Carbylamine reaction
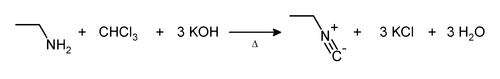
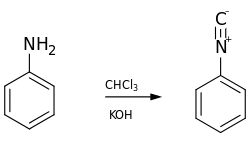
The carbylamine reaction, also known as Hoffman's isocyanide test is a chemical test for detection of primary amines.[1] In this reaction, the analyte is heated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide and chloroform. If a primary amine is present, the isocyanide (carbylamine) is formed which are foul smelling substances.
For example, the reaction with ethylamine:
The reaction with aniline:
The carbylamine test does not give a positive reaction with secondary and tertiary amines.
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.