C3orf60
| NDUFAF3 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | NDUFAF3, 2P1, C3orf60, E3-3, NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase complex assembly factor 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1913956 HomoloGene: 32460 GeneCards: NDUFAF3 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||||
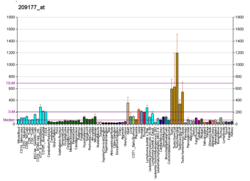 | |||||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 3: 49.02 – 49.02 Mb | Chr 9: 108.57 – 108.57 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex assembly factor 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NDUFAF3 gene.[3][4][5]
This gene encodes a nuclear protein of unknown function. The similar rat nuclear protein is predominantly expressed in testis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[5]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Hammami-Hamza S, Doussau M, Allemand I, Segretain D, Gasc JM, Finaz C (Mar 2003). "2P1, a novel male mouse cDNA specifically expressed during meiosis". Int J Dev Biol. 47 (1): 71–6. PMID 12653254.
- ↑ Hartmann AM, Stamm S (Nov 1997). "Molecular cloning of a novel alternatively spliced nuclear protein". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1353 (3): 224–30. PMID 9349717. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(97)00090-0.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: C3orf60 chromosome 3 open reading frame 60".
External links
- Human NDUFAF3 genome location and NDUFAF3 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network.". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. PMID 16189514. doi:10.1038/nature04209.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. - Lehner B, Sanderson CM (2004). "A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation.". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1315–23. PMC 442147
 . PMID 15231747. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004.
. PMID 15231747. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. - Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing.". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. PMC 1083732
 . PMID 11256614. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058.
. PMID 11256614. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. - Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery.". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. PMID 8889548. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.