Sikorsky Memorial Airport
| Igor I. Sikorsky Memorial Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 USGS 1991 orthophoto | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | City of Bridgeport | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Bridgeport, Connecticut | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Stratford, Connecticut | ||||||||||||||
| Hub for | Tailwind Air Service | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 9 ft / 3 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°09′48″N 073°07′34″W / 41.16333°N 73.12611°WCoordinates: 41°09′48″N 073°07′34″W / 41.16333°N 73.12611°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | www.bridgeportct.gov/... | ||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||
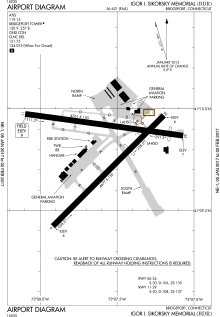 FAA Airport Diagram | |||||||||||||||
 BDR  BDR Location of airport in Connecticut/United States | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Helipads | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2015) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Igor I. Sikorsky Memorial Airport (IATA: BDR, ICAO: KBDR, FAA LID: BDR) is a public airport in Fairfield County, Connecticut,[1] owned by the city of Bridgeport. It is three miles (6 km) southeast of downtown,[1] in the town of Stratford. It was formerly Bridgeport Municipal Airport.
It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a national general aviation facility.[2] It has three Fixed-Base Operators (FBO's) and several private hangars. The last airline service was offered by US Helicopter, with scheduled flights to New York's Downtown Manhattan Heliport, continuing to John F. Kennedy International Airport. On September 25, 2009 US Helicopter shut down.
History
The airport was originally Avon Field, a racetrack where aircraft landed on the grass infield. It was the site of the country's first air show held in 1911, on the grounds of what is now St. Michaels Cemetery.[3] It became known as Mollison Field after Captain Jim Mollison's crash landing there in 1933 during an attempt to fly across the Atlantic. The City of Bridgeport purchased the airport in 1937, after which it became Bridgeport Municipal Airport.
On October 17, 1962 President John F. Kennedy gave a speech at this airport.[4]
In 1972 it was rededicated as the Igor I. Sikorsky Memorial Airport, honoring the airport's most famous tenant, Igor Sikorsky, who selected Stratford as the site for his Sikorsky Aviation Corporation in 1929.[5]
On November 2, 1992 President George H W Bush gave a speech at this airport.
In the 1950s American Airlines stopped at Bridgeport, one Convair a day each way; they left in 1960, replaced by Allegheny, which pulled out in 1975-76.
In the 1980s, the airport was served simultaneously by five carriers and or their regional affiliates: Business Express Airlines, Continental Airlines, Piedmont Airlines, US Air and United Express.[6] By 1992, airlines provided service from Bridgeport to several cities in the northeast, including Washington, DC, Philadelphia, Boston and Newark.[7]
The airport has been the subject of heated debate in Stratford and Bridgeport. While the City of Bridgeport owns the airport, the whole property is in the Town of Stratford. Before the end of World War II little more than salt marshes surrounded the airport, but in the 1950s and 1960s Stratford permitted extensive residential development in the Lordship area near the airfield. Bridgeport has pushed for runway and terminal expansion, hoping to attract new service to the airport, arguing that service to the airport is necessary for the growth of Bridgeport's economy. Stratford has opposed terminal expansion and runway lengthening that would interfere with existing roads. Even when the airport was served by major carriers, Stratford advocated for limits on flights because of noise in the Lordship and South End neighborhoods. In 2003 the Federal Aviation Administration mandated the lengthening of the two runways with unpaved safety overruns at each end. Stratford and Connecticut officials have resisted the FAA effort to install the overruns, but the FAA has notified Stratford, Bridgeport and state officials that it may obtain a federal court order to use eminent domain to complete the overruns.
In June 2006 US Helicopter began scheduled flights to New York's Downtown Manhattan Heliport, continuing to John F. Kennedy International Airport. This was the first airline service since 1999. On September 25, 2009 US Helicopter suddenly shut down.
In February 2007 state legislators from Bridgeport, in an effort to force expansion, introduced legislation allowing the State of Connecticut to take over the airport. Officials from Stratford would prefer the town take ownership of the airport and oppose the proposed state takeover.
Facilities and aircraft

Igor I. Sikorsky Memorial Airport covers 800 acres (324 ha) at an elevation of 9 feet (3 m) above mean sea level. It has two asphalt runways: 11/29 is 4,761 by 150 feet (1,451 x 46 m) and 6/24 is 4,677 by 150 feet (1,426 x 46 m). It has one asphalt helipad, 40 by 40 feet (12 x 12 m).[1]
In the year ending June 30, 2010 the airport had 67,951 aircraft operations, average 186 per day: 96% general aviation, 3% air taxi, and 1% military. 190 aircraft were then based at the airport: 74% single-engine, 13% jet, 11% multi-engine, and 3% helicopter.[1]
The Connecticut Wing Civil Air Patrol 022nd Stratford Eagles Composite Squadron (NER-CT-022) operates out of this airport.[8]
Airlines and destinations
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Tailwind Air Service | Boston, New Bedford, New York-Skyport |
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| FedEx Feeder operated by Wiggins Airways | Hartford |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 FAA Airport Master Record for BDR (Form 5010 PDF). Federal Aviation Administration. Effective May 31, 2012.
- ↑ "List of NPIAS Airports" (PDF). FAA.gov. Federal Aviation Administration. 21 October 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2016.
- ↑ http://lordshiphistory.com/LordshipAviation.html
- ↑ http://www.jfklibrary.org/Asset-Viewer/Archives/JFKWHA-140-002.aspx
- ↑ History of Sikorsky Memorial Airport from City of Bridgeport website
- ↑ The View from - Sikorsky Memorial Airport from New York Times website
- ↑ Small Airports: Convenience and Limits from New York Times website
- ↑ http://ct022.ctwg.cap.gov/ Civil Air Patrol 022nd
External links
- Sikorsky Memorial Airport at City of Bridgeport website
- Lordship aviation history
- Atlantic Aviation, a fixed-base operator (FBO)
- Three Wing Flying Services, a fixed-base operator (FBO)
- Volo Aviation, a fixed-base operator (FBO)
- Aerial image as of April 1991 from USGS The National Map
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective August 17, 2017
- FAA Terminal Procedures for BDR, effective August 17, 2017
- Resources for this airport:
- FAA airport information for BDR
- AirNav airport information for KBDR
- ASN accident history for BDR
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart, Terminal Procedures