Brixton
| Brixton | |
|---|---|
 Lambeth Town Hall | |
 Brixton | |
| Brixton shown within Greater London | |
| Population | 78,536 (2011 census)[1][2] |
| OS grid reference | TQ315755 |
| • Charing Cross | 3.8 mi (6.1 km) NNW |
| London borough | |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | LONDON |
| Postcode district | SE5 |
| Postcode district | SW2 |
| Postcode district | SW9 |
| Dialling code | 020 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| UK Parliament | |
| London Assembly | |
Brixton is a district of south London, England, within the London Borough of Lambeth. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.[3]
Brixton is mainly residential with a prominent street market and substantial retail sector.[4] It is a multiethnic community, with a large percentage of its population being of Caribbean descent.[5] It lies within Inner south London and is bordered by Stockwell, Clapham, Streatham, Camberwell, Tulse Hill and Herne Hill.[6] The district houses the main offices of the London Borough of Lambeth.[7]
Brixton is 2.7 miles (4.3 km) south-southwest of the geographical centre of London near Lambeth North tube station.[8][9]
History


Until the mid-20th century
The name Brixton is thought to originate from Brixistane, meaning the stone of Brixi, a Saxon lord. Brixi is thought to have erected a boundary stone to mark the meeting place of the ancient hundred court of Surrey. The location is unknown but is thought to be at the top of Brixton Hill, at a road known at the time as Bristow or Brixton Causeway, long before any settlement in the area. Brixton marks the rise from the marshes of North Lambeth up to the hills of Upper Norwood and Streatham. At the time the River Effra flowed from its source in Upper Norwood through Herne Hill to Brixton. At Brixton the river was crossed by low bridges for Roman roads to the south coast of Britain, now Brixton Road and Clapham Road. The main roads were connected through a network of medieval country lanes, such as Acre Lane, Coldharbour Lane, Brixton Water Lane and Lyham Road, formerly Black Lane. It was only at the end of the 18th century that villages and settlements formed around Brixton, as the original woodland was gradually reduced until the area was covered in farmland and market gardens known for game and strawberries.
The area remained undeveloped until the beginning of the 19th century, the main settlements being near Stockwell, Brixton Hill and Coldharbour Lane. With the opening of Vauxhall Bridge in 1816, improved access to Central London led to a process of suburban development. The largest single development, and one of the last in suburban character, was Angell Town, laid out in the 1850s on the east side of Brixton Road, and so named after a family that owned land in Lambeth from the late 17th century until well into the 20th.[10]
One of a few surviving windmills in London, built in 1816, is just off Brixton Hill and surrounded by houses built during Brixton's Victorian expansion. When the London sewerage system was constructed during the mid-19th century, its designer Sir Joseph Bazalgette incorporated flows from the River Effra, which used to flow through Brixton, into his 'high-level interceptor sewer', also known as the Effra sewer.
Brixton was transformed into a middle class suburb between the 1860s and 1890s. Railways linked Brixton with the centre of London when the Chatham Main Line was built through the area by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway in the 1860s. In 1880, Electric Avenue was so named after it became the first street in London to be lit by electricity. In this time, large expensive houses were constructed along the main roads in Brixton, which were converted into flats and boarding houses at the start of the 20th century as the middle classes were replaced by an influx of the working classes.
By 1925, Brixton attracted thousands of new people. It housed the largest shopping centre in South London at the time, as well as a thriving market, cinemas, pubs and a theatre. In the 1920s, Brixton was the shopping capital of South London with three large department stores and some of the earliest branches of what are now Britain's major national retailers. Today, Brixton Road is the main shopping area, fusing into Brixton Market. A prominent building on Brixton High Street (at 472–488 Brixton Road) is Morleys, an independent department store established in the 1920s.[11]
On the western boundary of Brixton with Clapham stands the Sunlight Laundry, an Art Deco factory building. Designed by architect F.E. Simpkins and erected in 1937, this is one of the few art deco buildings that is still owned by the firm that commissioned it and is still used for its original purpose.
The Brixton area was bombed during World War II, contributing to a severe housing crisis, which in turn led to urban decay. This was followed by slum clearances and the building of council housing. In the 1940s and 1950s, many immigrants, particularly from the West Indies, settled in Brixton.[10] More recent immigrants include a large Portuguese community (see Little Portugal) and other European citizens. Brixton also has an increasingly ageing population, which affects housing strategies in the area.[12]
1948: The Windrush generation


The first wave of immigrants (492 individuals) that formed the British African-Caribbean community arrived in 1948 at Tilbury Docks on the MV Empire Windrush from Jamaica and were temporarily housed in the Clapham South deep shelter. The nearest Labour Exchange (Jobcentre) was on Coldharbour Lane, Brixton, and the new arrivals spread out into local accommodation.[14][15][16]
Many immigrants only intended to stay in Britain for a few years, but although a number returned to the Caribbean, the majority remained to settle permanently.[14] The arrival of the passengers has become an important landmark in the history of modern Britain, and the image of West Indians filing off its gangplank has come to symbolise the beginning of modern British multicultural society.[14] In 1998 the area in front of the Tate Library in Brixton was renamed "Windrush Square" to mark the 50th anniversary of the arrival of the Windrush.[10]
1980s: Riots after police actions and Scarman Report

Brixton was the scene of riots in April 1981 at a time when Brixton underwent deep social and economic problems—high unemployment, high crime, poor housing, no amenities—in a predominantly African-Caribbean community.[17] The Metropolitan Police began Operation Swamp 81 at the beginning of April, aimed at reducing street crime, largely through the repeated use of the so-called sus law, which allowed police officers to stop and search any individual on the grounds of mere "suspicion" of possible wrongdoing. Plain clothes police officers were dispatched into Brixton, and within five days almost 1,000 people were stopped and searched under this law.[18] There was intense local indignation at this, since the vast majority of those stopped by the police were young black men. The riot resulted in almost 279 injuries to police and 45 injuries to members of the public,[19] more than a hundred vehicles were burned (including 56 police vehicles), and almost 150 buildings were damaged, with 30 burned. There were 82 arrests. Reports suggested that up to 5,000 people were involved in the riot.[20]
Following the 1981 Brixton riot the Government commissioned a public inquiry into the riot headed by Lord Scarman. The subsequent Scarman report was published in November 1981 and found unquestionable evidence of the disproportionate and indiscriminate use of 'stop and search' powers by the police against black people. The report made a number of recommendations and led to a new code for police behaviour in the Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984 and the creation of an independent Police Complaints Authority in 1985.[21] The 1999 Macpherson Report, an investigation into the murder of Stephen Lawrence, found that recommendations of the 1981 Scarman report had been ignored and concluded that the police force was "institutionally racist".[22]
The 1985 Brixton riot followed the police shooting of a local black woman, Dorothy 'Cherry' Groce, after the police had entered her house looking for her son Michael Groce. Although the Brixton area subsequently saw pioneering community policing initiatives, the continued death of young black men in police custody (and in one case the death of a man pointing a fake gun at people) coupled with general distrust of the police led to smaller scale protests through the 1990s.
1990s
The 1995 riots were initially sparked by the death of a black man (Wayne Douglas) in police custody and occurred in an atmosphere of discontent about the gentrification of Brixton.
Former Prime Minister John Major's own childhood roots in Brixton were used in a campaign poster during the Conservative Party's 1992 election campaign: "What does the Conservative Party offer a working class kid from Brixton? They made him Prime Minister."[23]
On 17 April 1999 neo-nazi bomber David Copeland planted a nail bomb in Electric Avenue, which exploded on a market day by the Iceland supermarket at the junction with Brixton Road (Brixton High Street). Copeland was sentenced to six concurrent life sentences in June 2000. The Brixton bombing is reported to have targeted the black community in Brixton. Copeland also bombed Brick Lane, the heart of East London's Bangladeshi and Asian community, and the Admiral Duncan pub in Soho, London, frequented predominantly by the gay community. The BBC reports that Copeland intended to ignite a race war across Britain with his bombing campaign.[24] A 2009 play about the events, The First Domino, was written by one victim in the Soho attack.[25]
JayDay Cannabis Festival
From 2001 to 2004, Brockwell Park hosted the annual Cannabis Festival, or JayDay, organised by the Cannabis Coalition. The police reportedly maintained a low profile, tolerating the smoking of cannabis.[26][27] In 2005 the London Borough of Lambeth rejected the application for a further Cannabis Festival on the following grounds:
"While Lambeth Council supports freedom of speech and the right to take part in a legitimate campaign, the council cannot condone illegal activities such as cannabis use and drug pushing – both of which have taken place at a previous festival held by the Cannabis Coalition. Indeed council officers monitoring the event in the past were approached by drug dealers who offered them drugs."[28]
Gentrification
There is debate regarding whether Brixton's recent renaissance is regeneration or gentrification.[29] Some believe the area has slowly undergone a process of gentrification since the 1990s and has resulted in many wealthy middle-class individuals taking advantage of the area's location and the thriving Bohemian art scene. However, others argue that the area is undergoing exciting regeneration.[30][31][32] In recent years Brixton has hosted a regular farmers' market on Station Road, as well as Pop-up restaurants and pop-up shops. New art galleries, delicatessens, bars, cafes and vintage clothing stores, particularly in and around Brixton Village Market have also opened, which some believe is gentrifying the area in a similar way to that in nearby Clapham.[33]
Brixton was awarded The Great Neighbourhood Award 2013 (covering the UK and Ireland) by The Academy of Urbanism.[34]
In April 2015, a Reclaim Brixton protest was held by local residents and activists.
Transition Town
Brixton was one of the first inner-city based 'Transition Town' projects in the UK.[35] Brockwell Park hosts the now annual Urban Green Fair, first held in summer 2007.[36]
Brixton Pound
| Brixton pound | |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| User(s) | Brixton |
The Brixton Pound was first trialled at Transition Town Brixton's 'Local Economy Day' 19 June 2008. It was then launched on 17 September 2009 by Transition Town Brixton.[37] The Brixton Pound is a local currency that is available as an alternative to the pound sterling.[38] The first trading day of the Brixton Pound was on 18 September 2009 with 80 local businesses accepting the currency.[39] Other towns in the UK that use their own currency include Bristol, Totnes in Devon, Stroud in Gloucestershire and Lewes in Sussex.
The Brixton Pound aims to boost the local economy and build a mutual support system amongst independent businesses by tying local shoppers to local shops and by encouraging local shops to source goods and services locally.[39] The notes are available in B£1, B£5, B£10 and B£20 denominations and depict local celebrities such as the community activist Olive Morris and the environmentalist James Lovelock. Lambeth council has endorsed the project[39] which the New Economics Foundation helped to develop.[40]
On 29 September 2011, the Brixton Pound launched an electronic version of the currency where users can pay by text message.
A second issue of the paper currency was launched, featuring a new set of well-known people with Brixton connections: On the B£1, the Black Cultural Archives founder Len Garrison, on the B£5, Los Angeles Lakers' Luol Deng, David Bowie on the B£10 and on the B£20, World War II secret agent Violette Szabo.
The reverse of the notes, designed by Brixton agency This Ain't Rock'n'Roll, feature notable local landmarks such as the Stockwell Skatepark, public art on Electric Avenue, Nuclear Dawn – one of the Brixton murals – and the Stirling Prize-winning Evelyn Grace Academy. All four notes feature a design motif inspired by Coldharbour Lane's Southwyck House (or "Barrier Block").
Housing
Housing estates

Brixton is home to six large housing estates: Stockwell Park Estate off Stockwell and Brixton Roads respectively; Myatt's Fields South and North off Vassall Road; Angell Town off Brixton Road on the boundary with Camberwell; Loughborough in the centre of Brixton; Moorlands Estate, situated off Coldharbour Lane; St Matthew's, located in the fork between Brixton Hill and Effra Road; Tulse Hill Estate a little further south of St. Matthews.[5] The six estates account for a large part of the Brixton residence.[4]
Estates like the Stockwell Park Estate and the Angell Town Estate were originally designed to accommodate high-level walkways which were envisaged to link the whole of Brixton. The ground-floor garages of these estates have proved to be a major security problem.[12] The Somerleyton Estate is dominated by Southwyck House (known locally as "Barrier Block"), a large horseshoe-shaped brick and concrete 1970s structure that backs onto Coldharbour Lane. The 176-apartment block was originally constructed in this shape to provide a noise barrier against Ringway 1, a proposed inner-London motorway that was planned to pass through Brixton and Camberwell, later abandoned.[41]

Some housing estates have been linked with urban decay and crime. New gates and iron bars have been constructed for the Loughborough Estate around Loughborough Road and Minet Road in response to a number of murders around the estate. The Loughborough Estate is home to more than 3,000 families and a mix of 1940s low-rise buildings and 1960s/1970s tower blocks and houses.[5] Problems of urban decay have been reported around Loughborough Junction, the catchment area for Loughborough Estate, the Angell Town Estate and the Moorlands Estate.[42]
Victorian buildings
Brixton still features some grand Victorian housing.[5] As bridges were built across the Thames in the early 19th century those working in the City of London and the London West End moved to south London. The earliest built development was in Washway, now Brixton Road. With the enclosing of the Manor of Lambeth, owned by the Archbishop of Canterbury, in 1806 and the opening of Vauxhall Bridge in 1816 development of terraced houses and detached villas started to line the main roads. St Matthew's Church in the centre of Brixton was consecrated in 1824, indicating a sizeable population by this time. The Rush Common enclosure stipulations dictated that the large terraced and detached houses that were built along the main roads were set back from the road, allowing for generous gardens. The windmill was erected in 1816 by John Ashby on Brixton Hill and the Surrey House of Correction, later Brixton prison, was established in 1819.[43]
Brixton Market

With the arrival of the railway in Brixton in the 1870s a building boom set in and Brixton developed into a major shopping centre. The first purpose-built department store, Bon Marché, was opened on Brixton Road in 1877 and Electric Avenue was one of the first shopping arcades to have electric lighting. The now famous Brixton Market began in Atlantic Road and was moved to Station Road in the 1920s to ease traffic congestion.[43] Brixton Market is open every day, selling a range of Afro-Caribbean products and reflects other communities in the local area with Indian and Vietnamese supermarkets and South American butchers amongst the shops and stalls.. London Farmers' Markets opened a farmers market on Brixton Station Road in September 2009. It is open every Sunday from 10am-2pm.
Culture
Brixton murals

After the riots in 1981 a series of murals were funded by the council. The murals portray nature, politics, community and ideas. The surviving murals include the Brixton Academy Mural (Stockwell Park Walk) by Stephen Pusey (1982) showing a mixed group of young people, intended to portray the natural harmony that could be found between children of mixed backgrounds in the local schools.
Entertainment

The Ritzy Cinema, Coldharbour Lane, is a formerly independent cinema now owned by Picturehouse Cinemas. The building was designed as the Electric Pavilion in 1910 by E. C. Homer and Lucas, one of England's first purpose-built cinemas.[44]
Brixton has a significant clubbing and live music scene. Large venues include Brixton Academy, Electric Brixton and Mass at St Matthew's Church. A range of smaller venues such as The Prince Albert, The Prince / DexClub, The Windmill, The Dogstar, Jamm, The Telegraph, Plan B, Hootananny, The 414, The Effra Tavern, Upstairs at the Ritzy, and The Grosvenor are a major part of London's live music scene.[45] The Brixton Splash is an annual one-day street party held since 2006. The event is community run, showcasing local talent and celebrating the cultural diversity and history of Brixton.[46]
Brixton is also home to a 1970s purpose-built skatepark, named Stockwell Skatepark, but known locally as Brixton Beach after graffiti on the north wall of the park.
Music scene
In recent years Brixton has been at the forefront of UK Grime/Hip hop and Road Rap.
Religious sites
Brixton Synagogue
Brixton Synagogue at 49 Effra Road opened in 1913 and closed in 1986, with the congregation then amalgamating with the nearby Streatham Synagogue. The front of the building still exists.[47]
Christian churches

Brixton lies within the Anglican Diocese of Southwark.[48] The grade II* listed St Matthew's Church, located on Brixton Green, was built in 1822 by the architect C. F. Porden in the Greek Revival style.[49] It is one of the "Waterloo churches" built to celebrate Britain's victory at the Battle of Waterloo. St. Saviour's Church was a location filming site of Alfred Hitchcock's The Man Who Knew Too Much in 1955, identified in the film as Ambrose Chapel.
The 1868 parish church of St Jude, located on Dulwich Road, was designed by the architect John Kirk of Woolwich. It closed in 1975, and the parish merged with St Matthew's. The church building is today used as business premises by a publishing company.[50]
Christ Church on Brixton Road is an Art Nouveau and Byzantine-style Grade II* listed building built in 1902 by Beresford Pite,[51] and St Paul's church on Ferndale Road was originally built in 1958 as a Seventh-day Adventist church by John Soper.
Corpus Christi Church in Brixton comes under the remit of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Southwark.[52]
Brixton Mosque
The Masjid ibn Taymeeyah, or Brixton Mosque and Islamic Cultural Centre, is located in Gresham Road, close to Brixton Police Station. The mosque has facilities for both men and women and space for 400 worshippers during prayer.[53] Opened in 1990 it is one of the oldest mosques in South London. The mosque provides religious, social and financial support to its members.[54]
The mosque made international headlines when it was reported that Richard Reid, the so-called "shoe bomber", had attended the mosque. Abdul Haqq Baker, chairman of Brixton Mosque, told the BBC that Reid came to the mosque to learn about Islam but soon fell in with what he called "more extreme elements".[55] Zacarias Moussaoui, who was convicted of conspiring to kill citizens of the USA as part of 11 September 2001, terrorist attacks, made his initial steps into radical indoctrination in Brixton Mosque, where he met Reid, though he was expelled from the mosque after he turned up wearing combat fatigues and a backpack, and pressured the cleric to give him information on joining the jihad. Abdullah el-Faisal, a radical Muslim cleric who preached in the UK until imprisoned for stirring up hatred and later deported to Jamaica in 2007, was associated with the Brixton Mosque and began preaching to crowds of up to 500 people, but was ousted by its Salafi administration in 1993.[56][56] Afterward, he gave a lecture he called The Devil's Deception of the Saudi Salafis, scorning the Salafi Muslims (especially the members of the Brixton Mosque), calling them hypocrites and apostates (takfir).[57]
Brixton was a site of a conference after the London bombings, at which local Muslims condemned all use of terror and indiscriminate killing. Footage of the conference was included in a six-part ITV series called Mosque. It included local Muslims talking about the discrimination they face from people not able to differentiate between Muslims and terrorists, and the local Brixton community, on the whole, is described as welcoming towards Muslims.[58]
Policing, drugs and crime
Operation Swamp
Before the 1981 riot was the centre of "Operation Swamp 81" aimed at reducing street crime mainly through the heavy use of the so-called sus law, which allowed police to stop and search individuals on the basis of a mere "suspicion" of wrongdoing. Plainclothes police officers were dispatched into Brixton, and in five days almost 1,000 people were stopped and searched. The local community was not consulted about the operation and tensions between the black community and the police on the streets of Brixton reached breaking point. Local residents complained about young, inexperienced police officers being sent on the streets, provoking confrontation.[59]
Gang culture
In 2003 The Independent reported that around 200 "hardcore Yardies" are based in Lambeth, some operating as members of "Firehouse Posse" or Brixton's "Kartel Crew".[60] Yardies were historically associated with Jamaican immigrants and had a recognised stronghold in Brixton. Parts of Brixton were referred to as "Little Tivoli" after "Tivoli Gardens", a notorious "garrison community" in Jamaica ruled by gunmen.[61][62] In 1999 a scandal broke over Metropolitan Police detectives allowing two known Jamaican Yardies to stay in Britain as an intelligence tool. Eaton Green, one of the Yardies, escaped bail in Jamaica in 1991 and settled in Brixton, dealing in crack cocaine. Three months later Green was arrested by a Brixton constable, Steve Barker, and became a paid informer. Green provided intelligence about Yardie activity for two years, continuing the use of firearms and the dealing of crack throughout this time.[63]
Several gangs are headquartered in the Brixton area. The "Murderzone" (MZ) gang, which is involved in illegal drug dealing, hail from the Somerleyton Estate.[64] The "Poverty Driven Children"/"Pil dem crew" (PDC) are located in the Angell Town and Loughborough Junction area.[65][66] "Organised Crime" (OC), a gang linked with various shootings and an ongoing rivalry with the Peckham Boys, are based in the Myatts Field Estate.[67][68] "Guns and Shanks"/"Grind and Stack"/"Grip and Shoot" (GAS) is located mainly in Angell Town.[69]
In 2011, five of the most prominent members of the GAS Gang — Ricardo Giddings, Helder Demorais, Jamal Moore, Shaquille Haughton and Kyle Kinghorn — were sentenced to a total of 76 years in prison for the murder of rival gang member, fifteen-year-old Zac Olumegbon.[70]
Members of local gangs are mostly in their late teens or early 20s, with gang leaders usually being childhood friends. Brought up in some of London's poorest areas some gang members reportedly move from house to house on an almost nightly basis, making it hard to track them. According to the Metropolitan Police, these youth gangs are far from organised criminal masterminds; however, they continue to evade the police and have been responsible for numerous offences of homicide. Operation Trident officers stated that it is a "struggle" to persuade local people to testify, because of fear of reprisals. Trident officers stated that some gang members were "inept at handling powerful guns", and that gangs have machine guns, 9 mm. According to the detective many of the deactivated guns are shipped in from the Balkans and then reactivated.[71]
Drugs
Some media commentators persistently call Brixton "the drugs capital of London".[72] Val Shawcross, Labour representative on the London Assembly for Lambeth and Southwark, runs a "Brixton Drug Crime" campaign and she states on her website:
I have been raising the disgraceful state of Brixton and the existence of an open drugs market in the centre – with the Council, Mayor and the Metropolitan police... The police, the Drugs and Firearms Unit and Transport Operational Unit officers have been undertaking long-term surveillance of the area (Brixton Town Centre) culminating in a three-day operation at the end of June to arrest those dealing Class A drugs... The police will be carrying out continuing covert operations in Brixton and patrolling with drug detection dogs. This is a long-term crackdown with the aim on cleaning the dealers out of Brixton.(retrieved July 2008)[73]
For many decades, Brixton has had a reputation for cannabis use and the BBC has quoted a local resident as saying "People have always smoked cannabis in Brixton – everyone knows that, people have walked down the street smoking spliffs for years." This reputation was amplified by the "softly softly" police approach to cannabis that was piloted in Brixton in 2001 to 2005. Concerns were raised about "drug tourism" to the area.[42] The "softly-softly" pilot occurred in the context of a wider debate in Britain about the classification of cannabis. Despite the pilot being stopped and replaced by a "no deal" policy, the Metropolitan Police was in favour of a reclassification of cannabis from class B to class C. Cannabis was officially reclassified in Britain from a class B down to a class C drug in early 2004. In January 2009 the UK government reclassified cannabis back to a class B drug.[74][75][76]
Brian Paddick
In 2001 Brixton became subject of newspaper headlines due to the implementation of a pilot cannabis programme, also known as the "softly softly" approach, initiated by Brian Paddick, then Police Commander for the London Borough of Lambeth. Police officers were instructed not to arrest or charge people who were found to be in possession of cannabis. They were instead to issue on-the-spot warnings and confiscate the drugs. Although Paddick is credited with the idea, the pilot programme was sanctioned by the Commissioner of Police of the Metropolis, Sir John Stevens. Paddick asserts that he implemented the policy because he wanted his officers to deal with cannabis quickly and informally so that they could concentrate on heroin and crack cocaine offences, and street robbery and burglary, which were affecting the quality of life in Lambeth to a greater extent.[77] The pilot was ended December 2005 and was replaced by a so-called "no deal" policy on cannabis in Brixton following complaints about increasing numbers of dealers openly selling the drug.[78]
Paddick was a sergeant on the front line during the 1981 Brixton riot,[79] an experience which shaped his attitudes about confrontational police action and strengthened his belief in community policing.[80] In December 2000 he was appointed Police Commander for the London Borough of Lambeth where he worked until December 2002,[81] fulfilling his ambition of becoming head of policing in Brixton.[82] Paddick gained much support from the local community for his approach to policing and addressed a rally in his support in March 2002, leading Dominic Casciani from the BBC to comment:
If someone had said just five years ago that black, white, young and old, straight and gay, liberal and anarchist would all be standing together giving a standing ovation to a police commander in Brixton, people might have said they had smoked one spliff too many.[83]
Gun crime
In June 1998 gun crime in Brixton was reported on widely in connection with the linked murders of Avril Johnson and Michelle Carby, in Brixton and Stratford respectively. Both women were shot in their respective homes in separate, but connected, attacks; in addition, both victims were shot in the head.[84] In 2008 Tony Thompson, a former Time Out news editor, reported that "Gun crime began to escalate following a series of South London gang executions in the late 1990s." Thompson states that "Previous Met operations were seen as putting down the black community. Trident, from the start, was intelligence-led and had strong links with the black community."[85]
In 2001 the Metropolitan Police raised concerns over rapidly increasing gun crime in London. At the time Lambeth had the highest rate of robberies in London. In July 2001 two armed police officers shot dead black 29-year-old Derek Bennett in Brixton, Angell Town Estate, after Bennett brandished a gun-shaped cigarette lighter. The verdict of the subsequent inquest ruled that Bennett had been "lawfully killed", the verdict was upheld in a subsequent appeal.[86][87][88]
In December 2004 Operation Trident officers and armed officers were assisting Lambeth police in a number of stop and search operations targeting "suspected gunmen or vehicles that have been associated with firearms" and called "Operation Trident Swoop" by the police. The Metropolitan Police hoped that "the searches will deter suspects from carrying weapons and prevent shootings taking place, as well as possibly recovering weapons and leading to arrests."[89] Superintendent Jerry Savill, Lambeth Police has responsibility for policing in the Brixton area, stated:
This operation is aimed very specifically at people we have information to suggest may be involved in gun crime or other offences. We want to send out a very clear message to those who carry guns in Lambeth, don't. It is time to stop the vast majority of people in this borough feeling afraid to be on the street and make it the gunmen who are fearful of their community helping the police to arrest them.[89]
In September 2006 Brixton was the scene of a widely reported shooting, involving two boys being shot in the packed McDonald's on Brixton Road/Acre Lane.[90]
In 2007 firearm offences rose by 4 per cent in London, totalling 3,459 "gun-enabled" crimes, including 30 gun murders of which nine victims were aged 18 or under. A series of gun crimes in the Brixton, Clapham and Streatham, including the Murders of three boys in one week, lead some media commentators to call the area "gun capital".[91]
In popular culture
Music


References to Brixton in song started with the release of "Whoppi King" by Laurel Aitken in 1968 and "Brixton Cat" by Dice the Boss in 1969. This was later followed in August 1975 by a popular novelty song written and sung by Geraint Hughes and Jeff Calvert (who billed themselves as "Typically Tropical"): two white men who told the story of a Brixton bus-driver "going to Barbados" with "Coconut Airways" to escape the rain of London.
- The 1979 punk song "The Guns of Brixton" by The Clash deals with law enforcement violence in Brixton. Written by the group's bass player Paul Simonon, who grew up in Brixton, it had a strong reggae influence.
- Sex Gang Children, a post-punk band who are attributed with pioneering the goth movement, were formed and based in Brixton in the early 1980s.
- Andi Sex Gang lived in Brixton for many years.
- Before a Jam gig, well-known punk band The Misfits were involved in a fight and thrown into Brixton Prison, which led them to write their song "London Dungeon".
- Sneakbo, rapper
- Big Narstie, rapper
- Eddy Grant's 1982 album Killer on the Rampage contains his hit song "Electric Avenue", a reference to the well known shopping street in central Brixton, which was one of the first in the UK to have electric street lighting installed (when Brixton's character was very different). The song evokes images of poverty, violence and misery but also celebrates the energising vibe of the area.
- Simple Minds mention "Get out of Bombay... go up to Brixton" in their 1984 song 'Up on the Catwalk'.
- The song "Journey to the Centre of Brixton" by R.O.C.
- The song "Brixton, Bronx ou Baixada" by Brazilian rock-reggae band O Rappa, tells about social differences.
- The song "And God Created Brixton" features on the Carter USM album A World Without Dave. It mentions many of the most famous landmarks in the community including The Ritzy cinema and the prison.
- The subject of Maxi Priest's 1990 hit song "Close to You" is from Brixton.
- Amy Winehouse's song "Me and Mr Jones" features a reference to Brixton.
- California punk band Rancid wrote a song called "Brixton" that appeared on the Rock Stars Kill compilation, and later on B Sides and C Sides.
- The electronic band Chase and Status collaborated with Cee-Lo Green on their record Brixton Briefcase, which features on the album No More Idols.
- In the track "Buckingham Palace" on rapper Canibus' 1998 debut album Can-I-Bus, Brixton is mentioned in the lyrical line "From Brixton to Clapham Common, my lyrics invade Europe like Josef Stalin, I murder n***** for rhymin".
- Robbie Williams mentions "moving bricks to Brixton" in his 2012 song "Candy".
Film and television
- Director Richard Parry's 2001 film South West Nine (SW9), whose name refers to the postcode covering much of central Brixton, was shot here. Confusingly, this postcode is officially that of Stockwell – although the northern part of Brixton falls within the boundary – whereas SW2 (the Brixton Hill sorting office) also covers Tulse Hill A204 road, Streatham Hill and Brixton Hill.
- Sarah Manning, a fictional character from Orphan Black, the BBC America Series, was from Brixton.
Transport
Buses
Brixton is served by London Buses routes 2, 3, 35, 37, 45, 57, 59, 109, 118, 133, 137, 159, 196, 201, 250, 322, 333, 345, 355, 415, 417, 432, P4, P5, N2, N3, N35, N109, N133 and N137.
London Underground
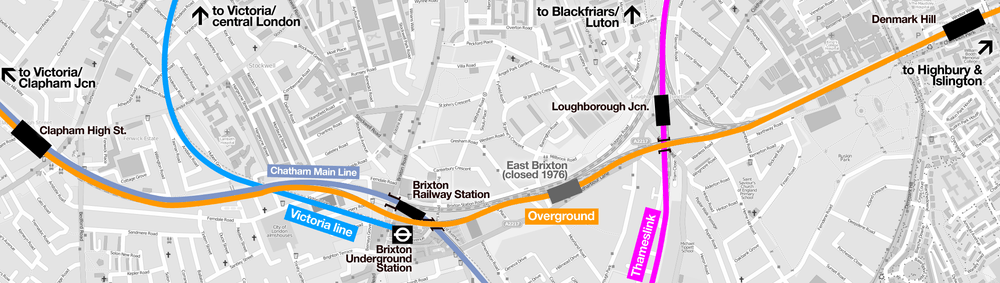
The nearest station is Brixton on the Victoria line.
National Rail
The nearest station is Brixton for Southeastern services towards London Victoria and Orpington.
Road Network
Brixton is located on several main roads. The A203, A204 and A2217 links the area to Vauxhall Bridge and the A23 London to Brighton road runs through the area from the north to the south. Brixton was due to be a major interchange of the South Cross Route, part of the London Ringways plan, which was cancelled in the 1970s.
Cross River Tram
Transport for London proposed to build the Cross River Tram from Camden Town to Brixton via central London, but this project was abandoned in 2008 due to lack of funding.
Notable people


Three people who have lived in Brixton have blue plaques marking their former homes:
- Havelock Ellis, pioneer sexologist lived at Dover Mansions on Canterbury Crescent[93]
- C. L. R. James, the writer and black political activist, lived in Railton Road,[94] above the offices of Race Today.[95]
- Dan Leno (1860–1904), an English music hall comedian famous for his drag acts (56 Akerman Road).
Other notable people with Brixton connections include:
- David Bowie was born at 40 Stansfield Road, Brixton.
- Former London Mayor Ken Livingstone grew up and lived for many years in Brixton.
- Former British Prime Minister John Major spent part of his childhood in a two-room flat off Coldharbour Lane living with his father, former Music Hall performer Tom Major-Ball. Although now in Brixton, the address at the time was in Camberwell prior to a minor boundary change. He then moved to a house on Burton Road, having been born in Worcester Park, Sutton. He began his political career as a local Lambeth Councillor while still living in the area.[96]
- Max Wall, comedian and music hall performer, was born in Brixton.
 Musician David Bowie
Musician David Bowie - Freddie Davies, the "parrot-faced" comedian and actor, was born in Brixton in 1937.
- Poly Styrene, the singer of the band X-Ray Spex, was born in Bromley in 1957 but grew up in Brixton.[97]
- Danny Williams, heavyweight boxer, was born in Brixton
- Paul Simonon and Mick Jones of The Clash are both from Brixton.
- Drum and bass producer Dillinja is from Brixton.
- Screenwriter, director Daniel Mulloy was born in Brixton.
- The band Alabama 3 were formed in Brixton.
- Linton Kwesi Johnson the poet is a long-time Brixton resident
- House music duo Basement Jaxx formed in Brixton.
- EBK, long-term resident of Brixton
- Fruitbat of power-pop punk band Carter the Unstoppable Sex Machine was a long-time Brixton resident.
- Joe Cornish, presenter of the BBC production Adam and Joe in the 1990s, and current comedy radio presenter on BBC6 Music with Adam Buxton.
- Bradley McIntosh, member of pop group S Club 7.
- Sharon Osbourne, wife of Ozzy Osbourne and daughter of Don Arden, was born in Brixton.
- Mike Skinner of the band "The Streets" moved to Brixton c. 2000 to pursue his recording career. Some of his songs are about living in Brixton.
- Skin, singer of the band Skunk Anansie, grew up in Brixton.
- Stereo MC's, acid jazz/club dance group, was formed and is still based in Brixton.
- Cult novelist Martin Millar lived here, and most of his novels are set in and around Brixton.
- Environmentalist James Lovelock, famous for proposing the Gaia hypothesis, was born and spent his childhood in Brixton.[98]
- Frank Reginald Carey, Second World War fighter ace, was born in Brixton.
- Jo Self, artist, long-term resident of Brixton.
- Adele, English singer, songwriter and musician, lived in Brixton as a child.
- Iwan Thomas, Olympic athlete.
- Nyron Nosworthy, professional footballer
- Shivani Kapoor, Indian model
- Timothy Glanfield, journalist and writer, is a longtime Brixton resident
- In the musical comedy Leave it to Jeeves, P. G. Wodehouse revealed that his iconic manservant Jeeves grew up in Brixton.
- Several members of the So Solid Crew.
- Sneakbo, rapper
- Big Narstie, rapper
- Luol Deng, player for the American basketball team Miami Heat, lived and played in Brixton.
- Alex Wheatle, novelist.
- Lisa Maffia, singer and TV personality, was brought up in Brixton.
- Bunmi Mojekwu, actress.
- James Dagwell, journalist and former BBC News presenter, lived in Brixton
- La Roux (Elly Jackson), musician, was born and raised in Brixton.
- Hew Locke, contemporary artist, a resident of more than 20 years, has cited Brixton and its market as an influence on his work.
- Mooji, spiritual teacher, lived in Brixton
- Nikki Sudden and Dave Kusworth, of the Jacobites shared a house on Norwood Road, Brixton, in the early 80s.
- Danny Kirwan of the band Fleetwood Mac was born and raised in Brixton.
References
- ↑ Brixton is made up of five wards with an average population of around 15,500 http://www.urban75.org/brixton/info/facts.html
- ↑ 2011 ward populations http://www.ukcensusdata.com/lambeth-e09000022#sthash.84kU3ROY.dpbs
- ↑ Mayor of London (February 2008). "London Plan (Consolidated with Alterations since 2004)" (PDF). Greater London Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 June 2010.
- 1 2 "Brixton Guide". All In London. 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 "History of Brixton". Myvillage.com.
- ↑ "Streetmap of Brixton". Streetmap EU Ltd. 2009. Archived from the original on 8 June 2011. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
- ↑ "Lambeth Council office locations". London Borough of Lambeth. 2009. Archived from the original on 15 June 2009. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
- ↑ "Where Is The Centre Of London? An Update". 30 April 2014. Archived from the original on 30 May 2016.
- ↑ "Distance between Brixton and Frazier Street, London, United Kingdom, (UK)".
- 1 2 3 "London Borough of Lambeth | A short history of Brixton". Lambeth.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013.
- ↑ "Morleys store, Brixton". morleys.co.uk. Morleys Stores Ltd. Archived from the original on 1 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- 1 2 "Stockwell Park Estate". Stockwellpark.com. Retrieved 5 December 2012.
- ↑ Windrush Square Archived 5 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Icons: A portrait of England. Retrieved 6 October 2006.
- 1 2 3 British history: The making of modern Britain, BBC Online: Mike Phillips, 1998. Retrieved 4 October 2006.
- ↑ "Small Island Read 2007: The Windrush Generation". Smallislandread.com. Archived from the original on 17 February 2012.
- ↑ "Empire Windrush History". Oceanlinermuseum.co.uk. 24 May 1948.
- ↑ Kettle, Martin & Hodges, Lucy (1982) Uprising!: Police, the People and the Riots in Britain's Cities
- ↑ Battle for Brixton, Youtube.com, Youtube.com
- ↑ "Battle 4 Brixton pt6 of 6". YouTube. 22 April 2008. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ "How smouldering tension erupted to set Brixton aflame", The Guardian, 13 April 1981
- ↑ "1981 riots timeline". Untold History Channel Four Television. Retrieved 6 March 2009
- ↑ "Q&A: Stephen Lawrence murder". BBC News. 5 May 2004. Retrieved 4 January 2008.
- ↑ Bennett, Gillian (1996). "'Camera, Lights Action!': The British General Election 1992 as Narrative Event". Folklore. 107: 94–97. JSTOR 1260921. doi:10.1080/0015587X.1996.9715921.
- ↑ "Profile: Copeland the killer". BBC News. 30 June 2000. Archived from the original on 20 July 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Emily-Ann Elliott (5 May 2009). "Bomb survivor writes Brighton play". The Argus. Retrieved 27 July 2011.
- ↑ "Jayday Cannabis March and Festival, Kennington Park to Brockwell Park, London". Urban75.org.
- ↑ "Jayday Cannabis March and Festival, Kennington Park to Brockwell Park through Brixton, 5th June 2004". Urban75.org. 5 June 2004.
- ↑ Schmoo.co.uk Archived 4 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine., cannabis coalition (uk)
- ↑ Dayle, Philip (24 October 2010). "Brixton: regeneration or gentrification?". The Guardian. London.
- ↑ "The Brixton rennaissance [sic]". The Happiness Project London. 21 November 2009.
- ↑ "Shops and more at Brixton Village – Space Makers Agency". Spacemakers.org.uk.
- ↑ "London's Brixton Market revamp: Bohemian style: arty hubs to see and be seen". Easyvoyage.co.uk.
- ↑ "COMMENT: Gentrification of Brixton leaves me conflicted". Brixton Blog. 26 April 2012.
- ↑ "Brixton". The Academy of Urbanism. Retrieved 5 December 2012.
- ↑ "Transition Towns wiki". Transitiontowns.org.
- ↑ Urbangreenfair.org Archived 25 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "The Brixton Pound". Site.transitiontownbrixton.org. Archived from the original on 29 May 2010.
- ↑ Hubberts Peak says: (16 September 2009). "Brixton Pound Moves Town Closer To 'Transition Town' Status". Thegreenvillage.co.uk.
- 1 2 3 Whateley, Laura (13 March 2012). "Brixton has run on the pound as shoppers clamour for local currency". The Times. London.
- ↑ "Brixton Pound ready for launch". Money.aol.co.uk. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016.
- ↑ "Brixton: Barrier Block". Urban75.org. Retrieved 5 August 2009.
- 1 2 "Brixton's gone to pot". BBC News. 16 May 2002. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- 1 2 Ideal Homes – Brixton Archived 9 April 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Ritzy Cinema | SW2 1JG". Myvillage.com.
- ↑ "London Brixton". Spoonfed.co.uk.
- ↑ "Brixton Splash street festival, 2010". urban75 blog. 1 August 2010. Retrieved 4 March 2011.
- ↑ Southlondon.org photo Archived 31 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Lambeth North Deanery". Church of England. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ↑ F. H. W. Sheppard (General Editor) (1956). "Brixton: Rush Common". Survey of London: volume 26: Lambeth: Southern area. Institute of Historical Research. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ↑ "East Brixton St Jude" (PDF). Former places of worship in the Diocese of Southwark. Church of England. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ↑ "East Brixton Rd Christ Church". Church of England. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ↑ "Corpus Christi Brixton Hill". Archdiocese of Southwark. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ↑ "Brixton Mosque and Islamic Cultural Centre". Salaam.co.uk. Retrieved 20 June 2010.
- ↑ "Brixton Mosque & Islamic Cultural Centre, Museums, Heritage UK". Totaltravel.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2008-12-09.
- ↑ "Shoe bomb suspect 'one of many'". BBC News. 26 December 2001. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- 1 2 Johnston, Philip (27 May 2007). "7 July preacher Abdullah El-Faisal deported". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 23 December 2007.
- ↑ "Video of lecture 'The Devil's Deception of the Saudi Salafis'".
- ↑ "islam in london brixton pt1 mosque salafis pure islam". YouTube. 3 April 2007.
- ↑ Battle for Brixton, Youtube.com Youtube.com
- ↑ "Focus: Gun Culture: Gun gangs of the capital | Find Articles at BNET".
- ↑ "Yardie gangs control cocaine network in Britain". The Times. Jamaica Gleaner. 25 February 2002. Archived from the original on 6 September 2008.
- ↑ Gangsinlondon blog Archived 10 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Police damned over Yardie chaos". The Guardian. London. 16 February 1999.
- ↑ "10 held in raids on 'Murder Zone' gang". London Evening Standard. 18 June 2008. Archived from the original on 9 January 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2010.
- ↑ "My escape from gangland". London Evening Standard. 14 March 2008. Archived from the original on 17 September 2008.
- ↑ Mirror.co.uk Archived 8 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Gun found in shop shooting probe". BBC News. 15 August 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ↑ Fresco, Adam; Hamilton, Fiona (8 August 2008). "Young passerby killed as gunmen open fire in street". The Times. London. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ↑ "The rise and fall of Brixton's GAS gang". 12 June 2012 – via www.bbc.co.uk.
- ↑ "Zac Olumegbon murder: Four teenagers jailed for life". BBC News. 21 December 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ Cowan, Rosie (7 March 2005). "Criminal gangs use Islam to intimidate victims". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Thompson, Tony (24 February 2002). "Drugs and Alcohol". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ "Brixton Drug Crime". Val Shawcross. Archived from the original on 6 January 2009.
- ↑ Hopkins, Nick (29 December 2001). "Police extend softly-softly pilot scheme on cannabis possession". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ "Cannabis will remain class C drug". BBC News. 19 January 2006. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Tiggey May; Martin Duffy; Hamish Warburton; Mike Hough (21 January 2007). "Policing cannabis as a Class C drug". Jrf.org.uk. Archived from the original on 20 October 2008.
- ↑ Moss, Stephen (18 September 2007). "The Man Who Would be Mayor [print version: Out But Not Down]". The Guardian (g2). London. pp. 12–15. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ↑ Bennetto, Jason (1 December 2005). "Brixton moves from 'softly softly' to zero tolerance on cannabis". The Independent. London.
- ↑ Hopkins, Nick (19 March 2002). "Trials and Errors of Controversial Cop: How Onslaught by Critics Took its Toll of Ambitious Gay Police Chief". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ↑ The Battle for Brixton, an April 2006 BBC2 documentary.
- ↑ Dodd, Vikram (28 November 2003). "The Guardian Profile : Brian Paddick". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ↑ "About Brian". BrianPaddick4London. 9 September 2007. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 22 September 2007.
- ↑ Casciani, Dominic (27 March 2002). "BBC.co.uk". BBC News.
- ↑ "BBC.co.uk". BBC News. 12 August 1998.
- ↑ "Ten years of Operation Trident". Time Out.
- ↑ "Police fears over rising gun crime". BBC News. 3 August 2001.
- ↑ IPCC.gov.uk Archived 2 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ UKonline.co.uk Archived 5 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 Metropolitan Police. "Operation Trident Swoop". Metropolitan Police Service.
- ↑ Boys shot in Brixton McDonald's Archived 6 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "The Metropolitan Police's Operation Trident on Gun Crime". Time Out London.
- ↑ "With tears and songs, London pays homage to 'starman in the sky' David Bowie". Sydney Morning Herald. 14 January 2016.
- ↑ "- English Heritage".
- ↑ "- English Heritage".
- ↑ John Fitzpatrick, "You never know when it's going to explode" (interview with C. L. R. James, 1989), Living Marxism, April 1989; reprinted Spiked Election.
- ↑ Archived 12 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Xray spex official site/poly's biography 1". X-rayspex.com.
- ↑ Brown, Andrew (31 December 2005). "Paramedic to the planet". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Brixton, London district. |
- Urban75: A resource of Brixton information, features, articles, contemporary photography and "Brixton then and now" comparisons
- London Borough of Lambeth's Draft Brixton Conservation Area Statement
| Adjacent places of Brixton | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Stockwell | Kennington | Camberwell |  |
| Clapham | |
Herne Hill | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Balham | Streatham Hill | Tulse Hill | ||