Bombay Stock Exchange
| BSE | |
 | |
 | |
| Type | Stock exchange |
|---|---|
| Location | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Coordinates | 18°55′47″N 72°50′01″E / 18.929681°N 72.833589°E |
| Founded | 9 July 1875 |
| Key people | Ashishkumar Chauhan (MD & CEO) |
| Currency | Indian rupee (₹) |
| No. of listings | 5,749 |
| Market cap | ₹ 94.65 Lakh Crore (Mar. 2016)[1] |
| Volume | ₹ 559674Crores (June 2014)[2] |
| Indices |
BSE SENSEX S&P BSE SmallCap S&P BSE MidCap S&P BSE LargeCap BSE 500 |
| Website |
www |
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is an Indian stock exchange located at Dalal Street, Kala Ghoda, Mumbai (formerly Bombay), Maharashtra, India.
Established in 1875, the BSE is Asia’s first stock exchange, It claims to be the world's fastest stock exchange, with a median trade speed of 6 microseconds,[3] The BSE is the world's 11th largest stock exchange with an overall market capitalization of more than $ 2 Trillion as of July, 2017.[4] More than 5500 companies are publicly listed on the BSE. Of these, as of November 2016, there are only 7,800 listed companies of which only 4000 trade on the stock exchanges at BSE and NSE. Hence the stocks trading at the BSE and NSE account for only about 4% of the Indian economy.[5]
History
Bombay Stock Exchange founded by Premchand Roychand. He was one of the most influential businessmen in 19th-century Bombay. A man who made a fortune in the stockbroking business and came to be known as the Cotton King, the Bullion King or just the Big Bull. He was also the founder of the Native Share and Stock Brokers Association, an institution that is now known as the BSE.[6]
The Bombay Stock Exchange is the oldest exchange in Asia. Its history dates back to 1855, when 22 stockbrokers[7] would gather under banyan trees in front of Mumbai's Town Hall. The location of these meetings changed many times to accommodate an increasing number of brokers. The group eventually moved to Dalal Street in 1874 and became an official organization known as "The Native Share & Stock Brokers Association" in 1875.
On August 31, 1957, the BSE became the first stock exchange to be recognized by the Indian Government under the Securities Contracts Regulation Act. In 1980, the exchange moved to the Phiroze Jeejeebhoy Towers at Dalal Street, Fort area. In 1986, it developed the S&P BSE SENSEX index, giving the BSE a means to measure the overall performance of the exchange. In 2000, the BSE used this index to open its derivatives market, trading S&P BSE SENSEX futures contracts. The development of S&P BSE SENSEX options along with equity derivatives followed in 2001 and 2002, expanding the BSE's trading platform.
Historically an open outcry floor trading exchange, the Bombay Stock Exchange switched to an electronic trading system developed by CMC Ltd. in 1995. It took the exchange only 50 days to make this transition. This automated, screen-based trading platform called BSE On-Line Trading (BOLT) had a capacity of 8 million orders per day. The BSE has also introduced a centralized exchange-based internet trading system, BSEWEBx.co.in to enable investors anywhere in the world to trade on the BSE platform.Now BSE has raised capital by issuing shares and as on 3rd may 2017 the BSE share which is traded in NSE only closed with Rs.999 . [8]
The BSE is also a Partner Exchange of the United Nations Sustainable Stock Exchange initiative, joining in September 2012.[9]
Timeline
1996 To 2000
- 19 August 1996 First major SENSEX revamp* 22 March 1999 Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL) set up with other financial institutions
- 1 June 1999 Interest rate swaps (IRS) / Forward Rate Agreements (FRA) allowed
- 15 July 1999 CDSL commences work
- 11 October 1999 SENSEX closed above 5000
- 11 February 2000 SENSEX crosses 6000 intra-day
- 9 June 2000 Equity Derivatives introduced
- There are co operatives society & joint stock companies & Multinational companies.
- Robert Owen was the first to start co operative society at year of 1844
- 13 July sensex hits life time high of 32000
2001 To 2010
- 1 March 2001 Corporatisation of Exchanges proposed by the Union Govt.
- 1 February 2001 BSE Webx Launched
- 1 June 2001 Index Options launched
- 4 June 2001 BSE PSU index introduced
- 15 June 2001 WDM operations at commenced
- 2 July 2001 Value at risk model introduced for margin requirement calculation
- 9 July 2001 Stock options launched
- 11 July 2001 BSE Teck launched, India’s First free float index
- 25 July 2001 Dollex 30 launched
- 1 November 2001 Stock futures launched
- 29 November 2001 100% book building allowed
- 31 December 2001 All securities clearing move to T+5 (trade date + 5 days)
- 1 February 2002 Two way fungibility for ADR/GDR
- 15 February 2002 Negotiated Dealing System (NDS) established
- 1 April 2002 T+3 settlement Introduced
- 1 January 2003 India’s first ETF on SENSEX – ‘SPICE' introduced
- 16 January 2003 Retail trading in G Sec
- 1 April 2003 T+2 settlement Introduced
- 1 June 2003 Bankex launched
- 1 September 2003 SENSEX shifted to free-float methodology
- 1 December 2003 T group launched
- 2 June 2004 SENSEX closes over 6000 for the first time (564.71 points, 11.14%)
- 17 May 2004 Second biggest fall of all time, Circuit filters used twice in a day (the Scheme) announced by SEBI
- 20 May 2005 The BSE (Corporatisation and Demutualisation) Scheme, 2005
- 8 August 2005 Incorporation of Bombay Stock Exchange Limited
- 12 August 2005 Certificate of Commencement of Business
- 19 August 2005 BSE became a Corporate Entity
- 7 February 2006 SENSEX closed above 10000
- 7 July 2006 BSE Gujarati website launched
- 21 October 2006 BSE Hindi website launched
- 2 November 2006 ishares BSE SENSEX India Tracker listed at Hong Kong Stock Exchange
- 2 January 2007 Launch of Unified Corporate Bond Reporting platform: Indian Corporate Debt Market (ICDM)
- 7 March 2007 Singapore Exchange Limited entered into an agreement to invest in a 5% stake in BSE
- 16 May 2007 Appointed Date under the Scheme i.e. Date on which Corporatisaton and Demutualisation was achieved. Notified by SEBI in the Official Gazette on 29 June 2007
- 10 January 2008 SENSEX All-time high 21206.77
- 1 October 2008 Currency Derivatives Introduced
- 18 May 2009 The SENSEX raised 2110.70 points (17.34%) and Index-wide upper circuit breaker applied
- 7 August 2009 BSE — USE Form Alliance to Develop Currency & Interest Rate
- 24 August 2009 BSE IPO Index launched
- 1 October 2009 Bombay Stock Exchange introduces trade details facility for the Investors
- 5 October 2009 BSE Introduces New Transaction Fee Structure for Cash Equity Segment
- 18 December 2009 BSE's new derivatives rates to lower transaction costs for all
- 4 January 2010 Market time changed to 9.0 a.m. – 3.30 p.m.
- 20 January 2010 BSE PSU website launched
- 22 April 2010 New DBM framework @ Rs.10 lakhs – 90% reduction in Membership Deposit
- 12 May 2010 Dissemination of Corporate Action information via SWIFT platform
- 23 July 2010 Options on BOLT
- 21 September 2010 First to introduce Mobile-based Trading
- 29 September 2010 Introduction of Smart Order Routing (SOR)
- 4 October 2010 EUREX — SENSEX Futures launch
- 11 October 2010 Launch of Fastrade on Web (FoW) – Exchange hosted platform
- 5 November 2010 SENSEX closes above 21,000 for the first time
- 12 November 2010 Commencement of Volatility Index
- 22 November 2010 Launch of SLB
- 10 December 2010 Launch of SIP
- 27 December 2010 Commencement of S&P BSE 500 Shariah Index
2011 To 2014
- 17 November 2011 Maharashtra and United Kingdom Environment Ministers launched Concept Note for BSE Carbon Index
- 30 December 2011, picks up a stake in the proxy advisory firm, Institutional Investor Advisory Services India Limited (IiAS)
- 7 January 2011 BSE Training Institute Ltd. with IGNOU launched India's first 2-year full-time MBA programme specialising in Financial Market
- 15 January 2011 Co-location facility at BSE&n[10] as BSE ties up with Standard and Poor's to use the S&P brand for Sensex and other indices.[11]
- 28 November 2013 Launch of Currency Derivatives (BSE CDX)
- 28 January 2014 Launch of Interest Rate Futures (BSE –IRF)
- 11 February 2014 Launch of Institutional Trading Platform on BSE SME
- 20 March 2014 BSE Launches New Debt Segment
- 4 April 2014 BSE SME exceeds USD 1 billion market capitalisation
- 7 April 2014 Launch of Equity Segment on BOLT Plus with Median Response Time of 200 (µs)
- 27 May 2014 BSE felicitated at The Asian Banker Summit 2014
- 26 September 2014 BSE inks MoU with BNY Mellon
- 22 October 2014 BSE inks strategic partnership with YES BANK
- 28 November 2014 BSE listed cos market cap crosses landmark 100 lakh crore
- 12 December 2014 Market Cap of BSE SME listed companies crosses landmark 10,000 crore
2015
- 8 January 2015 BSE commenced live trading from its Disaster Recovery site in Hyderabad [12]
- Asia Index Private Limited launches S&P BSE AllCap, S&P BSE SENSEX Leverage and Inverse Indices on 16 April 2015
- BSE gives Rs. 1.01 crore to Swachh Bharat Kosh on 22 April 2015
- BSE introduces overnight investment product on 18 May 2015
- BSE exceeds 1 billion derivatives contracts on its new Deutsche Börse T7 powered trading platform on 28 May 2015
- BSE celebrated its 140th Foundation Day on 9 July 2015
- BSE SME successfully completes listing of 100 SMEs under its SME umbrella on 16 July 2015
- BSE witnesses its fourth largest fall in history on a single day of 1,625 points dated 24 August 2015
- BSE becomes the fastest exchange in the world with a median response speed of 6 microseconds on 13 October 2015[13]
2016
- March 28, 2016 BSE StAR Mutual Fund Processes 81,000 orders worth Rs. 270 crore - Record Order in single day
- April 5, 2016 BSE & CMIE launch world’s first high-frequency data on unemployment and consumer sentiments
- April 28, 2016 BSE signs Memorandum of Understanding with Korea Exchange (KRX) to launch S&P BSE Sensex based derivatives contracts at KRX
- May 2, 2016 BSE Migrates Algorithm Trading Test Environment to Cloud Infrastructure
- June 9, 2016 BSE announces commencement of trading of Sovereign Gold Bonds
2017
- February 3, 2017 BSE become India's 1st listed Stock Exchange
- January 9, 2017 Hon'ble Prime Minister of India, Shri Narendra Modi inaugurated India International Exchange(IFSC) Ltd, India 1st International Exchange
Hours of operation
| Session | Timing |
|---|---|
| Pre-open Trading Session | 09:00 – 09:15 |
| Trading Session | 09:15 – 15:30 |
| Position Transfer Session | 15:40 – 16:00 |
| Closing Session | 15:40 – 16:00 |
| Option Exercise Session | 17:07 |

The hours of operation for the BSE quoted above are stated in terms of the local time (GMT + 5:30). BSE's normal trading sessions occur on all days of the week except weekends and holidays declared by the Exchange in advance.[14]
Indices
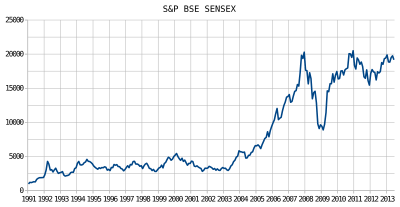

The launch of S&P BSE SENSEX in 1986 was later followed up in January 1989 by the introduction of the BSE National Index (Base: 1983–84 = 100). It comprised 100 stocks listed at five major stock exchanges in India – Mumbai, Calcutta, Delhi, Ahmedabad and Madras. The BSE National Index was renamed BSE-100[15] Index from 14 October 1996 and, since then, its calculations take into consideration only the prices of stocks listed at BSE.
BSE launched the dollar-linked version of BSE-100 index on 22 May 2006, the "BSE-200" and the "DOLLEX-200" on 27 May 1994, the BSE-500 Index and 5 sectoral indices in 1999, and the BSE-PSU Index, DOLLEX-300, and the BSE TECk Index (the country's first free-float based index) in 2001. Over the years, BSE shifted all its indices to the free-float methodology (except BSE-PSU index).
The BSE disseminates information on the Price-Earnings Ratio, the Price to Book Value Ratio, and the Dividend Yield Percentage of all its major indices on day-to-day basis. The values of all BSE indices are updated on a real-time basis during market hours and displayed through the BOLT system, the BSE website, and news wire agencies. All BSE Indices are reviewed periodically by the BSE Index Committee. This Committee, which comprises eminent independent finance professionals, frames the broad policy guidelines for the development and maintenance of all BSE indices. The BSE Index Cell carries out the day-to-day maintenance of all indices and conducts research on development of new indices.[16]
SENSEX is significantly correlated with the stock indices of other emerging markets.[17] The S&P BSE SmallCap Index accounts for 45% of the annual turnover, while the S&P BSE MidCap Index and the S&P BSE LargeCap Index account for 21% and 30% respectively.
Award
- Business World Digital Leadership and CIO Award
- The IDC Digital Transformation Awards 2017
- The Best Exchange of the year award for equity and currency derivatives in Tefla's Commodity Economic Outlook Award 2017
- Best Brand award 2017 by Economic Times
- CIO POWER LIST 2017
- Best Corporate film encompassing Vision, History, Value and Spirit of Excellence award, Best Corporate film on Employer Branding award and Most Influential HR Leaders in India award at World HRD Congress 2017
- 'Best Exchange of the year' award at 4th India Bullion & Jewellery awards 2017
- Red Hat Innovation Awards 2016 by Red Hat Solutions
- Skoch Achiever Award 2016 for SME Enablement
- Best IT Implementation Award 2016 in the “Most Complex Project Category” by PCQues
- InfoSec Maestros Awards 2016
- Lions CSR Precious Awards 2016 [18]
- Skoch Achiever Award 2016 for SME Enablement [19]
- BSE has been awarded PCQUEST Best IT Implementation Awards 2016 for New Data Centre & DR SITE in MOST COMPLEX PROJECT Category [20]
- Golden Peacock Global Award for Excellence in Corporate Governance for the year 2015[21]
- Lokmat HR Leadership Award at Mumbai in June-2014 [22]
- 50 most talented global HR leaders in Asia at the World HRD congress at Mumbai in February-2014 [23]
- FIICI-Frames Best Animation Film-International Category for the Investor Education television commercial [24]
- India Innovation Award for Big Data Implementation
- ICICI Lombard & ET Now Risk Manager Award in BFSI Category [25]
- SKOCH Order of Merit for E-Boss for qualifying among India’s Best 2013 [26]
- SKOCH Financial Award 2013 [27]
- Financial Inclusion Awards – 2011 [28]
- Indian Merchant Chamber Award in the Large Enterprise Category for use of Information Technology [29]
- Best Managed Financial Derivatives Exchange in the Asia Pacific by The Asian Banker [30]
- The Golden Peacock Global CSR Award for its initiatives in Corporate Social Responsibility [31]
- BSE has won NASSCOM – CNBC-TV18’s IT User Awards, 2010 in Financial Services category [32]
- BSE has won Skoch Virtual Corporation 2010 Award in the BSE StAR MF category [33]
- Responsibility Award (CSR), by the World Council of Corporate Governance
- Annual Reports and Accounts of BSE have been awarded the ICAI awards for excellence in financial reporting for four consecutive years from 2006 onwards [34]
- Human Resource Management at BSE has won the Asia – Pacific HRM awards for its efforts in employer branding through talent management at work, health management at work and excellence in HR through technology [35]
- CIO of the Year- Financial Sector: Ashishkumar Chauhan, Dy Chief Executive Officer, Bombay Stock Exchange [36]
- The World Council of Corporate Governance has awarded the Golden Peacock Global CSR Award in financial sector for BSE's initiatives in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in 2007.[37]
See also
References
- ↑ "Bombay Stock Exchange Holidays". Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 17 August 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ↑ "BSE becomes world's fastest stock exchange: Ashishkumar Chauhan - The Economic Times". The Economic Times. Retrieved 2015-12-09.
- ↑ "Investors' wealth hits $2 trillion mark as Sensex rallies". Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ↑ "National economic debate - Stock markets or rigged casinos - talk by Professor Dr. R. Vaidyanathan (IIM Bangalore) - 21 Jan 2011, Mumbai". www.youtube.com. National Economic Debates.
- ↑ http://www.livemint.com/Sundayapp/R5BUHntOmItyIJ2yE4G09M/Premchand-Roychand-Mumbais-original-share-king.html. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Mishra, Ashish K. (2015-05-23). "Livemint: Business news, financial news, current affairs and analysis of stock markets and Indian economy". http://www.livemint.com/. Retrieved 2017-06-17. External link in
|work=(help) - ↑ "BSEIndia". BSEIndia. Archived from the original on 22 January 2014. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ↑ "Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) commits to promoting sustainability". UNCTAD. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ bsp;— tie up with Netmagic.com
- 22 February 2012 Launch of BSE-GREENEX to promote investments in Green India
- 13 March 2012 Launch of BSE — SME Exchange Platform
- 30 March 2012 BSE launched trading in BRICSMART indices derivatives
- 19 February 2013 – SENSEX becomes S&P SENSEX
- ↑ Vyas Mohan (19 February 2013). "Sensex to carry S&P tag". Livemint. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ↑ Our Bureau. "BSE trading from Hyderabad DR site". The Hindu Business Line.
- ↑ "BSE becomes world's fastest stock exchange: Ashishkumar Chauhan - The Economic Times". The Economic Times. Retrieved 2016-01-10.
- ↑ "Session Timings". www.bseindia.com. Retrieved 2017-05-12.
- ↑ "BSE-100 (BSE100) Live Financial Chart". Investing.com. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ↑ "BSEIndia". BSEIndia. Retrieved 26 August 2010.
- ↑ "BSE SENSEX Index Chart — Yahoo! Finance". Finance.yahoo.com. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ↑ "LIONS CSR Precious Awards to BSE Ltd. - LIONS CSR Precious Awards". Facebook. 2016-03-26. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "Skoch Achiever Award 2016 for Banks". Skoch.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "BSEIndia - BSE has been awarded PCQUEST Best IT...". Facebook. 2016-03-13. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "Review Summary" (PDF). Goldenpeacockawards.com. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "World HRD Congress". Worldhrdcongress.com. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "CHRO Asia". Chroasia.org. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "FICCI BAF AWARDS 2015 : Winners List" (PDF). Ficca-frames.com. Retrieved 2016-04-28.
- ↑ "ET-ICICI". Indiatimes.com. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "Skoch Renaissance Awards 2013". Skoch.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ Bhupendra. "Bombay Stock Exchange". Financialinclusion.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "Financial Inclusion - Awardees". Financialinclusion.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ ":: IMC IT Awards - Excellence Awards in IT ::". Imc-itawards.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "Australia Securities Exchange wins Best Managed Clearing House of the Year 2014" (PDF). Asainbankerawards.com. Retrieved 2016-04-28.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 10 November 2014. Retrieved 12 September 2014.
- ↑ "Winners - NASSCOM". Nasscom.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ Administrator. "Skoch Digital Inclusion Awards 2012". digitalinclusion.in. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ↑ "ICAI AWARDS FOR EXCELLENCE IN FINANCIAL REPORTING (2008-09)" (PDF). 220.227.161.86. Retrieved 2016-04-28.
- ↑ "Asia Pacific HRM Congress 2015". asiapacifichrmcongress.com.
- ↑ Administrator. "CIO of the Year- Financial Sector: Ashishkumar Chauhan, Dy Chief Executive Officer, Bombay Stock Exchange". digitalinclusion.in.
- ↑ "Golden Peak Awards for CSR". Goldenpeacockawards.com/. Golden Peak Awards. Archived from the original on 10 November 2014. Retrieved 12 September 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bombay Stock Exchange. |
Coordinates: 18°55′47″N 72°50′01″E / 18.929681°N 72.833589°E