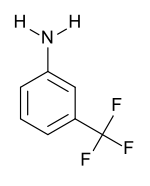
3-(Trifluoromethyl)aniline
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline | |
| Other names
3-Aminobenzotrifluoride; m-ABTF; m-Trifluoromethylaniline, 3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.404 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6F3N | |
| Molar mass | 161.12 g/mol |
| Density | 1.305 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 5 to 6 °C (41 to 43 °F; 278 to 279 K) |
| Boiling point | 187 to 188 °C (369 to 370 °F; 460 to 461 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3-(Trifluoromethyl)aniline is a compound with the molecular formula CF3C6H4NH2. It is an aromatic amine.
Drugs
3-(Trifluoromethyl)aniline is used in the production of:
- the herbicide fluometuron.[1] It is synthesized from benzotrifluoride via nitration followed by reduction to meta-H2NC6H4CF3. 3-(Trifluoromethyl)aniline is then converted to the urea, fluometuron.
- Flufenamic acid
- Morniflumate
- Ufenamate
- Flubanilate
- Salfluverine
- Colfenamate
References
- ↑ Siegemund, Günter "Aromatic Compounds with Fluorinated Side-Chains" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_349.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.