Bubalus
| Bubalus | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Bovinae |
| Tribe: | Bovini |
| Genus: | Bubalus C. H. Smith, 1827 |
| Species | |
|
Bubalus arnee | |
Bubalus is a genus of bovines that was first described by Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. This genus comprises the following living species:[1]
- Wild Asian water buffalo Bubalus arnee (Kerr, 1792)
- Lowland anoa Bubalus depressicornis (Smith, 1827)
- Tamaraw Bubalus mindorensis (Heude, 1888)
- Mountain anoa Bubalus quarlesi (Ouwens, 1910)
- and the domestic water buffalo Bubalus bubalis (Linnaeus, 1758)
The nomenclature and classification of domestic animals as species, subspecies, races or breeds has been discussed controversially for many years and was inconsistent between authors.[2] Assessors of the Food and Agriculture Organisation consider domestic water buffalo populations as breeds.[3]
Characteristics
Smith described Bubalus (from Greek βούβαλος, boúbalos) as low in proportion to the bulk with very solid limbs, a small dewlap and a long, slender tail; the head is large and the forehead narrow, very strong and convex; the eyes are large, and the ears mostly funnel-shaped; horns are lying flat or bending laterally with a certain direction to the rear; the female udder has four mammae.[4] Lydekker added that the line of back is nearly straight with 13 pairs of ribs; the tail is tufted and reaching about to the hocks; the horns are more or less markedly triangular for the greater part of their length and situated low down on the skull; the muzzle is broad, and the hair sparse in adults.[5]
Fossil species
The following extinct fossil species were described:
- Cebu dwarf buffalo Bubalus cebuensis (Croft, Heaney, Flynn and Bautista, 2006)[6]
- Short-horned water buffalo Bubalus mephistopheles (Hopwood, 1925)[7]
- European water buffalo Bubalus murrensis (Berckhemer, 1927)[8]
- Long-horned Javan water buffalo Bubalus palaeokerabau (E. Dubois 1908)[9]
- Bubalus grovesi (Rozzi, 2017)[10]
Valid names
The 2013 checklist of the Catalogue of Life lists as "accepted" five species binomina in the genus Bubalus:
- Bubalus bubalis (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Bubalus depressicornis (Smith, 1827)
- Bubalus mephistopheles Hopwood, 1925
- Bubalus mindorensis (Heude, 1888)
- Bubalus quarlesi (Ouwens, 1910)
Bubalus arnee is not listed.[11]
The Integrated Taxonomic Information System lists the same five species binomina as valid; it also lists six sub-species of Bubalus bubalis:[12]
- Bubalus bubalis arnee (Kerr, 1792)
- Bubalus bubalis bubalis (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Bubalus bubalis fulvus (Blanford, 1891)
- Bubalus bubalis kerabau (Fitzinger, 1860)
- Bubalus bubalis migona (Deraniyagala, 1952)
- Bubalus bubalis theerapati (Groves, 1996)
The specific epithet bubalus
Species in a number of genera have bubalus as specific epithet. They include:[11]
- Bubas bubalus (Olivier, 1811), a scarab
- Ceresa bubalus Fabricius, a buffalo treehopper
- Culicoides bubalus Delfinado, 1961, a biting midge
- Edwardsina bubalus Zwick, 1977, a fly
- Hemiphractus bubalus (Jiménez de la Espada, 1870), a frog
- Ictiobus bubalus (Rafinesque, 1818), the Smallmouth Buffalo fish
- Leptoperla bubalus Theischinger, 1980, an insect in the family Gripopterygidae
- Maarbarus bubalus Kirby, a treehopper
- Onthophagus bubalus Harold, 1867, a scarab
- Velarifictorus bubalus Gorochov, 1992, a field cricket
Gallery (anatomy)
.jpg) Buffalo skull.
Buffalo skull.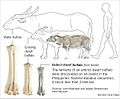 Comparative bone of different breeds of buffalo.
Comparative bone of different breeds of buffalo. Buffalo's kidney.
Buffalo's kidney.
References
- ↑ Groves, C.; Grubb, P. (2011). Ungulate Taxonomy. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 1421400936.
- ↑ Gentry, A. Clutton-Brock, J., Groves, C. P. (2004). The naming of wild animal species and their domestic derivatives. Journal of Archaeological Science 31: 645–651.
- ↑ FAO (2013). Breeds from species: Buffalo. Domestic Animal Diversity Information System, Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, Rome.
- ↑ Hamilton Smith, C. (1827). Bubalus. In: Griffith, E. (ed.) The animal kingdom arranged in conformity with its organization. Class Mammalia, Volume 5. London: Geo. B. Whittaker.
- ↑ Lydekker, R. 1913. Catalogue of the ungulate mammals in the British Museum (Natural History). London: British Museum (Natural History).
- ↑ Croft, D. A., Heaney, L. R., Flynn, J. J., Bautista, A. P. (2006). Fossil remains of a new, diminutive Bubalus (Artiodactyla: Bovidae: Bovini) from Cebu island, Philippines. Journal of Mammalogy 87(5): 1037–1051.
- ↑ Hopwood, A. T. (1925). A new species of buffalo from the Pleistocene of China. Annals and Magazine of Natural History. Series 9, Vol. XVI: 238–239.
- ↑ Schreiber, H. D., Munk, W. (2002). A skull fragment of Bubalus murrensis (Berckhemer, 1927) (Mammalia, Bovinae) from the Pleistocene of Bruchsal-Buchenau (NE-Karlsruhe, SW-Germany). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie (12): 737–748.
- ↑ http://fossilworks.org/bridge.pl?a=taxonInfo&taxon_no=162371.
- ↑ Rozzi, Roberto. (2017). A new extinct dwarfed buffalo from Sulawesi and the evolution of the subgenus Anoa: An interdisciplinary perspective. Quaternary Science Reviews 157: 188-205.
- 1 2 Roskov Y., Kunze T., Paglinawan L., Orrell T., Nicolson D., Culham A., Bailly N., Kirk P., Bourgoin T., Baillargeon G., Hernandez F., De Wever A., eds (2013). Bubalus. Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life, 2013 Annual Checklist. Reading, UK.
- ↑ ITIS Results of: Search in every Kingdom for Scientific Name containing 'Bubalus' Archived March 12, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.. Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Accessed january 2014.
See also
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Buffalo (animal). |