Buys-Ballot (crater)
|
LRO image | |
| Coordinates | 20°48′N 174°30′E / 20.8°N 174.5°ECoordinates: 20°48′N 174°30′E / 20.8°N 174.5°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 55 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 186° at sunrise |
| Eponym | C.H.D. Buys Ballot |

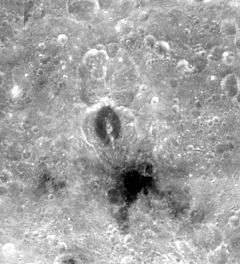
Buys-Ballot is an oddly-shaped lunar crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies just to the northwest of the small lunar mare named Lacus Luxuriae, and southeast of the crater Freundlich. Other nearby craters of note are Anderson to the southwest and Dante to the northeast.
This formation has a distinctive shape for a crater, having a prominent extension to the south that nearly doubles the dimension compared to the width across the maximum west-east cross-section. It vaguely resembles a pear, with the thinner end to the south and the bulge to the north. Despite the odd shape, this crater has not been significantly eroded and only a few tiny craterlets mark the interior or the rim.
Running down the middle of the crater along its longest dimension is a ridge that divides the southern part in half. This ridge extends as far north as the widest part before coming to an end. The floor at this widest part has been partially resurfaced by basaltic lava, leaving an oval area around the northern edge of the central ridge surrounded by a patch of material with a lower albedo than the surroundings. The remainder of the interior floor is somewhat rough and irregular, particularly in the southern half.
Attached to the northern end of the crater is another odd formation consisting of the satellite craters Buys-Ballot Y and Z. These two nearly resemble mirror images of each other, being joined down the center by a narrow ridge line and extending nearly twice as far to the north as their individual widths in the east-west direction. The main difference between the two is that there is a concentric formation at the north end of the crater Y. The interior surfaces of both craters are irregular.
The crater lies within the Freundlich-Sharonov Basin.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Buys-Ballot.
| Buys-Ballot | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 19.4° N | 179.5° E | 22 km |
| Q | 19.5° N | 172.7° E | 58 km |
| Y | 22.9° N | 174.0° E | 31 km |
| Z | 22.5° N | 174.5° E | 58 km |
External links
References
- Wood, Chuck (2006-09-04). "Another Schiller". Lunar Photo of the Day. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2006-09-15.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
