Bufagin
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Properties | |
| C24H34O5 | |
| Molar mass | 402.53 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bufagin is a toxic steroid C24H34O5[1] obtained from toad's milk, the poisonous secretion of a skin gland on the back of the neck of a large toad (Rhinella marina, synonym Bufo marinus, the Cane Toad). The toad produces this secretion when it is injured, scared or provoked. Bufagin resembles chemical substances from digitalis in physiological activity and chemical structure.
Bufagin also refers to any of several similar substances found as components of the mixture bufotoxin in secretions of other toads, as well as plants and mushrooms.
Chemistry
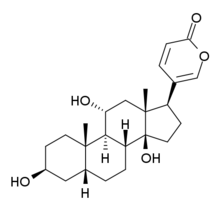
Bufagin and bufagins are bufadienolide derivatives. This means they are steroids with a pyran- (delta-)lactone ring attached to ring D (the five-membered one). The difference to digitalis compounds is that the latter have a furan- (gamma-)lactone ring that has one carbon atom and one double bond less.
Effects of bufagins
Some bufagins have effects similar to poisoning by digitalis, having effects on the cardiac muscle, causing ventricular fibrillation. Some also have local anesthetic action. The analgesic effects have also been proven,[2] by acting as Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitors on the binding sites of the cell membrane. The anti-cancer properties in leukemia and melanoma cells, and the inhibition of the proliferation of prostate cancer cells, have also been investigated in cellular models.[3][4][5] Some of the bufagin toxins are used in low doses in traditional Chinese medicine for similar applications as digoxin is used for in Western medicine (i.e. treatment of heart conditions such as atrial fibrillation).[6]
There are at least 86 identified bufadienolides. Examples of bufagins are:
- Arenobufagin, from the Argentine Toad (Chaunus arenarum, synonym Bufo arenarum);
- Cinobufagin, from the Chusan Island Toad (Bufo gargarizans);
- Gamabufagin, from the Japanese Toad (Bufo japonicus);
- Marinobufagin, from Bufo rubescens and the Cane Toad (Bufo marinus);
- Quercicobufagin, from the Oak Toad (Anaxyrus quercicus, synonym Bufo quercicus);
- Regularobufagin, from the Square-marked Toad (Amietophrynus regularis, synonym Bufo regularis);
- Vallicepobufagin, from the Gulf Coast Toad (Incilius valliceps, synonym Bufo valliceps);
- Viridibufagin, from the European Green Toad (Bufo viridis)
These bufagins, and especially cinobufagin, have given rise to a large number of derivatives evaluated as potential anti-tumor drugs.
References
- ↑ ChemicalBook: bufagin
- ↑ Wang, G.; G. Sun; et al. (1994). "The application of traditional Chinese medicine to the management of hepatic cancerous pain". J Tradit Chin Med. 14 (2): 132–138. PMID 7967697.
- ↑ Jiun-Yih Yeh; William J. Huang; Shu-Fen Kan; Paulus S. Wang (2002). "Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cells". The Prostate. 54 (2): 112–124. PMID 12497584. doi:10.1002/pros.10172.
- ↑ Jing, Y.; H. Ohizumi; et al. (1994). "Selective inhibitory effect of bufalin on growth of human tumor cells in vitro: association with the induction of apoptosis in leukemia HL-60 cells". Jpn J Cancer Res. 85 (6): 645–651. PMID 8063619. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.1994.tb02408.x.
- ↑ Yin, P. H.; Liu, X; Qiu, Y. Y.; Cai, J. F.; Qin, J. M.; Zhu, H. R.; Li, Q (2012). "Anti-tumor activity and apoptosis-regulation mechanisms of bufalin in various cancers: New hope for cancer patients". Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 13 (11): 5339–43. PMID 23317181. doi:10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.11.5339.
- ↑ Bick, RJ; Poindexter, BJ; Sweney, RR; Dasgupta, A (2002). "Effects of Chan Su, a traditional Chinese medicine, on the calcium transients of isolated cardiomyocytes: Cardiotoxicity due to more than Na, K-ATPase blocking". Life Sciences. 72 (6): 699–709. PMID 12467910. doi:10.1016/s0024-3205(02)02302-0.