Bone metastasis
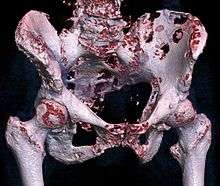
Bone metastases, or metastatic bone disease, is a class of cancer metastases that results from primary tumor invasion to bone. Bone-originating primary tumors such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing's sarcoma are rare.[1] Unlike hematological malignancies that originate in the blood and form non-solid tumors, bone metastases generally arise from epithelial tumors and form a solid mass inside the bone. Bone metastases cause severe pain, characterized by a dull, constant ache with periodic spikes of incident pain.[2]
Sources of bone metastases

Bone is the third most common location for metastasis, after the lung and liver.[5] While any type of cancer is capable of forming metastatic tumors within bone, the microenvironment of the marrow tends to favor particular types of cancer, including prostate, breast, and lung cancers.[3] Particularly in prostate cancer, bone metastases tend to be the only site of metastasis.[2] The most common sites of bone metastases are the spine, pelvis, ribs, skull, and proximal femur.[6]
Common primary tumors
Phenotypes
Under normal conditions, bone undergoes a continuous remodeling through osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and osteoblast-mediated bone deposition.[3] These processes are normally tightly regulated within bone to maintain bone structure and calcium homeostasis in the body. Disregulation of these processes by tumor cells leads to either osteoblastic or osteolytic phenotypes, reflective of the underlying mechanism of development.[3] Typically, osteolytic metastases are more aggressive than osteoblastic metastases, which have a slower course. Regardless of the phenotype, though, bone metastases show osteoclast proliferation and hypertrophy.[7]
Primary tumors
- Osteoblastic lesions
- Osteolytic lesions
- Mixed lesions
Symptoms
Bone metastases are a major clinical concern that can cause severe pain, bone fractures, spinal cord compression, hypercalcemia, anemia, spinal instability, decreased mobility, and rapid degradation in the quality of life for patients.[8][9] Patients have described the pain as a dull ache that grows worse over time, with intermittent periods of sharp, jagged pain.[2] Even under controlled pain management, these periods of breakthrough pain can occur rapidly, without warning, several times a day.[10] Pain may be worse at night and partially relieved by activity.[6] Metastases to weightbearing bones may become symptomatic early in the course of disease as compared to metastases to the flat bones of the rib or sternum.[6]
- Effects of bone metastasis
- severe pain
- bone fractures
- spinal cord compression
- hypercalcemia
- anemia
- spinal instability
- decreased mobility
Causes of symptoms
- Acidosis
Acidosis is the increased acidity in a given location, whether it is blood, urine, or tissues. Osteoclasts generate extracellular protons, lowering the pH of the extracellular matrix (ECM) around the osteoclast to approximately 4.5.[11] Nociceptors in the bone trigger a pain response in the brain in response to this acidosis.[12] It is thought that this is the primary source of the dull, chronic pain experienced by patients with bone metastasis.
- Bone restructuring
The uncoupled regulation of the osteoclasts and osteoblasts leads to malformation of the bone.[2] Malformed bones are unable to withstand the normal mechanical stresses placed on them in day-to-day activity, leading to fractures, spinal compression, and spinal instability. Malformed bones may also mechanically trigger pain receptors both within the bone and in the surrounding tissue.
Workup
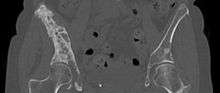
A CT scan can detect bone metastases before becoming symptomatic in patients diagnosed with tumors with risk of spread to the bones. Even sclerotic bone metastases are generally less radiodense than enostoses, and it has been suggested that bone metastasis should be the favored diagnosis between the two for bone lesions lower than a cutoff of 1060 Hounsfield units (HU).[13]
Treatment
The goals of the treatment for bone metastases include pain control, prevention and treatment of fractures, maintenance of patient function, and local tumor control.[6] Treatment options are determined by multiple factors, including performance status, life expectancy, impact on quality of life, and overall status of clinical disease.
Pain management
The World Health Organization's pain ladder was designed for the management of cancer-associated pain, and mainly involves various strength of opioids. Mild pain or breakthrough pain may be treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Other treatments include bisphosphonates, corticosteroids, radiotherapy, and radionucleotides.[2] Percutaneous osteoplasty involves the use of bone cement to reduce pain and improve mobility.[14] In palliative therapy, the main options are external radiation and radiopharmaceuticals.[15] High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) has CE approval for palliative care for bone metastasis, though treatments are still in investigatory phases as more information is needed to study effectiveness in order to obtain full approval in countries such as the USA.
Thermal ablation techniques are increasingly being used in the palliative treatment of painful metastatic bone disease. Although the majority of patients experience complete or partial relief of pain following external radiation therapy, the effect is not immediate and has been shown in some studies to be transient in more than half of patients.[16] For patients who are not eligible or do not respond to traditional therapies ( i.e. radiation therapy, chemotherapy, palliative surgery, bisphosphonates or analgesic medications), thermal ablation techniques have been explored as alternatives for pain reduction. Several multi-center clinical trials studying the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of moderate to severe pain in patients with metastatic bone disease have shown significant decreases in patient reported pain after treatment.[17][18] These studies are limited, however, to patients with one or two metastatic sites; pain from multiple tumors can be difficult to localize for directed therapy. More recently, cryoablation has also been explored as a potentially effective alternative as the area of destruction created by this technique can be monitored more effectively by CT than radiofrequency ablation, a potential advantage when treating tumors adjacent to critical structures.[19]
Monthly injections of radium-223 chloride (as Xofigo, formerly called Alpharadin) have been approved by the FDA in May 2013 for castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) with bone metastases.
A Cochrane review of calcitonin for the treatment of metastatic bone pain indicated no benefit in reduction of bone pain, complications, or quality of life.[20]
See also
References
- ↑ MedlinePlus Overview bonecancer
- 1 2 3 4 5 Jimenez-Andrade JM, Mantyh WG, Bloom AP, Ferng AS, Geffre CP, Mantyh PW (June 2010). "Bone cancer pain". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1198: 173–81. PMID 20536932. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05429.x.
- 1 2 3 4 Guise T (October 2010). "Examining the metastatic niche: targeting the microenvironment". Semin. Oncol. 37 (Suppl 2): S2–14. PMID 21111245. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.10.007.
- ↑ List of included entries and references is found on main image page in Commons: Commons:File:Metastasis sites for common cancers.svg#Summary
- ↑ Vigorita, Vincent (2007). Orthopaedic Pathology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 527. ISBN 0781796709.
- 1 2 3 4 Jacofsky, David (2004). "Metastatic Disease to Bone". Hospital Physician.
- ↑ Halvorson KG, Sevcik MA, Ghilardi JR, Rosol TJ, Mantyh PW (September 2006). "Similarities and differences in tumor growth, skeletal remodeling and pain in an osteolytic and osteoblastic model of bone cancer". Clin J Pain. 22 (7): 587–600. PMID 16926574. doi:10.1097/01.ajp.0000210902.67849.e6.
- ↑ Coleman RE (October 2006). "Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity". Clin. Cancer Res. 12 (20 Pt 2): 6243s–9s. PMID 17062708. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0931.
- ↑ Mercadante S (January 1997). "Malignant bone pain: pathophysiology and treatment". Pain. 69 (1–2): 1–18. PMID 9060007. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(96)03267-8.
- ↑ Zeppetella G (March 2009). "Impact and management of breakthrough pain in cancer". Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care. 3 (1): 1–6. PMID 19365156. doi:10.1097/SPC.0b013e3283260658.
- ↑ Teitelbaum SL (February 2007). "Osteoclasts: what do they do and how do they do it?". Am. J. Pathol. 170 (2): 427–35. PMC 1851862
 . PMID 17255310. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.060834.
. PMID 17255310. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.060834. - ↑ Julius D, Basbaum AI (September 2001). "Molecular mechanisms of nociception". Nature. 413 (6852): 203–10. PMID 11557989. doi:10.1038/35093019.
- ↑ Ulano, Adam; Bredella, Miriam A.; Burke, Patrick; Chebib, Ivan; Simeone, F. Joseph; Huang, Ambrose J.; Torriani, Martin; Chang, Connie Y. (2016). "Distinguishing Untreated Osteoblastic Metastases From Enostoses Using CT Attenuation Measurements". American Journal of Roentgenology. 207 (2): 362–368. ISSN 0361-803X. doi:10.2214/AJR.15.15559.
- ↑ Anselmetti, Giovanni Carlo (June 2010). "Osteoplasty: Percutaneous Bone Cement Injection beyond the Spine". US National Library of Medicine: National Institutes of Health. 27: 199–208. PMC 3036518
 . PMID 21629409. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1253518.
. PMID 21629409. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1253518. - ↑ Criteria for Palliation of Bone Metastases – Clinical Applications from International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved November 2011
- ↑ Tong, Daphne; Gillick, Laurence; Hendrickson, Frank R. (1982-09-01). "The palliation of symptomatic osseous metastases final results of the study by the radiation therapy oncology group". Cancer. 50 (5): 893–899. ISSN 1097-0142. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19820901)50:53.0.CO;2-Y.
- ↑ Dupuy, Damian E.; Liu, Dawei; Hartfeil, Donna; Hanna, Lucy; Blume, Jeffrey D.; Ahrar, Kamran; Lopez, Robert; Safran, Howard; DiPetrillo, Thomas (2010-02-15). "Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastases". Cancer. 116 (4): 989–997. ISSN 1097-0142. PMC 2819592
 . PMID 20041484. doi:10.1002/cncr.24837.
. PMID 20041484. doi:10.1002/cncr.24837. - ↑ Goetz, Matthew P.; Callstrom, Matthew R.; Charboneau, J. William; Farrell, Michael A.; Maus, Timothy P.; Welch, Timothy J.; Wong, Gilbert Y.; Sloan, Jeff A.; Novotny, Paul J. (2004-01-15). "Percutaneous Image-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Painful Metastases Involving Bone: A Multicenter Study". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 22 (2): 300–306. ISSN 0732-183X. PMID 14722039. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.03.097.
- ↑ Callstrom, Matthew R.; Dupuy, Damian E.; Solomon, Stephen B.; Beres, Robert A.; Littrup, Peter J.; Davis, Kirkland W.; Paz-Fumagalli, Ricardo; Hoffman, Cheryl; Atwell, Thomas D. (2013-03-01). "Percutaneous image-guided cryoablation of painful metastases involving bone". Cancer. 119 (5): 1033–1041. ISSN 1097-0142. PMID 23065947. doi:10.1002/cncr.27793.
- ↑ Martinez-Zapata, MJ (2012). "Calcitonin used to treat metastatic bone pain". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003223.pub2.
Further reading
- Bellahcène A, Castronovo V (January 1997). "Expression of bone matrix proteins in human breast cancer: potential roles in microcalcification formation and in the genesis of bone metastases". Bull Cancer. 84 (1): 17–24. PMID 9180854.
- Furger KA, Menon RK, Tuck AB, Bramwell VH, Chambers AF (November 2001). "The functional and clinical roles of osteopontin in cancer and metastasis". Curr. Mol. Med. 1 (5): 621–32. PMID 11899236. doi:10.2174/1566524013363339.
- Ibrahim T, Leong I, Sanchez-Sweatman O, et al. (2000). "Expression of bone sialoprotein and osteopontin in breast cancer bone metastases". Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 18 (3): 253–60. PMID 11315099.
- Chung, Leland W.K.; Isaacs, William B.; Simons, Jonathan W. (2007). Prostate Cancer: Biology, Genetics, and the New Therapeutics. Humana Press. ISBN 978-1-59745-224-3.