Cape Fear River
| Cape Fear River | |
|---|---|
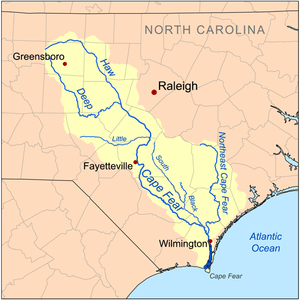 Map of the Cape Fear River drainage basin | |
| Country | United States |
| Basin features | |
| Main source | North Carolina |
| River mouth | Atlantic Ocean |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Length | 202 mi (325 km) |
| Discharge |
|
The Cape Fear River is a 202 miles (325 km) long[1] blackwater river in east central North Carolina in the United States. It flows into the Atlantic Ocean near Cape Fear, from which it takes its name.
History
In October 1662, the English explorer William Hilton Jr. made a three-week reconnaissance of the lower reaches of the Cape Fear River.
- "ye [þe] 4th Octob. we weighed, and went into ye Haven, where was 5.6.7.8 fathoms water, and in a weeks time, spent with ye indians, and in sounding ye River and ye ship turning up alway against ye wind, we gott up 15. or 16. leagues into ye river; and after in our long boate, half of us went 15. leagues further, till at ye head of ye river we could not tell, which of ye many rivers to take, and so returned to our ship, and as we went and came, we found many faire and deep rivers, all ye way running into this Charles River."
Hilton's report contained favorable comments on the fish, fowl, and wildlife of the region. He noted "vast meddows, besides upland fields," "greatt swamps laden with varieties of great oakes, and other trees of all sorts," and the potential for good growing conditions. Hilton wrote that the Indians were "very poor and silly Creatures," that he had observed fewer than one hundred of them, but that they were "very theevish." He wished "all Englishmen, that know how to improve and use a plentiful Countrey and condition, not to delay to posses it...."[2]
During his 1664 visit, Hilton remained almost two months on the Cape Fear. The explorers spent much of their time on the Northeast Branch which they felt was the main channel. They anchored their ship, "Adventure", and rowed the ship's long-boat on trips up several tributaries. The longest of these explorations was four days' travel up-stream and two back down.
As the Hilton party left the Cape Fear they "made a purchase of the river and land of Cape Fair, of Wat Coosa...." They found a warning near the mouth of the river left by the New Englanders (of the ill-fated colony earlier that year) which disparaged the country and warned against settlement there. Hilton's report concluded with a rebuttal to that warning:
- "we have seen facing both sides of the river and branches of Cape Fear aforesaid, as good land and as well timbered as any we have seen in any other part of the world, sufficient to accommodate thousands of our English nation, and lying commodiously by the said river's side."
Course

It is formed at Haywood, near the county line between Lee and Chatham counties, by the confluence of the Deep and Haw rivers just below Jordan Lake. It flows southeast past Lillington, Fayetteville, and Elizabethtown, then receives the Black River approximately 10 miles (16 km) northwest of Wilmington. At Wilmington, it receives the Northeast Cape Fear River and Brunswick River, turns south, widening as an estuary and entering the Atlantic approximately 3 miles (5 km) west of Cape Fear.
During the colonial era, the river provided a principal transportation route to the interior of North Carolina. Today the river is navigable as far as Fayetteville through a series of locks and dams. The estuary of the river furnishes a segment of the route of the Intracoastal Waterway.
The East Coast Greenway runs along the River.
Bridges
- Cape Fear Memorial Bridge
- S. Thomas Rhodes Bridge
See also
- List of North Carolina rivers
- USS North Carolina
- Cape Fear Museum
- South Atlantic-Gulf Water Resource Region
References
- ↑ Cape Fear River Archived April 1, 2005, at the Wayback Machine., The Columbia Gazetteer of North America. Note that despite the gazetteer's claim of the river being the longest entirely within North Carolina, the Neuse River is longer
- ↑ Quoted in Gregory E. Rutledge (2013). The Epic Trickster in American Literature. Routledge Studies in Twentieth-Century Literature. Routledge. p. 157. ISBN 9781136194832.
Sources and external links
- Cape Fear River discharge data
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cape Fear River
 The port in Wilmington on the Cape Fear River estuary
The port in Wilmington on the Cape Fear River estuary Lock and Dam No. 1 on the Cape Fear River in Bladen County
Lock and Dam No. 1 on the Cape Fear River in Bladen County- U.S. Coast Guard vessel on the Cape Fear, photographed from the USS North Carolina
- A cargo ship navigating the mouth of the Cape Fear River at Southport
- A closeup of a cargo ship passing by Southport
 Sunset over the Cape Fear River flowing under the S. Thomas Rhodes Bridge.
Sunset over the Cape Fear River flowing under the S. Thomas Rhodes Bridge.
Coordinates: 33°53′8″N 78°0′46″W / 33.88556°N 78.01278°W