C1S
| C1S | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||
| Aliases | C1S, EDSPD2, complement C1s | ||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1355312 HomoloGene: 1314 GeneCards: C1S | ||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||
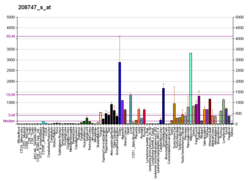 | |||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 12: 6.99 – 7.07 Mb | Chr 6: 124.53 – 124.54 Mb | |||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Complement C1s subcomponent is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C1S gene.[3]
Interactions
C1S has been shown to interact with C1R.[4][5]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: C1S Complement component 1, s subcomponent".
- ↑ Thielens NM, Enrie K, Lacroix M, Jaquinod M, Hernandez JF, Esser AF, Arlaud GJ (April 1999). "The N-terminal CUB-epidermal growth factor module pair of human complement protease C1r binds Ca2+ with high affinity and mediates Ca2+-dependent interaction with C1s". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14): 9149–59. PMID 10092586. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9149.
- ↑ Thiel S, Petersen SV, Vorup-Jensen T, Matsushita M, Fujita T, Stover CM, Schwaeble WJ, Jensenius JC (July 2000). "Interaction of C1q and mannan-binding lectin (MBL) with C1r, C1s, MBL-associated serine proteases 1 and 2, and the MBL-associated protein MAp19". J. Immunol. 165 (2): 878–87. PMID 10878362. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.165.2.878.
External links
- Human C1S genome location and C1S gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Luo C, Thielens NM, Gagnon J, Gal P, Sarvari M, Tseng Y, Tosi M, Zavodszky P, Arlaud GJ, Schumaker VN (1992). "Recombinant human complement subcomponent C1s lacking beta-hydroxyasparagine, sialic acid, and one of its two carbohydrate chains still reassembles with C1q and C1r to form a functional C1 complex". Biochemistry. 31 (17): 4254–62. PMID 1533159. doi:10.1021/bi00132a015.
- Illy C, Thielens NM, Gagnon J, Arlaud GJ (1991). "Effect of lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination on the Ca(2+)-dependent interactions of human C1s. Location of the iodination sites". Biochemistry. 30 (29): 7135–41. PMID 1854725. doi:10.1021/bi00243a014.
- Hess D, Schaller J, Rickli EE (1991). "Identification of the disulfide bonds of human complement C1s". Biochemistry. 30 (11): 2827–33. PMID 2007122. doi:10.1021/bi00225a014.
- Thielens NM, Van Dorsselaer A, Gagnon J, Arlaud GJ (1990). "Chemical and functional characterization of a fragment of C1-s containing the epidermal growth factor homology region". Biochemistry. 29 (14): 3570–8. PMID 2141278. doi:10.1021/bi00466a021.
- Busby TF, Ingham KC (1990). "NH2-terminal calcium-binding domain of human complement C1s- mediates the interaction of C1r- with C1q". Biochemistry. 29 (19): 4613–8. PMID 2372546. doi:10.1021/bi00471a016.
- Kusumoto H, Hirosawa S, Salier JP, Hagen FS, Kurachi K (1988). "Human genes for complement components C1r and C1s in a close tail-to-tail arrangement". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (19): 7307–11. PMC 282175
 . PMID 2459702. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.19.7307.
. PMID 2459702. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.19.7307. - Katz Y, Strunk RC (1989). "Synthesis and regulation of C1 inhibitor in human skin fibroblasts". J. Immunol. 142 (6): 2041–5. PMID 2537870.
- Tosi M, Duponchel C, Meo T, Couture-Tosi E (1989). "Complement genes C1r and C1s feature an intronless serine protease domain closely related to haptoglobin". J. Mol. Biol. 208 (4): 709–14. PMID 2553984. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(89)90161-7.
- Tosi M, Duponchel C, Meo T, Julier C (1987). "Complete cDNA sequence of human complement Cls and close physical linkage of the homologous genes Cls and Clr". Biochemistry. 26 (26): 8516–24. PMID 2831944. doi:10.1021/bi00400a004.
- Nguyen VC, Tosi M, Gross MS, Cohen-Haguenauer O, Jegou-Foubert C, de Tand MF, Meo T, Frézal J (1988). "Assignment of the complement serine protease genes C1r and C1s to chromosome 12 region 12p13". Hum. Genet. 78 (4): 363–8. PMID 2834284. doi:10.1007/BF00291737.
- Spycher SE, Nick H, Rickli EE (1986). "Human complement component C1s. Partial sequence determination of the heavy chain and identification of the peptide bond cleaved during activation". Eur. J. Biochem. 156 (1): 49–57. PMID 3007145. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09546.x.
- Mackinnon CM, Carter PE, Smyth SJ, Dunbar B, Fothergill JE (1987). "Molecular cloning of cDNA for human complement component C1s. The complete amino acid sequence". Eur. J. Biochem. 169 (3): 547–53. PMID 3500856. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13644.x.
- Kauffman D, Hofmann T, Bennick A, Keller P (1986). "Basic proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva: complete covalent structures of proteins IB-1 and IB-6". Biochemistry. 25 (9): 2387–92. PMID 3521730. doi:10.1021/bi00357a013.
- Bock SC, Skriver K, Nielsen E, Thøgersen HC, Wiman B, Donaldson VH, Eddy RL, Marrinan J, Radziejewska E, Huber R (1986). "Human C1 inhibitor: primary structure, cDNA cloning, and chromosomal localization". Biochemistry. 25 (15): 4292–301. PMID 3756141. doi:10.1021/bi00363a018.
- Carter PE, Dunbar B, Fothergill JE (1983). "The serine proteinase chain of human complement component C1s. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and N-terminal sequences of the fragments". Biochem. J. 215 (3): 565–71. PMC 1152437
 . PMID 6362661. doi:10.1042/bj2150565.
. PMID 6362661. doi:10.1042/bj2150565. - Nilsson T, Sjöholm I, Wiman B (1983). "Structural and circular-dichroism studies on the interaction between human C1-esterase inhibitor and C1s". Biochem. J. 213 (3): 617–24. PMC 1152176
 . PMID 6604523. doi:10.1042/bj2130617.
. PMID 6604523. doi:10.1042/bj2130617. - Rossi V, Gaboriaud C, Lacroix M, Ulrich J, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Gagnon J, Arlaud GJ (1995). "Structure of the catalytic region of human complement protease C1s: study by chemical cross-linking and three-dimensional homology modeling". Biochemistry. 34 (22): 7311–21. PMID 7779774. doi:10.1021/bi00022a004.
- Bersch B, Hernandez JF, Marion D, Arlaud GJ (1998). "Solution structure of the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like module of human complement protease C1r, an atypical member of the EGF family". Biochemistry. 37 (5): 1204–14. PMID 9477945. doi:10.1021/bi971851v.
- Endo Y, Takahashi M, Nakao M, Saiga H, Sekine H, Matsushita M, Nonaka M, Fujita T (1998). "Two lineages of mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease (MASP) in vertebrates". J. Immunol. 161 (9): 4924–30. PMID 9794427.
- Inoue N, Saito T, Masuda R, Suzuki Y, Ohtomi M, Sakiyama H (1998). "Selective complement C1s deficiency caused by homozygous four-base deletion in the C1s gene". Hum. Genet. 103 (4): 415–8. PMID 9856483. doi:10.1007/s004390050843.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.

