtable at the Textile Museum of Washington, D.C. (with the presence of Noemi Speiser). Dorothy Burnham is an historian in textile, Canada. She start working at the Royal Ontario Museum in 1929 as a second assistant "draftsman" and became its first curator. She is an authority in textile history.
- Burnham, Dorothy K., (1981). The Comfortable Art: Tradition Spinning and Weaving in Canada. Chapter 2. Indian and French Braiding, National Museum of Canada, Ottawa. En français, L'art des étoffes: filage et tissage traditionnels au Canada. Chapitre 2. Indian and French Braiding, National Museum of Canada, Ottawa.
Jouppien, Jerry H. "The Ceinture Flechee: A Pictorial Gallery. Published by J. H. Jouppien, April 2017, 135pp, 80 colour plates-- for information go to ceintureflechee@gmail.com
- Speiser, Noémi, (1983). The Manual of Braiding. Published by the author, Basel. Switzerland. Reedition:1988-1991-1997. Noémi Speiser is an international authority on Braids, having researched the subject over 35 years.
Bibliography
Monique Genest LeBlanc :Mémoire de Maîtrise : La ceinture fléchée au Québec, 1991, un. Laval, Québec. Ethnologie des Francophones en Amérique du Nord, département d’Histoire, faculté des Lettres
Monique Genest LeBlanc : Thèse de doctorat : Introduction de la ceinture fléchée chez les Amérindiens : création d’un symbole de statut social, 1996, Un. Laval, Québec,
Monique Genest LeBlanc : « Une cinture à flesche » Sa présence au Bas-Canada, son cheminement vers l’Ouest, son introduction chez les Amérindiens. 2003, Les presses de l’université Laval, Québec.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ceinture fléchée. |
- Sash Weaver, personal Web site of sash weaver Carol James, author of the book Fingerweaving Untangled, containing instructional videos and other resources.
- Étchiboy, Métis company that weaves sashes on looms.
- Artisant du Fléché Lessons on different technical fabrication of the Fléché motifs