Belgium national football team
 | |||
| Nickname(s) |
De Rode Duivels Les Diables Rouges Die Roten Teufel (The Red Devils) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Association | Royal Belgian Football Association (KBVB/URBSFA/KBFV)[upper-alpha 1] | ||
| Confederation | UEFA (Europe) | ||
| Head coach | Roberto Martínez | ||
| Captain | Eden Hazard | ||
| Most caps | Jan Ceulemans (96) | ||
| Top scorer |
Bernard Voorhoof, Paul Van Himst (30) | ||
| Home stadium | King Baudouin Stadium | ||
| FIFA code | BEL | ||
| |||
| FIFA ranking | |||
| Current |
10 | ||
| Highest | 1 (November 2015 – March 2016[2]) | ||
| Lowest | 71 (June 2007[2]) | ||
| Elo ranking | |||
| Current |
12 | ||
| Highest | 2 (September 1920[4]) | ||
| Lowest | 74 (September 2009[4]) | ||
| First international | |||
|
(Uccle, Belgium; 1 May 1904) | |||
| Biggest win | |||
|
(Brussels, Belgium; 4 June 1994) (Brussels, Belgium; 28 February 2001) | |||
| Biggest defeat | |||
|
(London, England; 17 April 1909)[upper-alpha 2] | |||
| World Cup | |||
| Appearances | 12 (first in 1930) | ||
| Best result | Fourth place, 1986 | ||
| European Championship | |||
| Appearances | 5 (first in 1972) | ||
| Best result | Runners-up, 1980 | ||
Medal record
| |||
The Belgian national football team has officially represented Belgium in association football since their maiden match in 1904. The squad is under the global jurisdiction of FIFA and is governed in Europe by UEFA—both of which were co-founded by the Belgian team's supervising body, the Royal Belgian Football Association (RBFA). Periods of regular Belgian representation at the highest international level, from 1920 to 1938 and from 1970 to 2002, have alternated with mostly unsuccessful qualification rounds. Most of Belgium's home games are played at the King Baudouin Stadium in Brussels.
Belgium's national team has participated in three quadrennial major football competitions. It appeared in the end stages of twelve FIFA World Cups and five UEFA European Football Championships, and featured at three Olympic football tournaments, including the 1920 Olympic tournament which they won. Other notable performances are victories over four reigning world champions—West Germany, Brazil, Argentina and France—between 1954 and 2002. Belgium has long-standing football rivalries with its Dutch and French counterparts, having played both teams nearly every year from 1905 to 1967. The squad has been known as the Red Devils since 1906; its fan club is named "1895".
During the national player career of forward Paul Van Himst, the most-praised Belgian footballer of the 20th century, Belgium took third place at Euro 1972. After that, they experienced two golden ages with many gifted players. In the first period, which lasted from the 1980s to the early 1990s, the team finished as runners-up at Euro 1980 and fourth in the 1986 World Cup. In the second, under guidance of Marc Wilmots in the 2010s, Belgium topped the FIFA World Rankings for the first time in November 2015. Between September 2016 and October 2017, they are competing in the European qualifiers for the 2018 World Cup.
History
Belgium was one of the first mainland European countries to play association football.[6] Its practice in Belgium began on 26 October 1863, after an Irish student walked into the Josephites College of Melle with a leather ball.[7] Initially an elitist pastime,[8] during the following decades association football supplanted rugby as Belgium's most popular football sport.[9] On 1 September 1895, ten clubs for football, athletics, cricket and cycling founded the Belgian sports board Union Belge des Sociétés de Sports Athlétiques (UBSSA);[9][10] a year later UBSSA organised the first annual league in Belgian football.[9]

On 11 October 1900, Beerschot AC honorary president Jorge Díaz announced that Antwerp would host a series of challenge matches between Europe's best football teams.[11] After some organisational problems, on 28 April 1901, Beerschot's pitch hosted its first tournament, in which a Belgian A-squad and a Dutch B-team contested the Coupe Vanden Abeele.[12][13] Belgium won,[14] and beat the Netherlands in all three follow-up games;[15] FIFA does not recognise these results because Belgium fielded some English players.[15] On 1 May 1904, the Belgians played their first official game, against France at the Stade du Vivier d'Oie in Uccle; their draw left the Évence Coppée Trophy unclaimed.[16] Twenty days later, the football boards of both countries were among the seven FIFA founders.[17][18] At that time, the Belgian squad was chosen by a committee drawn from the country's six or seven major clubs.[19] In 1906, the national team players received the nickname Red Devils because of their red jerseys,[20] and four years later, Scottish ex-footballer William Maxwell replaced the UBSSA committee as their manager.[21] From 1912, UBSSA governed football only and was renamed UBSFA.[upper-alpha 3][1][9] During the Great War, the national team only played unrecognised friendlies, with games in and against France.[22][23]
At the 1920 Summer Olympics, in their first official Olympic appearance, the Red Devils won the gold medal on home soil after a controversial final in which their Czechoslovak opponents left the pitch.[24] This triumph led them to an all-time high second place in the World Football Elo Ratings.[4] In the three 1920s Summer Olympics, they achieved fair results (four wins in seven games), and played their first intercontinental match, against Argentina.[22] Over the following decade, however, Belgium lost all of their matches at the first three FIFA World Cup final tournaments.[22] According to historian Richard Henshaw, "The growth of [football] in Scandinavia, Central Europe, and South America left Belgium far behind".[25] Although World War II hindered international football events in the 1940s, the Belgian team remained active with unofficial matches against squads of other allied nations.[26]
%2C_penalty_Copp%C3%A9e.jpg)
Belgium qualified for only one of eight major tournaments during the 1950s and the 1960s: the 1954 World Cup. The day before the tournament began, the RBFA was among the three UEFA founders.[27] Dutch journalists considered the draw of the 1954 Belgian team in their opener against England to be the most surprising result of that match day, even more than Switzerland's victory over the Italian "football stars".[28] However, Belgium were eliminated after a loss to Italy in the second (and last) group match.[29] Two bright spots in these decades were wins against World Cup holders: West Germany in 1954, and Brazil in 1963.[22] Between these, Belgium defeated Hungary's Golden Team in 1956.[22] The combination of failure in competitive games, and success in exhibition matches, gave the Belgians the mock title of "world champion of the friendlies".[30][31]
The team's performance improved during the early 1970s, under manager Raymond Goethals. Fully dressed in white, as the White Devils,[32] Belgium had their first victories at World and European Championships at the 1970 World Cup and Euro 1972.[33][34] En route to that Euro appearance, their first, they eliminated reigning European champions Italy by winning the two-legged play-offs on aggregate. At the end stage, they finished third by winning the consolation match against Hungary.[34] In 1973, the denial of a match-winning goal in their last 1974 FIFA World Cup qualification game for UEFA Group 3 cost Belgium their appearance at the finals,[35] causing Belgium to become the only nation ever to miss a World Cup final round despite not allowing a goal during the qualifiers.[36] The next two attempts to reach a major finals were also fruitless.[37][38]
Beginning with a second-place finish at Euro 1980,[39] the 1980s and the early 1990s are generally considered as Belgium's first golden age.[40] Coached by Guy Thys, they achieved their spot in the 1980 final with an unbeaten record in the group phase; in the final, they narrowly lost the title to West Germany with the score 1–2.[39] Starting with the 1982 World Cup, and ending with the 2002 World Cup, the national team qualified for six consecutive World Cup end stages and mostly progressed to the second round.[41] During this period, managers Guy Thys, Paul Van Himst and Robert Waseige each guided a Belgian selection past the first round.[42][43][44] In addition to receiving individual FIFA recognitions,[45][46] the team reached the semi-finals of the 1986 World Cup.[47] After reaching the Euro 1980 final, they were unsuccessful at subsequent European Championships, with early exits from their appearances at Euro 1984 and Euro 2000.[48][49] During the late 1990s, they played three friendly tournaments in Morocco, Cyprus and Japan,[50][51] sharing the 1999 Kirin Cup with Peru in the latter.[52] The greatest talents of the Belgian team during this golden age were retired from international football by 2000,[53] yet in 2002, Belgium defeated reigning world and European champions France,[22] and reached the World Cup round of 16.[44]
After the 2002 World Cup, the team weakened with the loss of more veterans and coach Waseige.[54][55] They missed out five successive major finals from Euro 2004 until Euro 2012, and went through an equal number of head coaches.[56] A 2005 win over reigning European champions Greece meant nothing but a small comfort.[22] In between, a promising new generation was maturing at the 2007 European U-21 Championship; Belgium's squad qualified for the following year's Summer Olympics in Beijing,[57] where the Young Red Devils squad finished fourth.[58] Seventeen of them appeared in the senior national team,[53] albeit without making an immediate impact. Belgium finished in second (and last) place at the Kirin Cup in May 2009,[59] and lost against the 125th FIFA-ranked Armenian team in September 2009.[2] After Georges Leekens' second stint as national manager,[60][61] his assistant Marc Wilmots became the caretaker in May 2012.[62]
After two matches as interim coach, Wilmots agreed to replace Leekens as manager.[63] Following his appointment, the team's results improved,[64] such that some foreign media regarded it as another Belgian golden generation.[65][66][67] The young Belgian squad qualified as unbeaten group winners for the 2014 World Cup finals,[68] and earned Belgium's second-ever place in a World Cup quarter-finals with a four-game winning streak.[69] Belgium qualified for Euro 2016 with a match to spare in October 2015,[70] and took the top spot in the FIFA World Rankings for the first time in November 2015,[71] to stay first for five months.[2][72] In the following year, Belgium could not confirm their role as outsider at the European Championship with a quarter-final elimination by the 26th FIFA-ranked Welsh team;[2][73] this prompted the RBFA to dismiss Wilmots.[74] In the 2018 World Cup qualifying allocation, they were seeded first in their group.[75][76]
Kit


In home matches, the team's outfield players traditionally wear the colours of the Belgian flag: black, yellow and red.[77][78][79] Red dominates the strip and is often the sole jersey colour.[78][79] The away colours are usually white, black or both;[80] in 2014, the squad introduced a third, yellow kit.[81] Their shirts are often trimmed with tricolores at the margins.[79][82] Since 1981, the RBFA emblem has been the national team's badge;[79][83] the previous badge was a yellow lion on a black shield,[78][79] similar to the escutcheon of the national coat of arms.[84]
For their first unofficial match in 1901, the Belgian team wore white jerseys with tricoloured bands on the upper arms.[12] Around their third unofficial game in 1902, the choice was made for a "shirt with national colours ... [that would indicate,] with a stripe, the number of times every player has participated in an encounter".[14] Since 1904, Belgium's classic all-red jersey design has been altered twice. In 1904–05, the squad briefly wore satin shirts with three horizontal bands in red, yellow and black; according to sports journalist Victor Boin, the shirts set "the ugliness record".[19] During the 1970s, manager Raymond Goethals chose an all-white combination to improve the team's visibility during evening matches.[32][85]
Six clothing manufacturers have supplied the official team strip. Since 2014, it has been produced by Adidas,[86] who was also the supplier from 1974 to 1980, and from 1982 to 1991.[87] Former kit manufacturers are Umbro (early 1970s),[85][87] Admiral (1981–1982),[upper-alpha 4][87] Diadora (1992–1999),[87] Nike (1999–2010) and BURRDA (2010–2014).[upper-alpha 5][87][89]
Home stadium

Numerous former and current venues in 11 urban areas have hosted Belgium's home games.[22] Most of these matches have been played in Brussels at the Heysel Plateau, on the site of the present-day King Baudouin Stadium—a multipurpose facility with a seating capacity of 50,122.[90] Its field also hosts the team's final trainings before domestic games. Since 2007, most physical preparation takes place at the National Football Centre in Tubize,[91] or at Anderlecht's training ground in the Neerpede quarter.[92][93] Apart from Belgian home friendlies, at the international level Belgium's national stadium has also hosted six European Championship games.[94][95]
In 1930, for the country's centennial, the venue was inaugurated as the Jubilee Stadium with an unofficial match between Belgium and the Netherlands.[96] At that time, the stadium had a capacity of 75,000.[97] In 1946, it was renamed Heysel Stadium after its city quarter. This new name became associated with the tragedy preceding the 1985 European Cup final between Juventus and Liverpool; 39 spectators died after riots in the then antiquated building.[98][99] Three years after the disaster, plans were unveiled for a renovation;[100] in 1995, after two years of work, the modernised stadium was named after the late King Baudouin.[101] In May 2013, the Brussels-Capital Region announced that the King Baudouin Stadium would be replaced by Eurostadium, elsewhere on the Heysel Plateau;[102] two years later, a 2019 date was set for the stadium's completion.[103]
Team image
Media coverage

The first live coverage of a Belgian sporting event occurred on 3 May 1931, when journalist Gust De Muynck commentated on the football game between Belgium and the Netherlands on radio.[104] Later, football broadcasts were also televised. As 60 per cent of Belgians speak Dutch and 40 per cent French,[105] commentaries for the national team matches are provided in both languages. The games are not broadcast in German—Belgium's third official language.[105] During Belgium's tournament appearances in the 1980s and the early 1990s, Rik De Saedeleer crowned himself the nation's most famous football commentator with his emotional and humorous reports.[106]
Initially the matches were transmitted mainly on public television channels: the former BRTN in Dutch, and the RTBF in French. Since 1994, commercial channels such as vtm and its sister channel Kanaal 2, and VIER in Flanders, have purchased broadcasting rights.[1] As of November 2016, the Euro 2016 round-of-16 match against Hungary was the most-watched programme in Belgian television history, with an audience of over four million viewers out of 11.3 million Belgian citizens.[105][107][108]
In April 2014, the VRT started transmitting a nine-piece, behind-the-scenes documentary about the national team filmed during the 2014 World Cup qualifiers, titled Iedereen Duivel (Everybody Devil).[109] Cable broadband provider Telenet broadcast an eight-part documentary about individual players titled Rode Helden (Red Heroes).[110]
Side activities

Multiple events were organised for the fans during the squad's peak popularity in the 2010s. During the 2014 World Cup qualifiers, a string of interactive events called the Devil Challenges were organised.[111] The premise was that small groups of international players would do a favour in return for each of the five comprehensive chores their supporters completed ("colour Belgium red", "gather 500,000 decibels", etc.), all of which were accomplished.[112] In June 2013, the Belgian national team's first ever Fan Day attracted over 20,000 supporters;[113] a second was held after the 2014 World Cup.[114] On the days of Belgium's 2014 World Cup group matches, large dance events titled Dance with the Devils took place in three Belgian cities.[115] This type of happening was repeated during Belgium's Euro 2016 group matches.[116]
Occasionally, the Belgian team directly supported charity. Between 1914 and 1941 they played at minimum five unofficial games of which the returns were for charitable purposes: two against France,[23][117] and three against the Netherlands.[96][118] In mid-1986, when the Belgian delegation reached the Mexico World Cup semi-finals, the squad started a project titled Casa Hogar, an idea of delegation leader Michel D'Hooghe.[119] Casa Hogar is a home for street children in the Mexican industrial city of Toluca, to which the footballers donated part of their tournament bonuses.[120] In August 2013, the national team supported four social projects through the charity fund Football+ Foundation, by playing an A-match with a plus sign on the shoulders of their jerseys and auctioning the shirts.[121]
In 2002, the national squad held its first anti-racism campaign in which they posed with slogans.[122] A home Euro 2012 qualifier was given the theme of respect for diversity in 2010; this UEFA-supported action was part of the European FARE Action Week.[123] Ex-Red Devil Dimitri Mbuyu—the first black Belgium player (in 1987)[53][124]—was engaged as godfather, and other foreign, current, and former footballers who played in the Belgian top division participated.[125]
Nickname and logo
After a 1905 match, a Dutch reporter wrote that three Belgian footballers "work[ed] as devils".[126] A year later Léopold FC manager Pierre Walckiers nicknamed the players Red Devils, inspired by their jersey colour, and the achievement of three successive victories in 1906.[20][22] Because of their white home shirts in the 1970s, they were temporarily known as the White Devils.[32] Since 2012, the team logo is a red trident (or three-pronged pitchfork),[127] an item that is often associated with the devil.[128] Before that, the national squad had three official anthropomorphous mascots. The first was a lion in team kit named Diabolix,[129] a reference to the central symbol in the Belgian coat of arms that appeared on the team jerseys from 1905 to 1980.[79][130] In accordance with their epithet, the next mascots were a red super-devil and a fan-made modern devil.[129]
Supporters
—Historian Richard Henshaw, 1979[9]
Fans of the Belgian national team display the country's tricolour national flag, usually with an emphasis on the red element. In 2012, local supporter clubs merged into one large Belgian federation named "1895" after the foundation year of the RBFA. One year later, 1895 had 24,000 members.[131] The nationwide interest in the football squad has also been reflected by the occasional presence of Belgian monarchs at their matches since 1914.[132][133][134] One of the greatest moments for the Belgian team and their 12th man was in mid-1986 when the Belgian delegation at the Mexico World Cup received a warm "welcome home". When the World Cup semi-finalists appeared on the balcony of Brussels Town Hall, the adjoining Grand Place square was filled with an ecstatic crowd that cheered as though their squad had won a major tournament.[135]

The team's deterioration after the 2002 World Cup lead to their absence from the end stages of the next five major tournaments, and strained their popularity. Between 2004 and 2010, local journalists called the Belgian footballing nation "mortally ill".[136][137] Some fans continued to support their squad in bad times. Ludo Rollenberg was one of the most loyal fans attending the team's games worldwide since 1990, missing only the Japanese Kirin Cup in 1999, and two other matches by 2006.[138] He was the only supporter to attend their game in Armenia in 2009.[139]
Just before the kick-off of a 2014 World Cup home qualifier, Belgium's footballers saw a first tifo banner, sized 10.5 by 11.5 metres (34 by 38 ft) depicting a devil in the national colours.[140] The presence of many Belgian players in top leagues abroad, such as the Premier League,[141] and promising results under Marc Wilmots, increased fans' enthusiasm and belief in a successful World Cup campaign.[113][142] Because of this popularity peak, two Belgian monuments were decorated in national colours for the 2014 FIFA World Cup event; the Manneken Pis statue received a child-sized version of the new Belgian uniform,[143] and facets of the Atomium's upper sphere were covered in black, yellow and red vinyl.[144]
Rivalries
.jpg)
Belgium's main football rivals are its neighbours the Netherlands and France, with which it shares close cultural and political relations.[145][146] The matchup between the Belgian and Dutch team is known as the Low Countries derby;[96] as of November 2016 they have played each other in 126 official games.[147] The clash between the Belgian and French sides is nicknamed le Match Sympathique in French ("the Friendly Match");[148] they have contested 73 official games as of November 2016.[147]
Belgium won the first four—unofficial—matches against the Netherlands,[14] but lost their first FIFA-recognised contest.[22] The two national teams played each other biannually between 1905 and 1964, except during the World Wars.[22] They have met 18 times in major tournament campaigns, and have played at least 35 friendly cup matches: in Belgium for the Coupe Vanden Abeele, and in the Netherlands for the Rotterdamsch Nieuwsblad-Beker.[13][126] The overall balance favours the Netherlands, with 55 wins against 41 Belgian victories.[147] The Low Countries' squads co-operated in fundraising initiatives between 1925 and 1941; they played five unofficial games for charity, FIFA and the Belgian Olympic Committee.[96][118][149]
The first match between Belgium and France, the Évence Coppée Trophy played in 1904, was the first official game for both teams and the first official football match between independent countries on the European continent.[150] Until 1967, the sides met almost annually.[22] As of November 2016, France has played most often against Belgium in international football.[147] Belgium have the better record, with 30 wins to France's 24.[147]
Management
.jpg)
Since 1904, the RBFA, 24 permanent managers and two caretaker managers have officially been in charge of the national team;[upper-alpha 6][21][56] this includes one national footballer selector.[21] As of November 2016, a crew of over 20 RBFA employees guides the player group,[153] including their Spanish manager Roberto Martínez, his assistants Graeme Jones and Thierry Henry, and goalkeeping coaches Erwin Lemmens and Iñaki Bergara.[154][155] As of 28 March 2017, Marc Wilmots is statistically the best performing Belgium manager with an average of 2.18 points per match.[upper-alpha 7] Under him, Belgium reached the top FIFA ranking spot in 2015, which earned him the title of Best Coach of the Year at the 2015 Globe Soccer Awards.[156] Under Guy Thys, the squad achieved record results at World and European championships; World Soccer magazine accordingly proclaimed him Manager of the Year in 1986.[157]
Rather than developing innovative team formations or styles of play, Belgium's managers applied conventional tactics. At the three 1930s World Cups, the Red Devils were aligned in a contemporary 2–3–5 "pyramid".[158][159][160] In 1954, Doug Livingstone's squad played in a 3–2–5 "WM" arrangement during World Cup matches.[29] Throughout most of their tournament games in the 1970s, the 1980s and the 1990s, the team played in a 4–4–2 formation.[33][42][43] Since Raymond Goethals' stint in the 1970s, a key strength of the Belgian squad has been their systematic use of the offside trap,[161] a defensive tactic that was already intensively applied in the 1960s by Anderlecht coach Pierre Sinibaldi.[162] According to football journalist Wim De Bock, "master tactician" Goethals represented the "conservative, defensive football of the Belgian national team"; he added that in the 1970s, the contrast between the Belgian playing style and the Total Football of their Dutch rivals "could not be bigger".[163]
In an attempt to win a game at the 1998 World Cup, Georges Leekens chose a 4–3–3 arrangement for Belgium's second and third group matches.[164] Robert Waseige, Belgium coach around 2000, said that "above all, [his] 4–4–2 system [was] holy", in the sense that he left good attackers on the bench to keep his favourite formation.[165] Wilmots opted for the 4–3–3 line-up again,[166] with the intention of showing dominant football against any country.[167]
Players
Current squad
The following 26 players were convocated for the unofficial friendly match against Czech Republic and the 2018 World Cup qualifier against Estonia, on 5 and 9 June 2017 respectively, and were able to play.[168][169] Note that the RBFA lists all wingers as forwards.
Caps, goals and player numbers are correct as of 9 June 2017 after the game against Estonia;[170] only FIFA-recognised matches are included.[upper-alpha 8]
Recent call-ups
The following footballers were part of a national selection in the past 12 months,[173][174] but are not part of the current squad.
| Pos. | Player | Date of birth (age) | Caps | Goals | Club | Latest call-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF | Thomas Meunier INJ | 12 September 1991 | 15 | 1 | v. | |
| DF | Timmy Simons | 11 December 1976 | 94 | 6 | v. | |
| DF | Luis Pedro Cavanda | 2 January 1991 | 2 | 0 | v. | |
| DF | Christian Kabasele INJ | 24 February 1991 | 1 | 0 | v. | |
| DF | Nicolas Lombaerts | 20 March 1985 | 38 | 3 | v. | |
| DF | Sébastien Pocognoli | 1 August 1987 | 13 | 0 | v. | |
| DF | Jordan Lukaku | 25 July 1994 | 7 | 0 | v. | |
| MF | Moussa Dembélé INJ | 16 July 1987 | 68 | 5 | v. | |
| MF | Steven Defour | 15 April 1988 | 49 | 2 | v. | |
| FW | Eden Hazard INJ (captain) | 7 January 1991 | 76 | 17 | v. | |
- Notes
- INJ = Not part of the current squad due to injury
- WD = Withdrew from this squad due to injury
- PRE = Preliminary squad / standby
Notable

Between 1904 and 1980, mainly attacking Belgium players were recognised as talented footballers. In the team's first decade, striker Robert De Veen was very productive with 26 goals in 23 international appearances.[177] Richard Henshaw described Alphonse Six as "Belgium's greatest player in the prewar period ... [who] was often called the most skillful forward outside Great Britain".[25] The key player of the victorious 1920 Olympic squad was Robert Coppée, who scored a hat-trick against Spain's Ricardo Zamora,[178] and the penalty in the final.[179] Other outstanding Belgian strikers in the interwar period were top scorer Bernard Voorhoof and "Belgium's football grandmaster" Raymond Braine,[53][180] considered "one of the greatest players of the era".[181]
Gifted players in the 1940s and the 1950s included centre-back Louis Carré and attackers Jef Mermans, Pol Anoul and Rik Coppens;[25] at the 1954 World Cup, Anoul shone with three goals,[29] and newspaper L'Équipe named Coppens the event's best centre forward.[182] The 1960s and the early 1970s were the glory days of forward and four-time Belgian Golden Shoe Paul Van Himst,[183] later elected Belgian UEFA Golden Player of 1954–2003 and Belgium's Player of the Century by IFFHS.[184][185] At the 1965 Ballon d'Or, Van Himst ranked fourth, achieving Belgium's highest ever position at the European football election.[186] Decades after Coppens and Van Himst had retired from playing football, a journalist on a Flemish television show asked them "Who [from both of you] was the best, actually?". Coppens replied: "I will ask Paul that ... If Paul says it was me, then he's right".[187] In 1966, striker Raoul Lambert and defending midfielder Wilfried Van Moer joined the national team;[53] while the UEFA praised Lambert for his skills at Euro 1972,[188] Van Moer won three Golden Shoes and equalled Van Himst's fourth rank at the Ballon d'Or in 1980.[183][189]
Belgium has seen two talented waves since 1980, from which several players in defensive positions gained international fame. In the 1980s and the early 1990s, goalkeepers Jean-Marie Pfaff and Michel Preud'homme were elected best custodians at FIFA World Cups,[45][46] while FIFA recognised midfielders Jan Ceulemans and Enzo Scifo as the propelling forces of Belgium's 1986 FIFA World Cup squad.[45][190] In 2002, after all players of this generation had retired,[53] Marc Wilmots became Belgium's top scorer at the World Cup with five goals.[44][164]
During the 12 years in which Belgium failed to qualify for major tournaments, another golden generation matured, most of whom later featured in foreign top football leagues; as of July 2013, 12 Belgian national team players would play the next season in the English Premier League.[141] Five players of this generation gained both prime individual and team awards in foreign top competitions or European club competitions:[upper-alpha 9] defenders Vincent Kompany and Jan Vertonghen,[191][192][193][194] wingers Eden Hazard and Kevin De Bruyne,[195][196][197][198] and forward Kevin Mirallas.[199][200] However, as of November 2016 none of them were regarded by FIFA or UEFA to be the best at their position in any major international tournament yet.[201][202]
Competitive record
FIFA World Cup
Belgium failed to progress past the first round of their earliest five World Cup participations. After two scoreless defeats at the inaugural World Cup in 1930,[158] the team scored in their first-round knockout games in the 1934 and 1938 editions—but only enough to save their honour.[159][160] In 1954, they tied with England (4–4 after extra time),[29] and in 1970, they won their first World Cup match, against El Salvador (3–0).[33] From 1982 until 2002, Belgium reached six successive World Cups by playing qualification rounds, advancing to the second phase five times.[41] In the 1982 FIFA World Cup opener, Belgium beat defending champions Argentina 1–0. Their tournament ended in the second group stage, after a Polish hat-trick by Zbigniew Boniek and a 0–1 loss against the Soviet Union.[42]
At Mexico 1986, the Belgian team achieved their best-ever World Cup run. In the knockout phase as underdogs they beat the Soviets after extra time (3–4);[203] the unnoticed offside position of Jan Ceulemans, during the initial ninety minutes, allowed him to equalise (2–2) and force the game into extra time.[204] They also beat Spain, in a penalty shoot-out after a 1–1 draw, but lost to eventual champions Argentina in the semi-final 2–0, and France in the third-place match (4–2).[47] In the 1990 FIFA World Cup, Belgium dominated periods of their second-round match against England;[205] Enzo Scifo and Jan Ceulemans hit the woodwork.[206] David Platt's volley in the final minute of extra time, described as "nearly blind" by Richard Witzig,[207] avoided an apparently goalless draw and led to the sudden elimination of the Belgians.[208]
In 1994, a 3–2 defeat to defending champions Germany saw Belgium go out in the second round again.[43] Afterwards, the entire Belgian delegation criticised referee Kurt Röthlisberger for not awarding a penalty for a foul on Belgian Josip Weber.[209] Three draws in the group stage of the 1998 World Cup were insufficient for Belgium to reach the knockout stage.[164] With two draws, the 2002 FIFA World Cup started poorly for Belgium, but they won the decisive group match against Russia 3–2. In the second round, they faced eventual World Cup winners Brazil; Belgium lost 2–0 after Marc Wilmots' headed opening goal was disallowed due to a "phantom foul" on Roque Júnior, as Witzig named it.[44][210]
In 2014, Belgium beat all their group opponents with a single-goal difference.[69] Thereafter, they played an entertaining round of 16 game against the United States,[211] in which American goalkeeper Tim Howard made 15 saves.[upper-alpha 10] However, they defeated the US 2–1 in extra time.[69] In a balanced quarter-final, Argentina eliminated Belgium, after a 1–0 victory.[213]
| Belgium's FIFA World Cup record | Qualification record | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host nation(s) and year |
Round | Pos | Pld | W | D* | L | GF | GA | Squad | Outcome | Pld | W | D | L | GF | GA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Round 1 | 11th of 13 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | Squad | Qualified as invitees | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15th of 16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | Squad | 2nd of 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13th of 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | Squad | 2nd of 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrew[214] | Withdrew | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group stage | 12th of 16 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 8 | Squad | 1st of 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | 2nd of 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd of 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1st of 4, playoff loss | 5 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 12 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group stage | 10th of 16 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 5 | Squad | 1st of 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | 2nd of 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 12 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd of 4 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group stage 2 | 10th of 24 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | Squad | 1st of 5 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fourth place | 4th of 24 | 7 | 2 | 2* | 3 | 12 | 15 | Squad | 2nd of 4, playoff win | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Round of 16 | 11th of 24 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 4 | Squad | 1st of 5 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11th of 24 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | Squad | 2nd of 6 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 16 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group stage | 19th of 32 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | Squad | 2nd of 5, playoff win | 10 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 23 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Round of 16 | 14th of 32 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 7 | Squad | 2nd of 5, playoff win | 10 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 27 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | 4th of 6 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 16 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4th of 6 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 13 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter-finals | 6th of 32 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 3 | Squad | 1st of 6 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 18 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To be determined | To be determined | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 24 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Best: fourth place | 12/20 | 41 | 14 | 9 | 18 | 52 | 66 | — | Total | 129 | 73 | 25 | 31 | 258 | 137 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UEFA European Championship
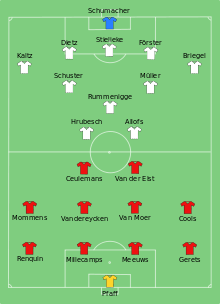
With four successful qualification campaigns out of thirteen, Belgium's performance in the European Championship does not compare to their World Cup record. Belgium has hosted or co-hosted the event twice; they were chosen to accommodate the 1972 European Football Championship from three candidates,[upper-alpha 11] and hosted UEFA Euro 2000 with the Netherlands.[49]
At Euro 1972, Belgium finished third after losing 1–2 against West Germany and beating Hungary 2–1.[34] The team's best continental result is their second place at Euro 1980 in Italy. By finishing as group winners, Belgium reached the final, to face West Germany. The West German Horst Hrubesch scored first, but René Vandereycken equalised courtesy of a penalty. Two minutes before the regular playing time ended, Hrubesch scored again denying Belgium a first European title.[39]
At Euro 1984, in their last and decisive group match against Denmark, the Belgian team took a 0–2 lead, but the Danes won the match 3–2.[48] Sixteen years later, Belgium automatically reappeared at UEFA's national team tournament as co-hosts. After winning the Euro 2000 opener against Sweden 2–1,[216] two 2–0 losses against eventual runners-up Italy and Turkey eliminated the Belgians from the tournament by the end of the group stage.[49]
In spite of winning with broad margins against the Republic of Ireland (3–0) and Hungary (0–4) at Euro 2016,[217][218] Belgium's second very talented generation disappointed with a quarter-final exit. As during the tournament's qualifiers, Wales got the better of Belgium, with a 3–1 win.[73]
| Belgium's UEFA European Championship record | Qualification record | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host nation(s) and year |
Round | Pos | Pld | W | D | L | GF | GA | Squad | Outcome | Pld | W | D | L | GF | GA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not enter | Did not enter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | Preliminary loss | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd of 4 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Third place | 3rd of 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | Squad | Quarter-finals win | 8 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 13 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | 1st of 4, playoff loss | 8 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Runners-up | 2nd of 8 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | Squad | 1st of 5 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 12 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group stage | 6th of 8 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 8 | Squad | 1st of 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | 3rd of 5 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 16 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd of 4 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd of 6 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 17 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group stage | 12th of 16 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 5 | Squad | Qualified as hosts | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not qualify | 3rd of 5 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 11 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5th of 8 | 14 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 14 | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd of 6 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 21 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter-finals | 7th of 24 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 5 | Squad | 1st of 6 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 24 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To be determined | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Best: runners-up | 5/15 | 17 | 7 | 2 | 8 | 22 | 25 | — | Total | 104 | 49 | 26 | 29 | 170 | 112 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Summer Olympic Games
Football tournaments for senior men's national teams took place in six Summer Olympics between 1908 and 1936. The Belgian squad participated in all three Olympic football tournaments in the 1920s and kept the gold medal at home at the 1920 edition.[22][219] Apart from the proper national team, two other Belgian delegations appeared at the Olympics. At the 1900 Summer Olympics, a Belgian representation with mainly students won bronze,[220] and at the 2008 edition, Belgium's U-23 selection placed fourth.[58]
Belgium's 1920 Olympic squad was given a bye into the quarter-finals, where they won 3–1 against Spain, and reached the semi-finals, where they beat the Netherlands 3–0. In the first half of their final against Czechoslovakia, the Belgians led 2–0.[219] Forward Robert Coppée converted a disputed early penalty, and the action in which attacker Henri Larnoe doubled the score was also a matter of debate.[24][178] After the dismissal of the Czechoslovak left-back Karel Steiner, the discontented visitors left the pitch in the 40th minute. Afterwards, the away team reported their reasons for protest to the Olympic organisation;[24] these complaints were dismissed and the Czechoslovaks were disqualified.[25] The 2–0 score was allowed to stand and Belgium were crowned the champions.[25]
| Belgium's Summer Olympic Games record | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host nation, city and year |
Round | Pld | W | D | L | GF | GA | Squad | ||
| No association football competition took place. | ||||||||||
| Tournaments played between clubs | ||||||||||
| Did not enter | ||||||||||
| Withdrew before the tournament[221] | ||||||||||
| Winners | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 1 | Squad | |||
| Round 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Squad | |||
| Quarter-finals | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 12 | Squad | |||
| No association football competition took place. | ||||||||||
| Did not enter | ||||||||||
| From the 1948 till 1988 Olympic Games, amateur selections played. Since 1992, football at the Olympics is an under-23 tournament. | ||||||||||
| Total | 3/6, 1 title | 7 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 18 | 21 | — | ||
| ||||||||||
Records and fixtures
As of 9 June 2017, the complete official match record of the Belgian national team comprises 751 games: 310 wins, 162 draws and 279 losses.[upper-alpha 8][22] During these games, the team scored 1,286 times and conceded 1,231 goals. Belgium reached its highest winning margin against San Marino (10–1) and Zambia (9–0).[22] Their longest winning streak is seven wins in two periods, and their unbeaten record is fourteen consecutive official games.[upper-alpha 8][22]
The entire match record can be examined on the following articles:
- Results in chronological order lists all individual games.
- Record per opponent shows the head-to-head record against other footballing nations.
- Statistics per manager compiles an overview per managerial period.
Upcoming fixtures are listed on the 2010s results page; these include the qualification matches for the 2018 FIFA World Cup.
Player records
.jpg)
As of 9 June 2017, the RBFA lists 683 players who appeared on the men's senior national team.[upper-alpha 12][53] With 96 caps, Jan Ceulemans featured most often;[177] he also started the most games as captain (48).[222] Hector Goetinck had the longest career as an international footballer: 17 years, 6 months and 10 days.[53]
Bernard Voorhoof and Paul Van Himst are the highest-scoring Belgium players, with 30 goals each.[177] Those who scored the most goals in one match are Robert De Veen, Bert De Cleyn and Josip Weber (5);[53] De Veen also holds the record for the most hat-tricks with three.[53] Belgium's fastest goal after the initial kick-off was scored by Christian Benteke, 8.1 seconds into the match against Gibraltar on 10 October 2016.[222][223]
See also
- Belgian Congo national football team (1948–60)
- Belgium national football B team
- Belgium national youth football team (U-15 – U-21 squads)
- Belgian First Division A
- Sport in Belgium
Footnotes
- ↑ The acronyms KBVB, URBSFA and KBFV come from the organisation's respective Dutch, French and German names: Koninklijke Belgische Voetbalbond, Union Royale Belge des Sociétés de Football-Association and Königliche Belgische Fußballverband.
The title of "Royal Union" was awarded on its 25th anniversary in 1920.[1] - ↑ Note that this match is not considered to be a full international by the English FA, and does not appear in the England team records.[5]
- ↑ UBSFA was the acronym for the organisation's French name: Union Belge des Sociétés de Football-Association.
In 1920 it received the title of "Royal Union" for its 25th year of existence, and hence became the Royal Belgian Football Association.[10] - ↑ Even in their last match of 1980, against Cyprus on 21 December, Belgium played in an Adidas outfit.[88] This suggests that Admiral's sponsorship started in 1981, contrary to what the 2014 article stated.
- ↑ The timeline in the 2014 overview article stated the switch from Diadora to Nike happened in 1998. However, the 1999 article focused on this kit sponsor change which took place in mid-1999.
- ↑ The interim managers were Louis Nicolay and Franky Vercauteren.[151][152]
- ↑ According to the "three points for a win" standard
- 1 2 3 Note that the friendlies against Romania on 14 November 2012 and against Luxembourg on 26 May 2014 are not FIFA-recognised due to an excessive number of substitutions according to the Laws of the Game.[171] The Belgian and Czech football federations were too late in asking that the match against Czech Republic on 5 June 2017 would be official.[172]
- ↑ Prime individual awards include being elected the season's or year's best player of a competition; prime team awards equal winning a competition. National top divisions, main national cup competitions, UEFA Champions League and UEFA Europa League are considered.
- ↑ FIFA's initial match statistics showed 16 saves, and many news sources continue to use this number. The official FIFA statistics were updated on 5 July 2014 to show 15 saves.[212]
- ↑ The other bids were from England and Italy,[215] whose teams did not reach the semi-finals.[34]
- ↑ Note that the RBFA does not count caps earned in the Belgian seven Summer Olympics matches, and that it does include Belgium's friendlies on 14 November 2012, 26 May 2014, and 5 June 2017 that are not FIFA-recognised due to an excessive number of substitutions according to the Laws of the Game.[171]
References
- 1 2 3 "The RBFA's History". RBFA. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "FIFA/Coca-Cola World Ranking". FIFA. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016.
- ↑ "World Football Elo Ratings". World Football Elo Ratings website. Archived from the original on 2 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 "World Football Elo Ratings: Belgium". World Football Elo Ratings website. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 18 Aug 2013.
- ↑ Jostein Nygård (4 Dec 2014). "England – International Results". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 26 April 2003. Retrieved 31 Aug 2015.
- ↑ See:
- Goldblatt 2008, p. 120,
- de Vries 2007, p. 57,
- Kassimeris 2007, p. 12.
- ↑ Dries Vanysacker (21 May 2015). "Belgische voetbalgeschiedenis begon in Gent" [Belgian football history began in Ghent]. Eos (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 13 Jun 2015.
- ↑ François Colin (1 Apr 2003). "Report. "Kroniek van het Belgisch voetbal" schetst ontstaan populairste sport" [Report. "The chronicle of Belgian football" sketches origins of most popular sport]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 11 June 2013. Retrieved 29 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Henshaw 1979, p. 75.
- 1 2 "Historique de l'URBSFA" [History of the RBFA] (in French). RBFA. Archived from the original on 7 May 2012. Retrieved 31 Oct 2015.
- ↑ Guldemont & Deps 1995, p. 64.
- 1 2 Fraiponts & Willocx 2003.
- 1 2 Matty Verkamman (9 Jan 1999). "Interlandvoetbal om 'koperen dingetje'/Sporteeuw (2) – 1901" [International football for 'the copper thingy'/Sports Century (2) – 1901]. Trouw (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 9 Apr 2015.
- 1 2 3 Hubert 1980, p. 12.
- 1 2 Hubert 1980, p. 13.
- ↑ "Belgium v France − a 109-year-old rivalry". UEFA. 13 Aug 2013. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 15 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "History of FIFA – Foundation". FIFA. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2014.
- ↑ Parrish & Nauright 2014, p. xv.
- 1 2 Boin 1945.
- 1 2 Guldemont & Deps 1995, p. 65.
- 1 2 3 Hassanin Mubarak (7 Aug 2003). "Belgium National Team Coaches". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 14 Sep 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Karel Stokkermans. "Belgium – List of International Matches". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 2 Sep 2013.
- 1 2 "Frankrijk–België" [France–Belgium]. De Telegraaf (in Dutch). 21 Mar 1916. Retrieved 11 Jun 2015 – via Delpher.
- 1 2 3 Juan Fauria í García (1993). "The 1920 Football (Soccer) Tournament" (PDF). ISOH magazine. 1 (4): 5–7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 December 2013. Retrieved 4 May 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Henshaw 1979, p. 76.
- ↑ "Belgium in exile - Belgische regering, vluchtelingen en soldaten in Groot-Brittannië" [Belgium in exile - Belgian government, refugees and soldiers in Great Britain] (PDF) (in Dutch). National Archives of Belgium: 31. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2016. Retrieved 18 Dec 2016.
- ↑ Mark Chaplin (5 May 2014). "The birth of UEFA". UEFA. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 28 Jun 2014.
- ↑ "België wist Engeland een gelijk spel af te dwingen" [Belgium managed to enforce a draw against England]. Amigoe di Curaçao (in Dutch). 18 Jun 1954. Retrieved 19 Dec 2016 – via Delpher.
- 1 2 3 4 "World Cup 1954 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Retro WK 1966: Engeland wint na meest omstreden goal van de eeuw, Duivels stranden in testmatch" [Retro WC 1966: England wins after most controversial goal of the century, Devils left stranded in test match]. voetbalnieuws.be (in Dutch). 31 May 2014. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 19 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Bernhart & Houtman 2014.
- 1 2 3 Bart Lagae (23 May 2002). "WK-geschiedenis. 1970. Witte Duivels smelten weg in Mexico" [WC history. 1970. White Devils melt away in Mexico]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 26 Apr 2015.
- 1 2 3 "World Cup 1970 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Karel Stokkermans; Martín Tabeira (31 Jan 2007). "European Championship 1972". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 10 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "Wonderbaarlijke ontsnappingen uit de Oranje-historie" [Miraculous escapes in Oranje history]. de Volkskrant (in Dutch). 19 Nov 2003. Archived from the original on 8 June 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- ↑ Snyder 2001.
- ↑ Karel Stokkermans; Martín Tabeira (20 Jun 2013). "European Championship 1976". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 24 Oct 2015.
- ↑ Karel Stokkermans; Sergio Henrique Jarreta (3 Jan 2000). "World Cup 1978 Qualifying". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 24 Oct 2015.
- 1 2 3 Karel Stokkermans; Martín Tabeira (28 Mar 2007). "European Championship 1980". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ David Runciman (16 Jun 2014). "Why You Should (and Should Not) be Excited About Belgium's New Golden Generation". The New Republic. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- 1 2 "2014 Fifa World Cup: Guide to Belgium's Group H". BBC. 23 May 2014. Retrieved 12 Jul 2016.
- 1 2 3 "World Cup 1982 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 "World Cup 1994 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Erlan Manaschev (3 Jul 2008). "World Cup 2002 – Match Details". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 "FIFA World Cup All-Star Team – Football world Cup All Star Team". Football.sporting99.com. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 28 Jun 2012.
- 1 2 "FIFA World Cups: Awards" (PDF). FIFA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 19 Jun 2007.
- 1 2 "World Cup 1986 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 Barrie Courtney (19 Jun 2004). "European Championship 1984 – Final Tournament – Full Details". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 26 November 2001. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 John Beuker; Karel Stokkermans (17 Jan 2004). "European Championship 2000". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Josef Bobrowsky (14 Jun 2000). "King Hassan II Tournament 1998". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Cyprus International Tournament 1999". RSSSF. 27 Feb 2001. Archived from the original on 26 July 2016. Retrieved 26 Jul 2016.
- ↑ José Luis Pierrend (11 Jun 2000). "Kirin Cup 1999". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "All Red Devils". RBFA. Retrieved 14 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Markov : "België verzwakt door vertrek Wilmots-Verheyen"" [Markov: "Belgium weakened by departure Wilmots-Verheyen"]. Gazet van Antwerpen (in Dutch). 8 Sep 2002. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Waseige resigns as Belgium coach". BreakingNews.ie. 17 Jun 2002. Archived from the original on 21 November 2015. Retrieved 15 Mar 2014.
- 1 2 Maarten Delvaux (6 Jun 2012). "Overzicht Belgische bondscoaches" [Overview Belgian national team coaches]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 18 Jul 2016.
- ↑ Gunther De Vos (18 Jun 2007). "Sterke generatie schrijft geschiedenis" [Strong generation writes history]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 Karel Stokkermans (14 Mar 2013). "Games of the XXIX. Olympiad – Football Tournament". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Hamdan Saaid (16 Jul 2009). "Kirin Cup 2009". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Ludo Vandewalle; Gunther De Vos; Ki. V. (3 May 2010). "Georges Leekens dan toch bondscoach" [Georges Leekens national manager after all]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Retrieved 10 Jul 2013.
- ↑ lbo; janm (13 May 2012). "Leekens verlaat Rode Duivels voor Club Brugge" [Leekens leaves Red Devils for Club Brugge]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Retrieved 10 Jul 2013.
- ↑ Maarten Delvaux; Bart Lagae (15 May 2012). "Marc Wilmots voorlopig interim-bondscoach" [Marc Wilmots provisional interim national manager]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Retrieved 9 Jul 2013.
- ↑ janm (6 Jun 2012). "Marc Wilmots is nieuwe bondscoach tot 2014" [Marc Wilmots is new national manager until 2014]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Retrieved 9 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "Argentina go second, Belgium & Uruguay rise". FIFA. 12 Sep 2013. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 12 Sep 2013.
- ↑ Tim Adams (24 Aug 2013). "Why Belgium is the hottest country in football". Esquire. Retrieved 15 Sep 2013.
- ↑ "Rote Teufel: Eine Goldene Generation mit königsblauer Disziplin" [Red Devils: A golden generation with royal blue discipline]. Bild (in German). 11 Sep 2013. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 15 Sep 2013.
- ↑ John Sinnott (10 Sep 2013). "Will Belgium win the World Cup?". CNN. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 15 Sep 2013.
- ↑ Karel Stokkermans; Juan Pablo Andrés; Erik Francisco Lugo (18 Jun 2015). "World Cup 2014 Qualifying". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 Neil Morrison (24 Jul 2014). "World Cup 2014 – Match Details". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Belgium stroll past Andorra to qualify". UEFA. 10 Oct 2015. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 3 Nov 2015.
- ↑ "Belgium go top, Chile and Austria soar". FIFA. 5 Nov 2015. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 5 Nov 2015.
- ↑ "Belgium and Turkey claim awards, Hungary return". FIFA. 3 Dec 2015. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 21 Jul 2016.
- 1 2 "Wales stun Belgium to reach Euro semifinal". ESPN FC. 1 Jul 2016. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 2 Jul 2016.
- ↑ maj (15 Jul 2016). "Marc Wilmots ontslagen als coach Rode Duivels" [Marc Wilmots dismissed as coach Red Devils]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 15 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "FIFA World Cup qualifying draw format". UEFA. 16 Jun 2015. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 21 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "FIFA/Coca-Cola World Ranking – July 2015 (UEFA)". FIFA. 9 Jul 2015. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 9 Jul 2015.
- ↑ "Belgium". Flags of the World. 6 Jun 2009. Retrieved 3 Oct 2009.
- 1 2 3 "fifa world cup 1930 group 4". Historical Football Kits. Archived from the original on 8 April 2016. Retrieved 10 Jul 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Goaaal! Fotomontage Rode Duivels – 1980" [Goaaal! Photo gallery Red Devils – 1980] (in Dutch). Belgian State Archives. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Goaaal! Fotomontage Rode Duivels" [Goaaal! Photo gallery Red Devils] (in Dutch). Belgian State Archives. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Maarten Delvaux (27 Feb 2014). "Met deze shirts spelen Rode Duivels op het WK" [Red Devils play at the WC in these shirts]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- ↑ "Goaaal! Fotomontage Rode Duivels – 1970" [Goaaal! Photo gallery Red Devils – 1970] (in Dutch). Belgian State Archives. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Voetbal: Nederland- België 3–0" [Football: The Netherlands-Belgium 3–0] (in Dutch). gahetNA (Genootschap voor het Nationaal Archief, het Nationaal Archief, Spaarnestad Photo). Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 7 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "Heraldic emblem and motto". Belgian Federal Government. Retrieved 31 Oct 2015.
- 1 2 "Rode Duivels, witte engelen" [Red Devils, white angels] (in Dutch). BRUZZZ. 5 Jun 2014. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 17 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "New Adidas Belgium 2014–15 Kits Released". Footy Headlines. 14 Aug 2014. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 3 Apr 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Ludo Vandewalle (24 May 2014). "Adidas na WK wellicht nieuwe kledingsponsor Duivels" [Adidas likely new Devils clothing sponsor after WC]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "1980: België klopt Cyprus met 0–2" [1980: Belgium beats Cyprus 0–2] (in Dutch). Sporza. Retrieved 28 Oct 2016.
- ↑ Sander Van den Broecke (1 Jul 1999). "Rode Duivels in "rood, klassiek en rustig" shirt" [Red Devils in "red, classic and serene" shirt]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 8 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "History King Baudouin Stadium". RBFA. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ Ludo Vandewalle (4 Sep 2007). "Duivels trainen voor het eerst in Tubeke" [Devils train for the first time in Tubeke]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ arvn (23 Mar 2013). "Rode Duivels trainen ontspannen in Neerpede" [Red Devils train relaxed in Neerpede]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Retrieved 31 Aug 2015.
- ↑ vml (31 Aug 2015). "Bosniërs trainen al eerste keer op Belgische bodem" [Bosnians train first time on Belgian soil already]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 21 November 2015. Retrieved 31 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "UEFA Euro 1972 – History – Germany-USSR". UEFA. 3 Oct 2003. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 12 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Pierre Winkler (17 Jan 2004). "European Championship 2000 – Full Details Final Tournament". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 12 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Karel Stokkermans (6 Mar 2014). "The "Derby der Lage Landen"". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2014.
- ↑ "België slaat Nederland met 4–1" [Belgium beats Netherlands 4–1]. Algemeen Handelsblad (in Dutch). 15 Sep 1930. Retrieved 8 Sep 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ Andrew Hussey (3 Apr 2005). "Lost lives that saved a sport". The Guardian. Retrieved 15 Jun 2006.
- ↑ Parrish & Nauright 2014, p. xxviii.
- ↑ "Heyzel-stadion wordt gesloopt" [Heyzel stadium to be demolished]. De Telegraaf (in Dutch). 29 Nov 1988. Retrieved 29 Aug 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ "Stadion – Geschiedenis – Koning Boudewijnstadion" [Stadium – History – King Baudouin Stadium] (in Dutch). Vzw Prosport Brussel. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 12 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Geert Sels (25 May 2013). "Koning Boudewijnstadion wordt afgebroken" [King Baudouin Stadium to be demolished]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Retrieved 9 Jul 2013.
- ↑ Michaël Van Damme; lej (20 Jun 2015). "Anderlecht speelt vanaf 2019 in nieuw stadion" [Anderlecht plays in new stadium from 2019]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Jun 2015.
- ↑ "Archiefmeester: Radio & voetbal" [Archive master: Radio & football] (in Dutch). Radio 1. 16 Mar 2014. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 13 Apr 2014.
- 1 2 3 "The World Factbook – Europe – Belgium". Central Intelligence Agency. 30 Jun 2016. Archived from the original on 10 July 2016. Retrieved 10 Jul 2016.
- ↑ Joeri Vlemings (5 Mar 2013). "Rik, de dertiende man van de Rode Duivels" [Rik, the thirteenth man of the Red Devils]. Het Laatste Nieuws (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ↑ "Opnieuw gigantisch hoge kijkcijfers voor wedstrijd van Rode Duivels" [Again high viewer numbers for Red Devils match]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). 27 Jun 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2016.
- ↑ "Kijkcijferrecord EK Rode Duivels verbroken" [Viewer record Red Devils' EC broken] (in Dutch). VRT. 1 Aug 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2016.
- ↑ "Nieuwe Vrt-reeks kijkt mee achter de schermen van de Rode Duivels" [New Vrt series watches behind the scenes of the Red Devils]. De Standaard (in Dutch). 3 Apr 2014. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 3 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "Docureeks 'Rode Helden' op Sporting Telenet" [Documentary series 'Red Heroes' on Sporting Telenet] (in Dutch). Telenet. 25 Apr 2014. Retrieved 17 May 2014.
- ↑ "The Challenges". IAB Community. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 7 Apr 2015.
- ↑ "Duiveluitdagingen stuwen Duivels naar Brazilië" [Devil Challenges push Devils to Brazil] (in Dutch). Sporza. 15 Oct 2013. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- 1 2 "Groot succes: 20.000 fans op eerste fandag Rode Duivels" [Great success: 20,000 fans on first fan day Red Devils]. Het Laatste Nieuws (in Dutch). 2 Jun 2013. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 30 Jun 2013.
- ↑ Kim De Raedt; Lin Louage (6 Jul 2014). "Rode Duivels bedanken 'beste supporters ter wereld' met fandag" [Red Devils thank 'best supporters in the world' with fan day]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 6 Jul 2014.
- ↑ "Dance with the Devils op 17, 22 en 26 juni" [Dance with the Devils on 17, 22 and 26 June] (in Dutch). Sportpaleis. 14 Feb 2014. Archived from the original on 11 August 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ↑ "Dance With The Devils" (in Dutch). Lotto Arena. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 9 Jun 2016.
- ↑ "Frankrijk–België (0–1)" [France–Belgium (0–1)]. Twentsch dagblad Tubantia (in Dutch). 21 Dec 1914. Retrieved 23 Jul 2016 – via Delpher.
- 1 2 "Rond den Wedstrijd Holland – België" [About the game Holland – Belgium]. Bataviaasch Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). 3 Feb 1941. Retrieved 11 Jun 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ Adolfo Garza (22 Jun 1998). "Bélgica en el alma" [Belgium in the soul]. La Nación (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 Aug 2015.
- ↑ François Colin (10 Jun 2011). "Retro. Ceulemans: 'Voor mij blijft EK 80 het hoogtepunt'" [Retro. Ceulemans: 'EC 80 is still the summit for me']. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Retrieved 21 Nov 2015.
- ↑ "Bied op de wedstrijdshirts van België-Frankrijk" [Place a bid on the match shirts of Belgium-France] (in Dutch). RBFA. 8 Aug 2013. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 15 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Goaaal! Voetbalaffiches" [Goaaal! Football posters] (in Dutch). RBFA. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 14 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "European Action Week against discrimination in football to kick off next week". Vienna Institute for International Dialogue and Cooperation. 8 Oct 2010. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 27 Jul 2013.
- ↑ Pierre Danvoye (2 Jul 2013). "Mununga: 'Ik was te naïef'" [Mununga: 'I was too naive']. Sport/Voetbalmagazine (in Dutch). Roeselare: Roularta Media Group. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 14 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Les Diables contre le racisme" [The Devils against racism] (in French). RTBF. 11 Oct 2010. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 24 Oct 2015.
- 1 2 "Den wedstrijd om den Rotterdamsch Nieuwsblad-Beker" [The match for the Rotterdamsch Nieuwsblad Cup]. Rotterdamsch Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). 16 May 1905. Retrieved 17 May 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ "Bob Madou doet duivelse marketingstrategie uit de doeken" [Bob Madou reveals devilish marketing strategy] (in Dutch). voka.be. 17 May 2016. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 28 Jun 2016.
- ↑ Russell 1987, p. 129.
- 1 2 mcu (6 Feb 2007). "Nieuwe mascotte voor Rode Duivels" [New mascot for Red Devils]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Retrieved 3 Jul 2014.
- ↑ "Fotocollectie – Evenals 74 jaar geleden speelt het Nederlands voetbalelftal a.s. woensdag tegen ..." [Photo collection – Just like 74 years ago the Dutch eleven play upcoming Wednesday against ...] (in Dutch). gahetNA (Genootschap voor het Nationaal Archief, het Nationaal Archief, Spaarnestad Photo). Retrieved 17 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "1895, een gigantisch succes" [1895, a gigantic success] (in Dutch). RBFA. 24 Jun 2013. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 9 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "Sport" [Sports]. Rotterdamsch Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). 26 Feb 1914. Retrieved 8 Sep 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ F. Vranckx (7 Jun 2013). "Ook koning Albert vanavond naar de Heizel" [King Albert also at the Heysel this evening]. Gazet van Antwerpen (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 8 Sep 2015.
- ↑ "Rode Duivels staan op tegen Bosnië-Herzegovina" [Red Devils arise against Bosnia-Herzegovina] (in Dutch). Sporza. 3 Sep 2015. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 8 Sep 2015.
- ↑ "België trakteert zijn helden op een volksfeest" [Belgium treats its heroes with a national feast] (in Dutch). Sporza. 20 Jun 2011. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 30 Jun 2014.
- ↑ Bennie Luyten (18 Nov 2004). "'Ons voetballand is doodziek'" ['Our footballing nation is terminally ill'] (in Dutch). sport.be.msn.com. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 18 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "Advocaat laat Rode Duivels doodziek achter" [Advocaat leaves Red Devils terminally ill]. belgiumsoccer.be (in Dutch). 15 Apr 2010. Retrieved 18 Jul 2013.
- ↑ "De enige echte fan van België" [Belgium's only real fan]. Algemeen Dagblad (in Dutch). 5 Oct 2006. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 30 Jun 2013.
- ↑ Ludo Vandewalle (9 Sep 2009). "De eenzame Duivels-supporter" [The lonesome Devils supporter]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Retrieved 30 Jun 2013.
- ↑ "De Rode Duivels zien vanavond hun eerste tifo" [The Red Devils see their first tifo tonight] (in Dutch). Sporza. 6 Jun 2013. Retrieved 4 Jul 2013.
- 1 2 Willems 2013.
- ↑ "Peiling: 'Rode Duivels raken tot in kwartfinales'" [Opinion poll: 'Red Devils reach the quarter finals']. voetbalnieuws.be (in Dutch). 17 Oct 2013. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 22 Nov 2015.
- ↑ "Manneken Pis in WK-shirt Rode Duivels" [Manneken Pis in Red Devils WC shirt]. De Standaard (in Dutch). 7 Mar 2014. Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 22 Mar 2014.
- ↑ Lin Louage (13 Jun 2014). "Atomium-bol in zwart, geel en rood" [Atomium sphere in black, yellow and red]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 28 June 2016. Retrieved 14 Jun 2014.
- ↑ "Relations to the Netherlands – Belgium". Government of the Netherlands. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "La France et la Belgique" [France and Belgium] (in French). France Diplomatie. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 22 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "FIFA Tournaments – Compare Teams". FIFA. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 16 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Guus Van Holland (11 Dec 1999). "De Rode Duivels" [The Red Devils]. NRC Handelsblad (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 20 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "De extra België-Holland-wedstrijd." [The extra Belgium-Holland game.]. Soerabaijasch Handelsblad (in Dutch). 26 Apr 1932. Retrieved 25 May 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ Karel Stokkermans (6 Mar 2014). "The "match sympatique" [sic]". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 28 Jun 2014.
- ↑ "Geschiedenis van de Rode Duivels" [History of the Red Devils] (in Dutch). Bel 2 Mundial. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2014.
- ↑ W. Verhaert (5 May 2009). "Vercauteren interim-bondscoach Rode Duivels" [Vercauteren caretaker manager Red Devils]. Gazet Van Antwerpen (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 19 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Red Devils Staff". RBFA. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 25 Apr 2015.
- ↑ "Thierry Henry joins Belgium coaching staff as assistant to Roberto Martínez". The Guardian. 26 Aug 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2016.
- ↑ Diederik Geypen (31 Aug 2016). "Komst van Martinez heeft ook een directe invloed op Courtois, Mignolet en Sels: "Dit wordt een aanpassing voor iedereen"" [Arrival of Martinez also has a direct influence on Courtois, Mignolet and Sels: "This will be an adaptation for everyone"] (in Dutch). voetbalkrant.com. Archived from the original on 9 October 2016. Retrieved 9 Oct 2016.
- ↑ "Globe Soccer Awards : le triplé pour le Barça, le doublé pour New York City" [Globe Soccer Awards: the triple for Barça, the double for New York City]. L'Équipe (in French). 27 Dec 2015. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Dec 2015.
- ↑ Jamie Rainbow (14 Dec 2012). "World Soccer Awards – previous winners". World Soccer. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 29 Apr 2015.
- 1 2 "World Cup 1930 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 "World Cup 1934 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- 1 2 "World Cup 1938 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Cools make it too hot for Spain". The Glasgow Herald. Google News. 16 Jun 1980. Retrieved 30 Jun 2014.
- ↑ Jean-Claude Matgen (27 Jan 2012). "Sinibaldi, le Béjart mauve" [Sinibaldi, the purple Béjart]. La Libre (in French). Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 9 Jul 2013.
- ↑ De Bock 2013.
- 1 2 3 "World Cup 1998 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 17 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Ludo Vandewalle (5 Oct 1999). "Behoudsgezinde bondscoach Robert Waseige verandert slechts uit noodzaak" [Conservative national manager Robert Waseige only changes out of necessity] (in Dutch). De Standaard. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 18 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Stéphane Vande Velde; Pierre Bilic (8 Oct 2014). "Marc Wilmots wil sommige Rode Duivels meer vrijheid geven" [Marc Wilmots want to give some Red Devils more freedom]. Sport/Voetbalmagazine (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 25 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Wilmots: "Dominant en intelligent proberen te spelen"" [Wilmots: "Trying to play dominantly and intelligently"] (in Dutch). Sporza. 10 Sep 2012. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 18 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Roberto Martinez maakt selectie bekend" (in Dutch). RBFA. 30 May 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2017.
- ↑ bla (4 Jun 2017). "België-Tsjechië geen officiële interland". De Standaard (in Dutch). Retrieved 4 Jun 2017.
- ↑ "Football Match Summary – June 9, 2017 – ESPN". ESPN FC. 28 Mar 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2017.
- 1 2 "Rules & Governance – Law 3: The number of players". The FA. Archived from the original on 25 October 2014. Retrieved 25 Oct 2014.
- ↑ "Welles-nietesspel rond oefenmatch tegen Tsjechië: Daarom was het geen officiële wedstrijd" (in Dutch). Sporza. 6 Jun 2017. Retrieved 6 Jun 2017.
- ↑ "Belgian Red Devils' squad list for UEFA Euro 2016". RBFA. 12 May 2016. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 28 Jun 2016.
- ↑ "Roberto Martínez announces selection". RBFA. 30 Sep 2016. Retrieved 1 Oct 2016.
- ↑ @BelRedDevils (24 Mar 2017). "R. Martínez : "@thommills will not be available. He's getting better but is not fully fit" #belgre #roadtorussia" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ↑ "Serieuze streep door de rekening: onderzoek brengt enkelbreuk aan het licht bij Hazard". Sporza. 4 Jun 2017. Retrieved 5 Jun 2017.
- 1 2 3 Karel Stokkermans (24 Jul 2014). "Belgium – Record International Players". Rec.Sport.Soccer Statistics Foundation (RSSSF). Archived from the original on 25 June 2016. Retrieved 27 Oct 2014.
- 1 2 "Olympic Football Tournament Antwerp 1920 – Belgium 3:1 (1:0) Spain – Overview". FIFA. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 26 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "Olympic Football Tournament Antwerp 1920 – Belgium 2:0 (2:0) Czechoslovakia – Overview". FIFA. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Raymond Braine nog steeds België's voetbalgrootmeester." [Raymond Braine still Belgium's football grandmaster.]. De Telegraaf (in Dutch). 9 Oct 1941. Retrieved 13 Jun 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ Murray 1998, p. 63.
- ↑ "Rik Coppens" (in Dutch). 29 Apr 2010. Retrieved 19 Jul 2016.
- 1 2 "Van Himst en Anderlecht kapen de Gouden Schoen" [Van Himst and Anderlecht seize the Golden Shoe] (in Dutch). Sporza. 22 Jan 2014. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 26 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Berend Scholten (21 Jan 2011). "Belgium still bows to Van Himst". UEFA. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- ↑ Marcelo Leme de Arruda (21 Jan 2000). "IFFHS' Players and Keepers of the Century for many countries". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2015.
- ↑ José Luis Pierrend (22 Jun 2005). "European Footballer of the Year ("Ballon d'Or") 1965". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Coppens: 'Als Paul zegt dat ik het was, dan heeft hij gelijk'" [Coppens: 'If Paul says it was me, then he is right'] (in Dutch). Sporza. 6 Feb 2015. Archived from the original on 6 February 2015. Retrieved 11 Aug 2015.
- ↑ "1972 team of the tournament". UEFA. 2 May 2011. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 23 Jan 2015.
- ↑ José Luis Pierrend (1 May 2005). "European Footballer of the Year ("Ballon d'Or") 1980". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "FIFA Classic Player: Scifo, a Red Devil with divine gifts". FIFA. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
- ↑ "Alan Pardew and Vincent Kompany's Premier League award". BBC Sport. 11 May 2012. Retrieved 16 Jan 2014.
- ↑ "Belgium – V. Kompany". Soccerway. Archived from the original on 6 February 2013. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ Nicholas Geeraerts (7 May 2012). "Jan Vertonghen 'Voetballer van het Jaar' in Nederland" [Jan Vertonghen 'Football player of the Year' in the Netherlands]. De Morgen (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 21 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Belgium – J. Vertonghen". Soccerway. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Mourinho and Hazard scoop Barclays season awards". Premier League. 22 May 2015. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ "Belgium – E. Hazard". Soccerway. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "De Bruyne is Speler van het Jaar volgens Duitse Journalisten" [De Bruyne is Player of the Year according to German journalists] (in Dutch). Sporza. 26 Jul 2015. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 26 Jul 2015.
- ↑ "Belgium – K. De Bruyne". Soccerway. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ rvh (4 May 2012). "Kevin Mirallas is speler van het jaar in Griekenland" [Kevin Mirallas is player of the year in Greece]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Retrieved 19 Aug 2014.
- ↑ "Belgium – K. Mirallas". Soccerway. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "FIFA Announces 2014 World Cup 'Dream Team' as Voted On by Fans". Bleacher Report. 23 Jul 2014. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 16 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "UEFA EURO 2016 Team of the Tournament revealed". UEFA. 11 Jul 2016. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 11 Jul 2016.
- ↑ Glen Levy (18 May 2010). "Top 10 World Cup Games – 3. Belgium 4–3 USSR 1986". Time. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 25 Apr 2015.
- ↑ vml (21 Jun 2014). "'Duivelsvloek' houdt al 28 jaar stand tegen Rusland, morgen ook?" ['Devil curse' already lasts for 28 years against Russia, tomorrow as well?]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Retrieved 20 Sep 2015.
- ↑ Edworthy 1997, pp. 138–139.
- ↑ Michaël Van Damme (26 Jun 2010). "26 juni 1990: de dag dat de goden blind waren" [26 June 1990: the day the gods were blind]. Het Nieuwsblad (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 19 Jul 2016.
- ↑ Witzig 2006, p. 167.
- ↑ "World Cup 1990 finals". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 21 April 2009. Retrieved 19 Jul 2016.
- ↑ Fred Buddenberg (4 Jul 1994). "Belgen furieus op Röthlisberger" [Belgians furious with Röthlisberger]. Trouw (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 20 Sep 2015.
- ↑ Witzig 2006, p. 289.
- ↑ Carl Bialik (10 Jul 2014). "U.S. vs. Belgium Was the Best Match of the World Cup So Far". FiveThirtyEight. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 25 Apr 2015.
- ↑ "Official FIFA statistics, updated 5 July 2014" (PDF). FIFA. 5 Jul 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 29 Dec 2014.
- ↑ "2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil – Matches – Argentina-Belgium – Live Statistics". FIFA. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Lisi 2007, p. 47.
- ↑ "Sportflitsen" [Sports flashes]. De Tijd (in Dutch). 14 Mar 1972. Retrieved 19 Sep 2015 – via Delpher.
- ↑ "Belgium start with a bang". UEFA. 10 Jun 2000. Archived from the original on 5 January 2001. Retrieved 30 Jun 2013.
- ↑ "Belgium ease to 3–0 victory vs. Rep. Ireland". ESPN FC. 18 Jun 2016. Archived from the original on 14 June 2016. Retrieved 2 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Hazard shines as Belgium thrash Hungary". ESPN FC. 26 Jun 2016. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 2 Jul 2016.
- 1 2 Karel Stokkermans; Mikael Jönsson (26 Jun 2008). "Games of the VIII. Olympiad – Football Tournament". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Søren Elbech; Karel Stokkermans (21 Jul 2011). "Games of the II. Olympiad – Football Tournament". RSSSF. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 27 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Swedish Olympic Committee 1913, p. 483.
- 1 2 "Games per date". RBFA. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 21 Jul 2016.
- ↑ "Benteke speeds into the record books". FIFA. 11 Oct 2016. Archived from the original on 15 October 2016. Retrieved 15 Oct 2016.
Bibliography
- Bernhart, Patrick; Houtman, Joost (2014). Zo werden wij wereldkampioen [That is how we became world champions] (in Dutch). Antwerp: Manteau. ISBN 978-90-223-2972-6. (Unpaginated version consulted online via Google Books; the particular phrase by Pelé can be retrieved with this search.)
- Boin, Victor (1945). Het gulden jubileumboek van de K.B.V.B. 1895–1945. Geschiedenis van de voetbalsport in Belgie en in Belgisch Kongo [The golden jubilee book of the R.B.F.A. 1895–1945. History of the football sport in Belgium and in Belgian Congo] (in Dutch). Brussels: Les Éditions Leclercq & De Haas. (Numberless page copy consulted online on 25 June 2014 on GOAAAL! Voetbalvaria (by RBFA))
- De Bock, Wim (2013). Houwaart de Mos Boskamp (in Dutch). Amsterdam: Uitgeverij De Buitenspelers. ISBN 978-90-71359-69-9. (Numberless book pages consulted online via Google Books)
- de Vries, André (2007). Flanders: A Cultural History. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-531493-9.
- Edworthy, Niall (1997). England: The Official F.A. History. London: Virgin Books. ISBN 978-1-85227-699-7.
- Fraiponts, Jean; Willocx, Dirk (2003). Kroniek van het Belgische voetbal / Pioniers en Rode Duivels – 1863–1906 [The chronicle of Belgian football / Pioneers and Red Devils – 1863–1906] (in Dutch). Antwerp: ASSOC.BE bvba. ISBN 978-90-77314-01-2. (Extract consulted online on 30 August 2010 on Beerschot Athletic Club)
- Goldblatt, David (2008). The Ball is Round. New York: Riverhead Trade. ISBN 978-1-59448-296-0.
- Guldemont, Henry; Deps, Bob (1995). 100 ans de football en Belgique: 1895–1995, Union royale belge des sociétés de football association [100 years of football in Belgium: 1895–1995, Royal Belgian Football Association] (in French). Brussels: Vif. ISBN 978-90-5466-151-1.
- Henshaw, Richard (1979). The Encyclopedia of World Soccer. Washington, D.C.: New Republic Books. ISBN 978-0-915220-34-2.
- Hubert, Christian (1980). Les diables rouges [The Red Devils] (in French). Brussels: Arts & voyages. ISBN 978-2-8016-0046-7.
- Kassimeris, Christos (2007). European Football in Black and White: Tackling Racism in Football. Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0-7391-1959-4.
- Lisi, Clemente Angelo (2007). A history of the World Cup: 1930–2006. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-5905-0.
- Murray, Bill (1998). The World's Game: A History of Soccer. Champaign, Illinois: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 978-0-252-06718-1.
- Parrish, Charles; Nauright, John (2014). Soccer around the World: A Cultural Guide to the World's Favorite Sport. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-61069-302-8.
- Russell, Jeffrey Burton (1987). The Devil: Perceptions of Evil from Antiquity to Primitive Christianity. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-9409-3.
- Snyder, John (2001). Soccer's Most Wanted. Washington, D.C.: Potomac Books, Inc. ISBN 978-1-57488-365-7. (Unpaginated version consulted online via Google Books; the particular fact is mentioned in chapter "The Only Time It Happened", section "10. Belgium".)
- Swedish Olympic Committee (1913). Erik Bergvall, ed. The Official Report of the Olympic Games of Stockholm 1912 (PDF). Stockholm: Wahlstrom and Widstrand.
- Willems, Raf (2013). Sympathy for the Devils (in Dutch). Tielt: Lannoo. ISBN 978-94-014-0758-8.
- Witzig, Richard (2006). The Global Art of Soccer. Harahan: CusiBoy Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9776688-0-9.
Further reading
- Aerts, Bart; Buyse, Frank; Colin, François; Cornez, Pierre; Decoster, Gilles; Deferme, Dirk; et al. (2013). De Rode Duivels. Het officiële boek [The Red Devils. The official book] (in Dutch). Veurne: Uitgeverij Kannibaal. ISBN 978-94-91376-66-5.
- Colin, François (2014). De Rode Duivels 1900–2014 [The Red Devils 1900–2014] (in Dutch). Veurne: Uitgeverij Kannibaal. ISBN 978-94-91376-77-1.
- Hubert, Christian (1994). De Montevideo à Orlando [From Montevideo to Orlando] (in French). Brussels: Labor. ISBN 978-2-8040-1009-6.
- Hubert, Christian (2006). Le siècle des Diables Rouges [The century of the Red Devils] (in French). Brussels: Luc Pire. ISBN 978-2-87415-684-7.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Belgium national football team. |
- RBFA official website (in Dutch) (in English) (in French)
- FIFA team profile
- ELO team records
- Belgian national team news website (in French)
- Official supporters' federation 1895 (in Dutch) (in French)
.jpg)
