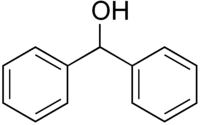
Diphenylmethanol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diphenylmethanol | |
| Other names
Benzhydrol Diphenylcarbinol Hydroxydiphenylmethane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.849 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H12O | |
| Molar mass | 184.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Density | 1.103 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 69 °C (156 °F; 342 K) |
| Boiling point | 298 °C (568 °F; 571 K) |
| 0.5 g/L (20 °C) | |
| -119.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36 R37 R38 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S27 S28 S29 S30 S33 S35 S36 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Benzophenone |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diphenylmethanol, (C6H5)2CHOH (also known as benzhydrol), is a secondary alcohol with a relative molecular mass of 184.23 g/mol. It has a melting point of 69 °C and a boiling point of 298 °C.
It has uses in perfume and pharmaceutical manufacture. In perfumery it is used as a fixative. In pharmaceutical manufacture it is used in the synthesis of antihistamines / antiallergenic agents and antihypertensive agents . It is used in the synthesis of Modafinil[2] and the Benzhydryl group is present in the structure of many histamine H1 antagonists like diphenylhydramine. Benzhydrol is also used in the production of agrochemicals as well as other organic compounds and as a terminating group in polymerizations.
Diphenylmethanol is an irritant to the eyes, skin and respiratory system.
Preparation
Diphenylmethanol may be prepared by a Grignard reaction between phenylmagnesium bromide and benzaldehyde, or by reducing benzophenone, with sodium borohydride or with zinc dust or with sodium amalgam and water.[3]
References
- ↑ MSDS
- ↑ EP 1583739
- ↑ F. Y. Wiselogle and H. Sonneborn, III (1941). "Benzohydrol". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 1, p. 90