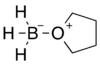Borane–tetrahydrofuran
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Properties | |||
| C4H11BO | |||
| Molar mass | 85.94 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Melting point | 66 °C (151 °F; 339 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Borane–tetrahydrofuran is a dipolar bond complex composed of borane and tetrahydrofuran (THF). These solutions are used for reductions and hydroboration, reactions that are useful in synthesis of organic compounds.[1]
Preparation and uses
The complex is commercially available but can also be generated by the dissolution of diborane in THF. A practical route to this is the oxidation of sodium borohydride with iodine in THF.[2]
The complex can reduce carboxylic acids to alcohols and is a common route for the reduction of amino acids to amino alcohols[3] (e.g. valinol). It adds across alkenes to give organoboron compounds that are useful intermediates.[4] The following organoboron reagents are prepared from borane-THF: 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, Alpine borane, diisopinocampheylborane. It is also used as a source of borane (BH3) for the formation of adducts.[5]
Safety
The solution is highly sensitive to air, requiring the use of air-free techniques.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 Marek Zaidlewicz, Herbert C. Brown, Santhosh F. Neelamkavil, "Borane–Tetrahydrofuran" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2008 John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb241.pub2
- ↑ Kanth, J. V. Bhaskar; Periasamy, Mariappan (1 September 1991). "Selective reduction of carboxylic acids into alcohols using sodium borohydride and iodine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 56 (20): 5964–5965. doi:10.1021/jo00020a052.
- ↑ McKennon, Marc J.; Meyers, A. I.; Drauz, Karlheinz; Schwarm, Michael (June 1993). "A convenient reduction of amino acids and their derivatives". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 58 (13): 3568–3571. doi:10.1021/jo00065a020.
- ↑ George W. Kabalka, John T. Maddox, Timothy Shoup, and Karla R. Bowers "A Simple And Convenient Method For The Oxidation Of Organoboranes Using Sodium Perborate: (+)-isopinocampheol" Org. Synth. 1996, vol. 73, p. 116. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.073.0116
- ↑ Karen V. L. Crépy and Tsuneo Imamoto "Preparation Of (S,S)-1,2-Bis-(tert-butylmethylphosphino)ethane ((s,s)-t-Bu-bisp*) As A Rhodium Complex" Org. Synth. 2005, vol. 82, 22. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.082.0022