Bradford Bishop
| Bradford Bishop | |
|---|---|
 Age progression sculpture of Bishop by Karen T. Taylor | |
| FBI Ten Most Wanted Fugitive | |
| Charges | Murder, a felony |
| Alias | Bradford Bishop, Brad Bishop, Bradford Bishop Jr. |
| Description | |
| Born |
William Bradford Bishop Jr. August 1, 1936 Pasadena, California, U.S. |
| Spouse | Annette Kathryn Bishop |
| Children | 3 |
| Status | |
| Added | April 10, 2014 |
| Number | 502 |
| Currently a Top Ten Fugitive | |
William Bradford Bishop Jr. (born August 1, 1936) is a former United States Foreign Service officer who has been a fugitive from justice since allegedly killing five members of his family in 1976.[1][2][3] On April 10, 2014, the FBI placed him on the list of its Ten Most Wanted Fugitives.[4]
Biography
William Bradford Bishop Jr. was born August 1, 1936, in Pasadena, California, to Lobelia and William Bradford Bishop, Sr. He received a BS in history from Yale University and an MA in international studies from Middlebury College.[2] Alternatively, he has been reported to have a bachelor's degree in American Studies from Yale and a master's degree in Italian from Middlebury College.[5] He also holds a master's degree in African Studies from UCLA.[6][7]
After his graduation from Yale in 1959, Bishop married Annette Wels, his high school sweetheart. The couple later had three sons. He then joined the U.S. Army and spent four years in the counterintelligence area. Bishop also learned to speak four foreign languages fluently: Italian, French, Serbo-Croatian, and Spanish.[8] After leaving the Army, Bishop joined the U.S. State Department and served in the Foreign Service in many postings overseas.[2] This included postings in the Italian cities of Verona, Milan, and Florence (where he did post-graduate work at the University of Florence) from 1968 to 1972).[2] He also served in Africa, including posts in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and in Gaborone, Botswana, from 1972 to 1974.[2] His last posting, which began in 1974, was at State Department Headquarters in Washington, D.C. as an Assistant Chief in the Division of Special Activities and Commercial Treaties. He was living in Bethesda, Maryland, with his wife, three sons, and his mother Lobelia.[2]
Bishop and his wife were both psychiatric patients.[6] Bishop suffered from depression and insomnia and was taking the medication Serax (oxazepam).[9]
Killings
By early 1976, Bishop was anticipating a promotion at work. On the afternoon of March 1, 1976, he learned he would not receive the promotion he had sought. After learning of this, Bishop told his secretary he did not feel well and left work early.[1] Shortly thereafter, police believe that he first drove from Foggy Bottom (the neighborhood where he worked at the U.S. State Department headquarters) to the bank where he withdrew several hundred dollars. He then drove to Montgomery Mall and bought a sledge hammer and gas can at Sears.[10] He then filled the gas can and family station wagon up at a gas station next to the mall.[10] From there, he drove to Poch's Hardware, which at the time was located next to Safeway, at the intersection of River Road and Falls Road. This is where police believe he purchased a shovel and pitchfork.[10] He returned to his home in Bethesda between 7:30 and 8 p.m. after the children were put to bed. The police investigation shows that his wife was probably killed first.[2] His mother, who was returning home from walking the family's golden retriever, was killed next.[2] Finally, his three sons (aged 5, 10, and 14) were killed while they slept in their beds in an upstairs bedroom.[2]
With the bodies loaded into the station wagon, Bishop allegedly drove 275 miles (443 km), about a six-hour drive, to a densely wooded swamp off North Carolina Highway 94, about 5 miles (8.0 km) south of Columbia, North Carolina.[10] There, on March 2, he dug a shallow hole where he piled the bodies, doused them with gasoline, and set them ablaze.[10] Later the same day, a North Carolina forest ranger was dispatched by a spotter in a fire tower to an area where smoke was rising from the trees; the fire spread over three acres (1.2 ha).[10] The ranger discovered the burned bodies along with a gas can, a pitchfork, and a shovel with a label of "OCH HDW", which was tracked to Poch's Hardware a week later.[10]
It was later confirmed that Bishop visited a sporting goods store in Jacksonville, North Carolina, that same day, where he used his credit card to purchase tennis shoes.[1] According to witnesses, he had the family dog with him on a leash and was possibly accompanied by a woman described as "dark skinned".[11] According to police reports, a week later on March 10, a neighbor of the Bishops grew concerned about the family's absence, claiming she had not seen them for about a week. The neighbor contacted local police, who dispatched a detective to the neighborhood. After meeting the neighbor, who had a key to the Bishop home, the detective entered the premises to see if anything was wrong. As he approached the front door, he found blood droplets on the front porch and entered the house to discover spattered blood on the floor and walls. The children's room was covered with blood. The detective stated that in his 12 years as a police officer, it was the worst crime scene he had ever observed. In addition, it was stated that one of the most disturbing pieces of evidence were marks on the ceiling of a bedroom where two boys were sleeping in bunk beds of the hammer swinging and hitting the ceiling. Dental records were used to confirm that the bodies found in North Carolina were of Bishop's family.[12]
On March 18, Bishop's a 1974 Chevy station wagon was found abandoned at an isolated campground in Elkmont, Tennessee[13] at the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, a few miles from the Appalachian Trail and about 400 miles (640 km) from the Columbia-area pyre.[1][10] The car contained dog biscuits, a bloody blanket, a shotgun, an ax and a shaving kit with Serax; the spare-tire well in the trunk was full of blood.[10] According to a witness, the car had been there since March 5–7. Police theorized that Bishop joined the flow of hikers on the Appalachian Trail. They attempted to follow his scent with bloodhounds without success. The following day, a grand jury indicted Bishop on five counts of first degree murder and other charges.[10]
Motives
Prior to the murders, in addition to his mental health issues, Bishop was having financial problems and living on money from his mother. Bishop's wife had confided to a friend that she might need to find work. It was also reported that Bishop was unhappy in his desk job at the State Department and wanted a promotion to a different overseas position. Bishop's wife had told a friend that neither she nor her mother-in-law had a desire to leave the United States.
Aftermath and sightings
Bishop had approximately one week of advance time before the authorities began looking for him and could have traveled on his diplomatic passport. Because of the methods of air travel and immigration in 1976 throughout much of the world, he could easily have avoided leaving a paper trail of any kind. Since 1976, Bishop has allegedly been sighted a number of times in various European countries, including Italy, Belgium, England, Finland, the Netherlands, Germany, Greece, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland.[3] The three most credible sightings noted by the United States Marshals Service are:
- In July 1978, a Swedish woman, who said she had collaborated with Bishop while on a business trip in Ethiopia, reported she had spotted him twice in a public park in Stockholm during a span of one week. She stated she was "absolutely certain" that the man was Bishop.[3]
- In January 1979, Bishop was reportedly seen by a former U.S. State Department colleague in a restroom in Sorrento, Italy. The colleague greeted the bearded man, whom he personally believed to be Bishop, eye-to-eye, asking the man impulsively, "Hey, you're Brad Bishop, aren't you?" The man panicked suddenly, responding in a distinctly American accent, "Oh no." He then ran swiftly out of the restroom and fled into the Sorrento alleyways.[3]
- On September 19, 1994, on a Basel, Switzerland, train platform, a neighbor who had known Bishop and his family in Bethesda was on vacation and reported that she had seen Bishop from a few feet away.[3] The neighbor described Bishop as "well-groomed" and in a car.[14]
Profile
The FBI states that Bishop was an avid outdoorsman who enjoyed camping and hiking. He had a pilot's license from when he was stationed in Africa. He enjoys riding motorcycles and working out every week. He is fond of dogs. He also enjoys scotch, peanuts, and spicy foods. He has a six-inch vertical scar on his lower back from surgery and has a cleft chin and mole on his left face cheek. Bishop may have had his father's Smith & Wesson M&P .38 Special revolver with the serial number C981967 and his Yale class ring with him when he vanished. He is also believed to have taken his diplomatic passport with him, as the family's diplomatic passports were all found at their home but his was missing.
Fugitive status
As of 2010, authorities believe he is alive, living in Switzerland, Italy or another location in Europe. He may still be in the U.S. in California and may have worked as a teacher or been involved in criminal activities.[15] It is widely believed that he may be living in Europe due to many more leads within this continent compared with the lack of leads elsewhere.
Adding to the hypothesis that Bishop may be living outside the U.S. is the fact that Bishop was known to manage and create IDs and passports while working for the U.S. government. It is possible that Bishop fled the week of the murders and created a new identity in a foreign nation. He may have used fake birth certificates and fake passports that he created before or during the week of the murders. He may have illegally manipulated immigration and citizenship into a foreign nation. Bishop spoke five languages fluently and could have assimilated into the countries of Switzerland, France, Spain, Italy, the United Kingdom, Yugoslavia and possibly Romania without many obstacles.
On October 9, 2014, the body of an unidentified man who resembled Bishop, who had been killed in a hit-and-run walking along an Alabama highway in 1981, was exhumed by the FBI in Scottsboro to have the DNA, teeth and fingerprints analyzed.[16] The DNA test indicated the deceased was not Bishop.[17]
In the media
After the initial national headlines, the Bishop case was the subject of articles in national publications like Reader's Digest and Time Magazine at milestone anniversaries. It was followed intermittently on an ad hoc basis by the Washington Post, the Washington Star, and the Washington Times as well as local Washington D.C. television stations. The case was featured on television shows such as NBC's Unsolved Mysteries, ABC's Vanished and Fox's America's Most Wanted. Bishop was profiled on AMW website 33 years to the day since his family's bodies were discovered, with a new age-enhanced bust of him with facial hair.
A German TV show, Aktenzeichen XY … ungelöst, also featured the case in its 250th episode on November 6, 1992, to find possible evidence of Bishop living abroad.
In 1978 the bluegrass group Coup de Grass recorded "The Ballad of Bradford Bishop," written by Steve Lasko and Steve Deady. It was featured on the album Rhythm and Bluegrass. Carolyn Banks's 1980 Viking novel The Darkroom was based on the Bradford Bishop murder case.
Ballet dancer Jacques d'Amboise revealed in his 2011 autobiography I Was a Dancer that he became a close friend of Bishop's parents, who were ballet fans, while he was still a teenager, and that when he was 17 and Bishop was 14, he lived with the family for a while. He described Bishop as very intelligent, reticent and intense. Years later, D'Amboise and his wife Carrie were meant to spend the night of the murders sleeping over at Bishop's home, but he was injured in a performance a few days earlier and they had to cancel. D'Amboise stated that he has wondered ever since if their presence that night would have prevented the murders or resulted in them being killed as well.[18]
In 1997, two county investigators said they believed Bishop's prior spy training may have helped him evade detection.[19]
In 2010, U.S. Marshals released more information, revealing for the first time on America's Most Wanted that, before the murders, Bishop had been corresponding with federal prison inmate Albert Kenneth Bankston in United States Penitentiary, Marion.[15] It is unknown why or how they were in contact.[15] America's Most Wanted posted the last letter, sent the day of the murders, on their website.[20]
In 2011, WUSA aired a story that there were reports Bishop had died in Hong Kong and then in France, but police used fingerprints to confirm that those reports were false.[21]
On April 10, Ronald Hosko, Assistant Director of the FBI's Criminal Investigative Division, revealed the fugitive update sculpture created by Karen T. Taylor.[22]
In early April 2014, WRC-TV in Washington, D.C. launched a webpage to display multiple investigative reports and extensive information on the Bishop case. This included samples of Bishop's handwriting, fingerprints, dental records and previously unseen Bishop family videos.[23]
On July 27, 2014, the search for Bishop was a featured story on The Hunt With John Walsh on CNN.
2014 age-progression sculpture
In 2014, at the request of the FBI, forensic artist Karen Taylor created an age progression sculpture to suggest Bishop's projected appearance at about age 77. Using Taylor's sculpture, several alternate images were created by Lisa Sheppard to show the addition of facial hair and glasses.[24]
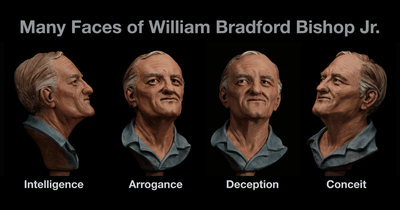 Different angles of age progression sculpture.
Different angles of age progression sculpture. What Bishop might look like with glasses.
What Bishop might look like with glasses.
See also
- Crime in Maryland
- John List, New Jersey man who killed his family at home in 1971 and remained at large under a new identity for 18 years
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Bishop still wanted in family's death". The News & Observer. Feb 26, 2006. Retrieved 2008-10-10.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "The Bishop Murders". TIME. March 22, 1976. Retrieved 2008-10-10.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Duggan, Paul (March 2, 2006). "Where Is Brad Bishop?". Washington Post. Retrieved 2008-10-10.
- ↑ "New Top Ten Fugitive — ‘Family Annihilator’ William Bradford Bishop, Jr. Wanted for 1976 Murders". fbi.gov. April 10, 2014. Archived from the original on April 16, 2014.
- ↑ "FBI — FBI Adds William Bradford Bishop to Ten Most Wanted Fugitives List". FBI.
- 1 2 "The Man Who Got Away". bethesdamagazine.com.
- ↑ "Brutality Unsolved: The Bishop Mystery". Washington Post.
- ↑ "After 30 years, Bishop killings still a mystery". Baltimore Sun. October 14, 2006. Retrieved 2012-07-10.
- ↑ "Brad Bishop home sold year after five in family slain there". Washington Post.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Tisha Thompson and Rick Yarborough. "Inside the Evidence Room in the Hunt for William Bradford Bishop". NBCWashington.com. Retrieved 2014-10-16.
- ↑ "Getting away with murder Manhunt: The 21-year-old search continues for a Bethesda man who murdered his family but kept the dog.". Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ↑ "William Bradford Bishop Jr., former State Department diplomat, added to FBI's "Most Wanted" list". Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ↑ "Missing Bishop Car Found in Smokies", Donald Baker, Washington Post, March 19, 1976.
- ↑ "William Bradford Bishop, Jr.". Reader's Digest. 1999. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2012-07-10.
- 1 2 3 "William Bradford Bishop". America's Most Wanted. 2010. Archived from the original on 2012-09-10. Retrieved 2012-07-10.
- ↑ "FBI exhumes body in hunt for ’10 Most Wanted’ fugitive search", by Andrew Russel, Global News.
- ↑ Tisha Thompson. "FBI: Body Exhumed in Alabama Not That of William Bradford Bishop". NBCWashington.com. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 2014-10-16.
- ↑ D'Amboise, Jacques. I Was a Dancer, Knopf, 2011. ISBN 978-1-4000-4234-0, Ch. 16: "A Close Call with Death", pp. 327-335
- ↑ "They Have the Clues, So Where's Their Man?". LA Times/Baltimore Sun. August 11, 1997. Retrieved 2012-07-10.
- ↑ "Bradford Bishop Letter" (PDF). America's Most Wanted. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-04-07. Retrieved 2012-07-10.
- ↑ "William Bradford Bishop Wanted In 1976 Bethesda Murder". WUSA (TV). Feb 23, 2011. Retrieved 2012-07-10.
- ↑ "William Bradford Bishop Added to FBI's Ten Most Wanted List". NBC News. April 10, 2014. Retrieved 2014-07-04.
- ↑ "The Decades Long Hunt for William Bradford Bishop". NBC News. April 9, 2014. Retrieved 2014-07-04.
- ↑ Jones, Steve (2014-04-10). "Video - NBC4 Washington". nbcwashington.com.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bradford Bishop. |
- Agents, Investigators Search Underground, Across the Country, and Around the World for FBI Ten Most Wanted Fugitive, FBI
- March 2006 Washington Post Article marking the 30-year anniversary of the Bishop murders
- Bradford Bishop's FBI Ten Most Wanted Poster
- Bethesda Magazine May-June 2013 article on Bishop
- NBC Washington Special Report on Bradford Bishop