Buffy coat
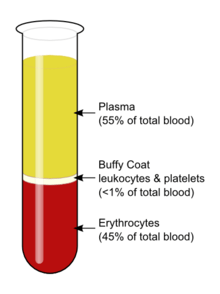

The buffy coat is the fraction of an anticoagulated blood sample that contains most of the white blood cells and platelets following density gradient centrifugation of the blood.
Description
After centrifugation, one can distinguish a layer of clear fluid (the plasma), a layer of red fluid containing most of the red blood cells, and a thin layer in between. Comprising less than 1% of the total volume of the blood sample, the buffy coat (so-called because it is usually buff in hue), contains most of the white blood cells and platelets. The buffy coat is used, for example, to extract DNA from the blood of mammals because mammalian red blood cells are anucleate and do not contain DNA.
The buffy coat is usually whitish in color, but is sometimes green if the blood sample contains large amounts of neutrophils, which are high in green-colored myeloperoxidase. The layer beneath the buffy coat contains granulocytes and red blood cells.
Diagnostic uses of the buffy coat
- Quantitative buffy coat (QBC) is a laboratory test to detect infection with malaria or other blood parasites. The blood is taken in a QBC capillary tube which is coated with acridine orange (a fluorescent dye) and centrifuged; the fluorescing parasites can then be observed under ultraviolet light at the interface between red blood cells and buffy coat. This test is more sensitive than the conventional thick smear and in > 90% of cases the species of parasite can also be identified.
- In cases of extremely low white blood cell count, it may be difficult to perform a manual differential of the various types of white cells, and it may be virtually impossible to obtain an automated differential. In such cases the medical technologist may obtain a buffy coat, from which a blood smear is made. This smear contains a much higher number of white blood cells than whole blood.
References
- Marieb, Elaine N. (2007). Human Anatomy & Physiology (Seventh ed.). San Francisco: Pearson Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 0-8053-5910-9.