Baudin expedition to Australia
The Baudin expedition of 1800 to 1803 was a French expedition to map the coast of New Holland (now Australia). Nicolas Baudin was selected as leader in October 1800. The expedition started with two ships, Géographe, captained by Baudin, and Naturaliste captained by Jacques Hamelin, and was accompanied by nine zoologists and botanists, including Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de la Tour, François Péron and Charles-Alexandre Lesueur as well as the geographer Pierre Faure.
Expedition

Napoléon Bonaparte, as First Consul, formally approved the expedition "to the coasts of New Holland",[1] after receiving a delegation consisting of Baudin and eminent members of the Institut National des Sciences et Arts on 25 March 1800. The explicit purpose of the voyage was to be ‘observation and research relating to Geography and Natural History.’[2]
The Baudin expedition departed Le Havre, France, on 19 October 1800. Because of delays in receiving his instructions and problems encountered in Isle de France (now Mauritius) they did not reach Cape Leeuwin on the south-west corner of the continent until May 1801. Upon rounding Cape Naturaliste, they entered Geographe Bay. During their exploration here they lost a longboat and a sailor, Assistant Helmsman Timothée Vasse. They then sailed north, but the ships became separated and did not meet again until they reached Timor. On their journeys the Géographe and the Naturaliste surveyed large stretches of the north-western coast. The expedition was severely affected by dysentery and fever, but sailed from Timor on 13 November 1801, back down the north-west and west coast, then across the Great Australian Bight, reaching Tasmania on 13 January 1802. They charted the whole length of Tasmania's east coast and there were extensive interactions with the Indigenous Tasmanians, with whom they had peaceful relationships. They notably produced precious ethnological studies of Indigenous Tasmanians.
The expedition then began surveying the south coast of Australia,[3] but then Captain Jacques Felix Emmanuel Hamelin in Naturaliste decided to make for Port Jackson (Sydney) as he was running short of food and water, and in need of anchors. En route, in April 1802, Hamelin explored the area of Western Port, Victoria, and gave names to places, a number of which have survived, for example, Ile des Français is now called French Island.
Meanwhile, Baudin in the Géographe continued westward, and in April 1802 encountered the British ship Investigator commanded by Matthew Flinders, also engaged in charting the coastline, at Encounter Bay in what is now South Australia. Flinders informed Baudin of his discovery of Kangaroo Island, St. Vincent’s and Spencer’s Gulfs. Baudin sailed on to the Nuyts Archipelago, the point reached by 't Gulden Zeepaert in 1627 before heading for Port Jackson as well for supplies.
In late 1802 the expedition was at Port Jackson, where the government sold 60 casks of flour and 25 casks of salt meat to Baudin to resupply his two vessels. The supplies permitted Naturaliste to return to France and Géographe to continue her explorations of the Australian coast.[4] Naturaliste took with her the Colony's staff surgeon, Mr. James Thomson, whom Governor Philip Gidley King had given permission to return to England.[5]
Before resuming the voyage Baudin purchased a 30 ton schooner, which he named the Casuarina, a smaller vessel which could conduct close inshore survey work. He sent the larger Naturaliste under Hamelin back to France with all the specimens that had been collected by Baudin and his crew. As the voyage had progressed Louis de Freycinet, now a Lieutenant, had shown his talents as an officer and a hydrographer and so was given command of the Casuarina. The expedition then headed for Tasmania and conducted further charting of Bass Strait before sailing west, following the west coast northward, and after another visit to Timor, undertook further exploration along the north coast of Australia. Plagued by contrary winds, ill health, and because 'the quadrupeds and emus were very sick',[6] it was decided on 7 July 1803 to return to France. On the return voyage, the ships stopped in Mauritius, where Baudin died of tuberculosis on 16 September 1803. The expedition finally reached France on 24 March 1804.
The scientific expedition was considered a great success, with more than 2500 new species discovered.
Outcomes

An inscription on a rock was left by members of Géographe on Kangaroo Island, in 1803, which reads, "Expédition de découverte par le commendant Baudin sur le Géographe, 1803", i.e. "Expedition of discovery by Captain Baudin in the Géographe, 1803". To protect it from erosion, the original rock is now housed at the Gateway Visitor Information Centre on Howard Drive, Penneshaw. Many Western Australian places still have French names today from Baudin's expedition: for example, Peron Peninsula, Depuch Island, Cape Levillain, Boullanger Island and Faure Island; and the Australian plant genus Guichenotia honours the name of Antoine Guichenot.
According to researchers from the University of Adelaide, during this expedition Baudin prepared a report for Napoleon on ways to invade and capture the British colony at Sydney Cove.[7][8] The Baudin expedition was intended to be a voyage of discovery that would further scientific knowledge and perhaps eclipse the achievements of Captain James Cook.
Crew
Among those joining the Baudin expedition were Sub-lieutenants Louis-Claude (Louis) de Saulses de Freycinet and his older brother Henri-Louis (Henri). Louis did not initially sail as a ‘geographer’. Both were eventually promoted to Lieutenant, and Louis was later given command of the schooner Casuarina, purchased in Sydney to enable improved inshore surveying. Another member of the expedition, someone who was ultimately to have a highly significant influence on its outcomes, was the 25-year-old assistant zoologist François Péron.
Officers and sailors
Captains: Nicolas Thomas Baudin (1754–1803) (Géographe) and Jacques Félix Emmanuel Hamelin (1768–1839) (Naturaliste).
Surgeon-Physician and naturalist: Pierre François Keraudren (1769–1858) (Le Géographe)(Preparations not on board)
Sub-lieutenants Louis de Freycinet and, his older brother, Henri-Louis de Freycinet
Sailors: Hyacinthe de Bougainville, midshipman second-class, and François-Antoine Boniface Heirisson, midshipman; Charles Baudin, midshipman.
Scientists and artists
A total of 24 various scientists and artists including five gardeners accompanied Baudin on the expedition. It was an unprecedented number to be assembled for a voyage at the time. However, after only six months at sea, and before reaching Australia, ten of the group were disembarked at Mauritius mainly due to illness. Subsequently, five others died. In fact, only six of the original group of scientists and artists would complete the journey home.
| Name | Profession | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Bailly, Charles | Zoologist | |
| Bernier, Pierre-François | Astronomer | Died at sea, 6 June 1803 |
| Bissy, Frédéric | Astronomer | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Boullanger, Charles-Pierre | Hydrographer | |
| Caguet, François | Gardener | Disembarked at Mauritius, 20 April 1801 |
| Delisse, Jacques | Botanist | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Depuch, Louis | Mineralogist | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 3 February 1803, where he died some days later |
| Dumont, Désiré | Zoologist | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Faure, Pierre | Geographer | Disembarked at Mauritius, 15 December 1803 |
| Garnier, Michel | Painter (de genre) | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Guichenot, Antoine | Gardener | |
| La Tour, Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de | Botanist | Left ship at Timor due to illness, 2 June 1803 |
| Lebrun, Louis | Technical draughtsman (Dessinateur-architecte) | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Lesueur, Charles-Alexandre | Painter (natural history) | |
| Levillain, Stanislas | Zoologist | Died at sea, 29 December 1801 |
| Mauge, René | Zoologist | Died at Maria Island, 21 February 1802 |
| Merlot | Gardener | Disembarked at Mauritius, 20 April 1801 |
| Michaux, André | Botanist | Disembarked at Mauritius, 20 April 1801 |
| Milbert, Jacques | Painter (landscape) | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Péron, François | Zoologist | |
| Petit, Nicolas-Martin | Painter (de genre) | |
| Riedlé, Anselme | Gardener (Chief) | Died at Timor, 21 October 1801 |
| Saint-Vincent, Bory de | Zoologist | Left ship at Mauritius due to illness, 25 April 1801 |
| Sautier, Antoine | Gardener | Died at sea, 15 November 1801 |
Publications
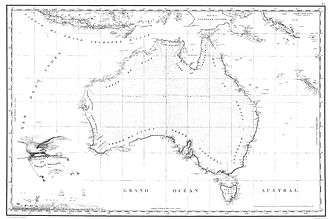
- François Péron, Voyage de découvertes aux terres australes (‘Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Lands’, three volumes, Paris, 1807–1816); this work included the Freycinet Map of 1811, the first published map showing the full outline of Australia
- Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot, Nouveau dictionnaire d'histoire naturelle (‘New Dictionary of Natural History’, 1816–1819): new bird species described
- Jacques Labillardière, Novae Hollandiae Plantarum Specimen (‘Specimens of the Plants of New Holland’, 1804–1806)
Collections
Over 200,000 specimens from the expedition were deposited in Muséum national d'histoire naturelle (zoology) and Jardin des Plantes (botany). Live plants, animals and birds were also sent to Empress Josephine Bonaparte's gardens at Château de Malmaison.
See also
References
- ↑ Horner, 1986, p.40
- ↑ ‘Plan of Itinerary for Citizen Baudin’ in Baudin, 2004, p.1.
- ↑ M.L. Freycinet, Carte Générale de la Nouvelle Hollande dressée par M. L. Freycinet Commandant de la Goëllette le Casuarina, An 1808. Louis Freycinet, Atlas Historique, Paris, 1811.
- ↑ Historical records of Australia (1915), Series 1 v.3 1801/02, p.600.
- ↑ Historical records of Australia (1915), Series 1 v.3 1801/02, p.718.
- ↑ Baudin p.561.
- ↑ "Sacre bleu! French invasion plan for Sydney". ABC News. 10 December 2012.
- ↑ Jean Fornasiero and John West-Sooby (transl. and eds.), French Designs on Colonial New South Wales: François Péron’s Memoir on the English Settlements in New Holland, Van Diemen’s Land and the Archipelagos of the Great Pacific Ocean, The Friends of the State Library of South Australia Inc., Adelaide, 2014. ISBN 9781876154738
- ↑ Péron, F. and Freycinet, L. (1816)Voyage de Découvertes aux Terres Australes, exécuté sur les corvettes Le Géographe, Le Naturaliste, et La Goëlette Le Casuarina, pendent les années 1800, 1801, 1802, 1803 et 1804; Historique: Tome Second. Internet Archive.
Further reading
- François Péron, Voyage de découverte aux terres Australes (3 volumes, Paris, 1807–1816)
- François Péron, A Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Hemisphere: Performed by Order of the Emperor Napoleon, During the Years 1801, 1802, 1803, and 1804, London, Richard Phillips, 1809.
- Christine Cornell (ed. & transl.), The Journal of Post Captain Nicolas Baudin, Adelaide, Friends of the State Library of South Australia, 1974.
- Horner, F. The French Reconnaissance: Baudin in Australia 1801—1803, Melbourne University Press, Melbourne, 1987 ISBN 0-522-84339-5.
- Jack Horner, "Extracting the truth about Baudin. -and his expedition to Australia, 1800-1804", Canberra Historical Journal, no.21, Mar 1988, pp. 42–44.
- Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot (1748–1831), Nouveau dictionnaire d'histoire naturelle (1816–1819)
- Jacqueline Bonnemains, Elliott Forsyth, Bernard Smith, Baudin in Australian Waters: The Artwork of the French Voyage of Discovery to the Southern Lands, 1800-1804, New York, Oxford U. Pr. with Australian Acad. of Sci., 1988.
- Madeleine Ly-Tio-Fane et Jacqueline Bonnemains, Le Géographe et Le Naturaliste à L’Ile-de-France 1801, 1803, Ultime Escale du Captaine Baudin: Deuxième Partie, Le Voyage de Découvertes aux Terres australes, Port Louis [Mauritius], MSM Limited, 2003.
- Steve Reynolds, Nicolas Baudin's Scientific Expedition To The Terres Australes, Marine Life Society of South Australia Journal, no.12, December 2001.
- Fornasiero, Jean; Monteath, Peter and West-Sooby, John. Encountering Terra Australis: the Australian voyages of Nicholas Baudin and Matthew Flinders, Kent Town, South Australia, Wakefield Press, 2004. ISBN 1-86254-625-8
- Jean Fornasiero and John West-Sooby, "Baudin's Books", Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol.39, Issue 2, May 2002, pp. 215–249.
- Jean Fornasiero, Peter Monteath and John West-Sooby, "Old quarrels and new approaches: Nicolas Baudin and Matthew Flinders", South Australian Geographical Journal, v.106, 2007, pp. (1)-15.
- Jean Fornasiero, ‘Deux observateurs del'homme aux Antipodes: Nicolas Baudin et François Péron’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- John West-Sooby, « Le "Sourire Grinçant" du Capitaine Baudin», Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 79–97.
- Jane Southwood and Donald Simpson, "Baudin's Doctors: French Medical Scientists in Australian Waters, 1801-1803", Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 152–164.
- J. P. Faivre, "De Nouveau sur L'expedition Baudin?", Revue Francaise d'Histoire d'Outre-Mer, Vol. 52, Issue 187, 1965, pp. 286–290.
- Robert J. King, "Jorgen Jorgensen and the Baudin Expedition", The Great Circle, Vol. 23, Issue 2, December 2001, pp. 44–52.
- Michel Jangoux, « La Premiere Relache Du 'Naturaliste' au Port Jackson (26 Avril-18 Mai 1802): le Temoignage du Capitaine Hamelin », Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 126–151.
- Michel Jangoux, « Les Zoologistes et Botanistes qui Accompagnerent le Capitaine Baudin aux Terres Australes», Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 55–78.
- Jangoux, Michel. Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- Michèle BATTESTI, ‘Nicolas Baudin, membre de l’état major du vice-amiral Bruix (mai/août 1799)’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- Jean Luc CHAPPEY, ‘Nicolas Baudin et la Société des Observateurs de l’Homme’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- Frédéric DURAND, ‘Les tristes escales timoraises de Nicolas Baudin’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- Claude WANQUET, ‘L’île de France au début du XIXe siècle 1800, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- Bernard METIVIER , ‘Lamarck et les invertébrés de l'expédition de découvertes aux Terres australes’,in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- François MOUREAU, ‘Bernardin de St Pierre, Nicolas Baudin et l’île de France : une rencontre improbable’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- José OLIVER, ‘Ténériffe, île-relâche des grands voyages d’exploration’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- R.Kingston, A not so Pacific voyage: the ‘floating laboratory’ of Nicolas Baudin, Endeavour, vol. XXXI, no. 4, December 2007, pp. 145–151. elsevier.com
- Jacques Vialle, « Le Destin Tragique de Pierre-François Bernier, Astronome de L'expedition Baudin », Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 165–170.
- Christian Jouanin, «Nicolas Baudin Charge de Reunir une Collection pour la future Imperatrice Josephine», Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 43–54.
- B. S. Baldwin, "Flinders and the French", Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society of Australasia. South Australian Branch, v.65, 1963–1964, pp. 53–67.
- B. S. Baldwin, "Publication of Baudin's Journal", South Australiana, Vol. 13, Issue 1, 1974, pp. 34–42.
- William P.Helling, "Redistributing the Blame: Baudin's Voyage to the Australian Seas", The Great Circle, Vol. 15 Issue 2, December 1993, pp. 107–127.
- Margaret Sankey, "The Aborigines of Port Jackson, as seen by the Baudin Expedition", Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. p117-125.
- Margaret Sankey, "The Baudin Expedition in review: old quarrels and new approaches", Australian Journal of French Studies, Vol. 41, Issue 2, May 2004, pp. 4–14.
- Margaret Sankey, "Writing the Voyage of Scientific Exploration: The Logbooks, Journals and Notes of the Baudin Expedition (1800-1804)", Intellectual History Review, Vol. 20 Issue 3, September 2010, pp. 401–413.
- Margaret Sankey, ‘La contribution des journaux de bord au travail ethnographique de l’expédition Baudin’, in Portés par l'air du temps: les voyages du Capitaine Baudin: Etudes sur le 18e siècle, vol.38, Bruxelles, Editions de l'Université de Bruxelles, 2010.
- Wolf Mayer, "The Geological Work of the Baudin Expedition in Australia (1801-1803): the Mineralogists, the Discoveries and the Legacy", Earth Sciences History, Vol. 28 Issue 2, 2009, pp. 293–324.
- Gregory C. Eccleston, "The neglect of Baudin’s manuscript charts of the Victorian coastline", The Globe, no.66, 2010, pp. 27–58.
- Trevor Lipscombe, "Two continents or one?: the Baudin expedition's unacknowledged achievements on the coast of Victoria", Victorian Historical Journal, v.78, no.1, May 2007, pp. 23–41.
- R. M. Barker, "The botanical legacy of 1802: South Australian plants collected by Robert Brown and Peter Good on Matthew Flinders' Investigator and by the French scientists on Baudin's Geographe and Naturaliste", Journal of the Adelaide Botanic Gardens, v.21, 31 January 2007, pp. 5–44.
- Anthony J. Brown, "Friends of humanity: the scientific origins, objectives and outcomes of the voyages of Nicolas Baudin and Matthew Flinders", South Australian Geographical Journal, v.98, 1999, pp. 52–60.
- Paul Fregosi, "Terre Napoleon: French colonial ambitions in Australia, 1793-1815", Quadrant (Sydney), v.32, no.6, June 1988, pp. 56–59.
- Leslie R.Marchant, "The Baudin expedition 1800-04 and the French scientific exploration of Australia", Early Days, v.9, no.6, 1988, pp. 65–72.
- Leslie R. Marchant, "The Baudin scientific mission of exploration and the French contribution to the maritime discovery of Australia", The Globe, no.23, 1985, pp. 11–31.
- Brian Plomley, "The French in D'Entrecasteaux Channel, 1802", Tasmanian Tramp, no.24, 1982/ 1983, pp. 17–27.
- N. J. B. Plomley, "The French in Van Diemen's Land: organisation and the fruits of discovery", Bulletin of the Centre for Tasmanian Historical Studies, v.2, no.1, 1988, pp. 4–21.
- N. J. B.Plomley, "Pre-settlement exploration of Tasmania and the natural sciences: The Clive Lord Memorial lecture 1983", Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania, v.118, Aug 1984, pp. 69–78.
- Miranda Hughes, "Tall tales or true stories: Baudin, Peron, and the Tasmanians, 1802", Nature in its Greatest Extent: Western Science in the Pacific. 1988, pp. 65–86.
- Miranda J.Hughes, "Philosophical travellers at the ends of the earth: Baudin, Peron and the Tasmanians", Australian Science in the Making, 1990, pp. 23–44.
- John Pearn, "French doctors at Sydney Cove: Gallic contact in the second decade after Phillip", Australia's Quest for Colonial Health: Some Influences on Early Health and Medicine in Australia, 1983, pp. 45–61.
- Phyllis Mander-Jones, "The artists who sailed with Baudin and Flinders", Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society of Australasia. South Australian Branch, v.66, 1964–1965, pp. 17–31.
- Rupert Gerritsen and Peter Reynders, "The Freycinet Map of 1811 − is it the First Complete Map of Australia?", Journal of Australian Naval History, vol.8, no.2, September 2011, pp. 8–29
- Sarah Thomas, The Encounter, 1802: Art of the Flinders and Baudin Voyages, Adelaide: Art Gallery of South Australia, 2002.
- Nicole Starbuck, "Nicolas Baudin: La relâche à Sydney et la deuxième campagne du Géographe", Michel Jangoux (ed.), Portés par l'air du Temps: les voyages du capitaine Baudin, in Etudes sur le 18e siècle, Bruxelles, vol.38, 2010, pp. 133–144.
- Nicole Starbuck, Baudin, Napoleon and the Exploration of Australia, London, Pickering & Chatto, 2013.