Bromocresol green
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,6-Dibromo-4-[7-(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-9,9-dioxo-8-oxa-9λ6-thiabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,5-trien-7-yl]-3-methyl-phenol | |
| Other names
3,3′,5,5′-Tetrabromo-m-cresolsulfonphthalein Bromcresol green | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | BCG |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.885 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H14Br4O5S | |
| Molar mass | 698.01 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Beige to brown powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) decomposes[1] |
| Sparingly soluble | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in benzene; very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether[2] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.90[3] |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 423 nm[1] |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36/38 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S24/25-S28-S37-S45 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
| Bromocresol green (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 3.8 | above pH 5.4 | |
| 3.8 | ⇌ | 5.4 |
Bromocresol green (BCG) is a dye of the triphenylmethane family (triarylmethane dyes). It is used as a pH indicator in applications such as growth mediums for microorganisms and titrations.
Properties

In aqueous solution, bromocresol green will ionize to give the monoanionic form (yellow), that further deprotonates at higher pH to give the dianionic form (blue),[4] which is stabilized by resonance:
The acid dissociation constant (pKa) of this reaction is 4.8.[5]
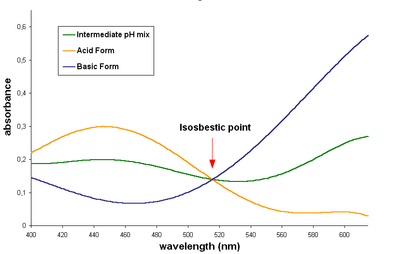
The acid and basic forms of this dye have an isosbestic point in their UV-Visible spectrum, around 515 nm, indicate that the two forms interconvert directly without forming any other substance.
An ethanol solution (0.04 wt%) of bromocresol green has been proposed for TLC staining and is suitable for visualisation of the compounds with functional groups whose pKa is below 5.0 (carboxylic acids, sulfonic acids, etc.). These appear as yellow spots on a light or dark blue background; no heating is necessary. Bromophenol blue solution can be used for the same purpose.
The compound is synthesized by bromination of cresol purple (m-cresolsulfonphthalein).
Uses
It is used as a pH indicator and as a tracking dye for DNA agarose gel electrophoresis. It can be used in its free acid form (light brown solid), or as a sodium salt (dark green solid). It is also an inhibitor of the prostaglandin E2 transport protein.
Safety
Bromocresol green may cause irritation. Skin and eye contact should be avoided.
References
- 1 2 "Bromocresol Green". Sigma Aldrich.
- ↑ http://chemicalland21.com/specialtychem/finechem/BROMOCRESOL%20GREEN.htm
- ↑ Kolthoff, I.M. Treatise on Analytical Chemistry, New York, Interscience Encyclopedia, Inc., 1959.
- ↑ Fred Senese. "Acid-Base Indicators". Frostburg State University Dept. of Chemistry.
- ↑ Diamond, D.; Lau, K. T.; Brady, S.; Cleary, J. (2008). "Integration of analytical measurements and wireless communications—Current issues and future strategies". Talanta. 75 (3): 606. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2007.11.022.

