Seismic wave
| Part of a series on |
| Earthquakes |
|---|
| Types |
|
|
| Causes |
| Characteristics |
|
|
| Measurement |
|
|
| Prediction |
| Other topics |
|
Earth Sciences Portal Category • Related topics |

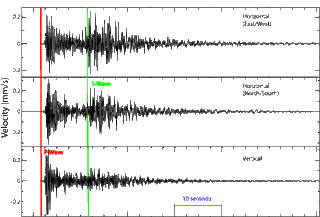
Seismic waves are waves of energy that travel through the Earth's layers, and are a result of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, magma movement, large landslides and large man-made explosions that give out low-frequency acoustic energy. Many other natural and anthropogenic sources create low-amplitude waves commonly referred to as ambient vibrations. Seismic waves are studied by geophysicists called seismologists. Seismic wave fields are recorded by a seismometer, hydrophone (in water), or accelerometer.
The propagation velocity of the waves depends on density and elasticity of the medium. Velocity tends to increase with depth and ranges from approximately 2 to 8 km/s in the Earth's crust, up to 13 km/s in the deep mantle.[2]
Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities; when reaching seismic observatories, their different travel times help scientists to locate the source of the hypocenter. In geophysics the refraction or reflection of seismic waves is used for research into the structure of the Earth's interior, and man-made vibrations are often generated to investigate shallow, subsurface structures.
Types
Among the many types of seismic waves, one can make a broad distinction between body waves, which travel through the Earth, and surface waves, which travel at the Earth's surface.[2]:48–50[3]:56–57
Other modes of wave propagation exist than those described in this article; though of comparatively minor importance for earth-borne waves, they are important in the case of asteroseismology.
- Body waves travel through the interior of the Earth.
- Surface waves travel across the surface. Surface waves decay more slowly with distance than body waves, which travel in three dimensions.
- Particle motion of surface waves is larger than that of body waves, so surface waves tend to cause more damage.
Body waves
Body waves travel through the interior of the Earth along paths controlled by the material properties in terms of density and modulus (stiffness). The density and modulus, in turn, vary according to temperature, composition, and material phase. This effect resembles the refraction of light waves. Two types of particle motion result in two types of body waves: Primary and Secondary waves.
Primary waves
Primary waves (P-waves) are compressional waves that are longitudinal in nature. P waves are pressure waves that travel faster than other waves through the earth to arrive at seismograph stations first, hence the name "Primary". These waves can travel through any type of material, including fluids, and can travel at nearly twice the speed of S waves. In air, they take the form of sound waves, hence they travel at the speed of sound. Typical speeds are 330 m/s in air, 1450 m/s in water and about 5000 m/s in granite.
Secondary waves
Secondary waves (S-waves) are shear waves that are transverse in nature. Following an earthquake event, S-waves arrive at seismograph stations after the faster-moving P-waves and displace the ground perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Depending on the propagational direction, the wave can take on different surface characteristics; for example, in the case of horizontally polarized S waves, the ground moves alternately to one side and then the other. S-waves can travel only through solids, as fluids (liquids and gases) do not support shear stresses. S-waves are slower than P-waves, and speeds are typically around 60% of that of P-waves in any given material.
Surface waves
Seismic surface waves travel along the Earth's surface. They can be classified as a form of mechanical surface waves. They are called surface waves, as they diminish as they get further from the surface. They travel more slowly than seismic body waves (P and S). In large earthquakes, surface waves can have an amplitude of several centimeters.[4]
Rayleigh waves
Rayleigh waves, also called ground roll, are surface waves that travel as ripples with motions that are similar to those of waves on the surface of water (note, however, that the associated particle motion at shallow depths is retrograde, and that the restoring force in Rayleigh and in other seismic waves is elastic, not gravitational as for water waves). The existence of these waves was predicted by John William Strutt, Lord Rayleigh, in 1885. They are slower than body waves, roughly 90% of the velocity of S waves for typical homogeneous elastic media. In the layered medium (like the crust and upper mantle) the velocity of the Rayleigh waves depends on their frequency and wavelength. See also Lamb waves.
Love waves
Love waves are horizontally polarized shear waves (SH waves), existing only in the presence of a semi-infinite medium overlain by an upper layer of finite thickness.[5] They are named after A.E.H. Love, a British mathematician who created a mathematical model of the waves in 1911. They usually travel slightly faster than Rayleigh waves, about 90% of the S wave velocity, and have the largest amplitude.
Stoneley waves
A Stoneley wave is a type of boundary wave (or interface wave) that propagates along a solid-fluid boundary or, under specific conditions, also along a solid-solid boundary. Amplitudes of Stoneley waves have their maximum values at the boundary between the two contacting media and decay exponentially towards the depth of each of them. These waves can be generated along the walls of a fluid-filled borehole, being an important source of coherent noise in VSPs and making up the low frequency component of the source in sonic logging.[6] The equation for Stoneley waves was first given by Dr. Robert Stoneley (1894–1976), Emeritus Professor of Seismology, Cambridge.[7]
Free oscillations of the Earth


Free oscillations of the Earth are standing waves, the result of interference between two surface waves traveling in opposite directions. Interference of Rayleigh waves results in spheroidal oscillation S while interference of Love waves gives toroidal oscillation T. The modes of oscillations are specified by three numbers, e.g., nSlm, where l is the angular order number (or spherical harmonic degree, see Spherical harmonics for more details). The number m is the azimuthal order number. It may take on 2l+1 values from -l to +l. The number n is the radial order number. It means the wave with n zero crossings in radius. For spherically symmetric Earth the period for given n and l does not depend on m.
Some examples of spheroidal oscillations are the "breathing" mode 0S0, which involves an expansion and contraction of the whole Earth, and has a period of about 20 minutes; and the "rugby" mode 0S2, which involves expansions along two alternating directions, and has a period of about 54 minutes. The mode 0S1 does not exist because it would require a change in the center of gravity, which would require an external force.[2]
Of the fundamental toroidal modes, 0T1 represents changes in Earth's rotation rate; although this occurs, it is much too slow to be useful in seismology. The mode 0T2 describes a twisting of the northern and southern hemispheres relative to each other; it has a period of about 44 minutes.[2]
The first observations of free oscillations of the Earth were done during the great 1960 earthquake in Chile. Presently periods of thousands modes are known. These data are used for determining some large scale structures of the Earth interior.
P and S waves in Earth's mantle and core
When an earthquake occurs, seismographs near the epicenter are able to record both P and S waves, but those at a greater distance no longer detect the high frequencies of the first S wave. Since shear waves cannot pass through liquids, this phenomenon was original evidence for the now well-established observation that the Earth has a liquid outer core, as demonstrated by Richard Dixon Oldham. This kind of observation has also been used to argue, by seismic testing, that the Moon has a solid core, although recent geodetic studies suggest the core is still molten.
Notation

The path that a wave takes between the focus and the observation point is often drawn as a ray diagram. An example of this is shown in a figure above. When reflections are taken into account there are an infinite number of paths that a wave can take. Each path is denoted by a set of letters that describe the trajectory and phase through the Earth. In general an upper case denotes a transmitted wave and a lower case denotes a reflected wave. The two exceptions to this seem to be "g" and "n".[8]
| c | the wave reflects off the outer core |
| d | a wave that has been reflected off a discontinuity at depth d |
| g | a wave that only travels through the crust |
| i | a wave that reflects off the inner core |
| I | a P-wave in the inner core |
| h | a reflection off a discontinuity in the inner core |
| J | an S wave in the inner core |
| K | a P-wave in the outer core |
| L | a Love wave sometimes called LT-Wave (Both caps, while an Lt is different) |
| n | a wave that travels along the boundary between the crust and mantle |
| P | a P wave in the mantle |
| p | a P wave ascending to the surface from the focus |
| R | a Rayleigh wave |
| S | an S wave in the mantle |
| s | an S wave ascending to the surface from the focus |
| w | the wave reflects off the bottom of the ocean |
| No letter is used when the wave reflects off of the surfaces |
For example:
- ScP is a wave that begins traveling towards the center of the Earth as an S wave. Upon reaching the outer core the wave reflects as a P wave.
- sPKIKP is a wave path that begins traveling towards the surface as an S-wave. At the surface it reflects as a P-wave. The P-wave then travels through the outer core, the inner core, the outer core, and the mantle.
Usefulness of P and S waves in locating an event

In the case of local or nearby earthquakes, the difference in the arrival times of the P and S waves can be used to determine the distance to the event. In the case of earthquakes that have occurred at global distances, three or more geographically diverse observing stations (using a common clock) recording P-wave arrivals permits the computation of a unique time and location on the planet for the event. Typically, dozens or even hundreds of P-wave arrivals are used to calculate hypocenters. The misfit generated by a hypocenter calculation is known as "the residual". Residuals of 0.5 second or less are typical for distant events, residuals of 0.1–0.2 s typical for local events, meaning most reported P arrivals fit the computed hypocenter that well. Typically a location program will start by assuming the event occurred at a depth of about 33 km; then it minimizes the residual by adjusting depth. Most events occur at depths shallower than about 40 km, but some occur as deep as 700 km.

A quick way to determine the distance from a location to the origin of a seismic wave less than 200 km away is to take the difference in arrival time of the P wave and the S wave in seconds and multiply by 8 kilometers per second. Modern seismic arrays use more complicated earthquake location techniques.
At teleseismic distances, the first arriving P waves have necessarily travelled deep into the mantle, and perhaps have even refracted into the outer core of the planet, before travelling back up to the Earth's surface where the seismographic stations are located. The waves travel more quickly than if they had traveled in a straight line from the earthquake. This is due to the appreciably increased velocities within the planet, and is termed Huygens' Principle. Density in the planet increases with depth, which would slow the waves, but the modulus of the rock increases much more, so deeper means faster. Therefore, a longer route can take a shorter time.
The travel time must be calculated very accurately in order to compute a precise hypocenter. Since P waves move at many kilometers per second, being off on travel-time calculation by even a half second can mean an error of many kilometers in terms of distance. In practice, P arrivals from many stations are used and the errors cancel out, so the computed epicenter is likely to be quite accurate, on the order of 10–50 km or so around the world. Dense arrays of nearby sensors such as those that exist in California can provide accuracy of roughly a kilometer, and much greater accuracy is possible when timing is measured directly by cross-correlation of seismogram waveforms.
See also
References
- ↑ G. R. Helffrich & B. J. Wood (2002). "The Earth's mantle" (PDF). Nature. Macmillan Magazines. 412 (2 August): 501; Figure 1. doi:10.1038/35087500. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 August 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Peter M. Shearer (2009). Introduction to Seismology. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88210-1. (Also see errata)
- ↑ Seth Stein; Michael Wysession (1 April 2009). An Introduction to Seismology, Earthquakes, and Earth Structure. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-14443-1131-0.
- ↑ Sammis CG, Henyey TL. Geophysics Field Measurements, page 12. Academic Press; 1987
- ↑ Sheriff, R. E., Geldart, L. P. (1995). Exploration Seismology (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 52. ISBN 0-521-46826-4.
- ↑ Schlumberger Oilfield Glossary. Stoneley wave.
- ↑ Robert Stoneley, 1929 – 2008.. Obituary of his son with reference to discovery of Stoneley waves.
- ↑ The notation is taken from Bullen, K.E.; Bolt, Bruce A. (1985). An introduction to the theory of seismology (4th ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521283892. and Lee, William H.K.; Jennings, Paul; Kisslinger, Carl; et al., eds. (2002). International handbook of earthquake and engineering seismology. Amsterdam: Academic Press. ISBN 9780080489223.
External links
| The Wikibook Historical Geology has a page on the topic of: Seismic waves |