Eclipse of Thales
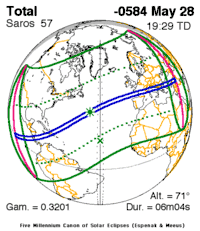
The Greek philosopher Thales of Miletus accurately predicted a solar eclipse, according to The Histories of Herodotus. If Herodotus's account is accurate, this eclipse is the earliest recorded as being known in advance of its occurrence. Many historians believe that the predicted eclipse was the solar eclipse of May 28, 585 BC.[1] How exactly Thales predicted the eclipse remains uncertain; some historians claim the eclipse was never predicted at all.[2] Others have argued for different dates.[3]
According to Herodotus, the appearance of the eclipse was interpreted as an omen, and interrupted a battle in a long-standing war between the Medes and the Lydians. The fighting immediately stopped, and they agreed to a truce. Because astronomers can calculate the dates of historical eclipses, Isaac Asimov described this battle as the earliest historical event whose date is known with precision to the day and described the prediction as "the birth of science".[4]
Herodotus' account
Herodotus' The Histories 1.73-74 states that a war started in the period between the Medes and the Lydians. There were two reasons for the war; the two sides' clashing interests in Anatolia, but also there was a motive of revenge. Some Scythian hunters employed by the Medes who once returned empty-handed were insulted by King Cyaxares. In revenge the hunters slaughtered one of his sons and served him to the Medes. The hunters then fled to Sardis, the capital of the Lydians. When Cyaxares asked for the Scythians to be returned to him, Alyattes II refused to hand them over; in response, the Medes invaded.
Afterwards, on the refusal of Alyattes to give up his suppliants when Cyaxares sent to demand them of him, war broke out between the Lydians and the Medes, and continued for five years, with various success. In the course of it the Medes gained many victories over the Lydians, and the Lydians also gained many victories over the Medes. Among their other battles there was one night engagement. As, however, the balance had not inclined in favour of either nation, another combat took place in the sixth year, in the course of which, just as the battle was growing warm, day was on a sudden changed into night. This event had been foretold by Thales, the Milesian, who forewarned the Ionians of it, fixing for it the very year in which it actually took place. The Medes and Lydians, when they observed the change, ceased fighting, and were alike anxious to have terms of peace agreed on.[5]
As part of the terms of the peace agreement, Alyattes's daughter Aryenis was married to Cyaxares's son Astyages, and the Halys River (now known as the Kızılırmak River) was declared to be the border of the two warring nations.
An alternative theory regarding the date of the battle suggests that Herodotus was recounting carelessly events that he did not witness personally, and that furthermore the solar eclipse story is a misinterpretation of his text.[6] According to this view, what happened could have been a lunar eclipse right before moonrise, at dusk. If the warriors had planned their battle activities expecting a full moon as in the previous few days, it would have been quite a shock to have dusk fall suddenly as an occluded moon rose. If this theory is correct, the battle's date would be not 585 BC (date given by Pliny based on date of solar eclipse), but possibly 3 Sept 609 BC or 4 July 587 BC, dates when such dusk-time lunar eclipses did occur.[6]
Thales' prediction
While doubt has been cast on the truth of the story, there are other accounts of it besides that of Herodotus. Diogenes Laertius says that Xenophanes, who lived in the same century as Thales, was impressed with the prediction, and he also gives additional testimonies from the pre-Socratics Democritus and Heraclitus.[7]
At the time of Thales' purported prediction it was not yet known that eclipses were caused by the Moon coming between the Earth and the Sun, a fact that would not be discovered until over a century later by either Anaxagoras or Empedocles.[8]
If the account is true, it has been suggested that Thales would have had to calculate the timing of any eclipse by recognizing patterns in the periodicities of eclipses.[7] It has been postulated that Thales may have used the Saros cycle in his determination, or that he may have had some knowledge of Babylonian astronomy, but as there is no known cycle that can be reliably used to predict an eclipse for a given location, any accurate prediction would have been down to luck.[7]
The eclipse
The eclipse peaked over the Atlantic Ocean at 37°54′N 46°12′W / 37.9°N 46.2°W and the umbral path reached south-western Anatolia in the evening hours, and the Halys River is just within the error margin for delta-T provided.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ (This date is based on the proleptic Julian calendar, which does not include a "year zero"; astronomically the year is -584.)
- 1 2 Eclipse path map from NASA http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsearch/SEsearchmap.php?Ecl=-05840528
- ↑ Stephenson, F. Richard, and Louay J. Fatoohi. "Thale's Prediction of a Solar Eclipse." Journal for the History of Astronomy 28 (1997): 279
- ↑ "Happy Birthday to Science", by Tom Mandel, at the Chicago Sun-Times (archived at HighBeam Research); published May 28, 1990; retrieved April 11, 2014
- ↑ The Histories. Herodotus.
- 1 2 Thomas D. Worthen, "Herodotus's Report on Thales's Eclipse," Electronic Antiquity vol. 3.7 (May 1997), and Thomas De Voe Worthen, "The Eclipse of 585 BCE"
- 1 2 3 Panchenko, D. (2004). "Thales's Prediction of a Solar Eclipse". Journal for the History of Astronomy: 275–.
- ↑ Westfall, John; Sheehan, William (2014). Celestial Shadows: Eclipses, Transits, and Occultations. Springer. p. 109. ISBN 978-1-4939-1535-4.
- K. Leloux, "THE BATTLE OF THE ECLIPSE (MAY 28, 585 BC): A Discussion of the Lydo-Median treaty and the Halys border", in Polemos, 19-2 (2016), p. 31-54
- Alden A. Mosshammer, "Thales' Eclipse", Transactions of the American Philological Association, Vol. 111, 1981, pp. 145–155 (JSTOR)
- G. B. Airy, "On the Eclipses of Agathocles, Thales, and Xerxes", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Vol. 143, 1853, pp. 179–200
- Herodotus, The Histories, translated by Robin Waterfield, (1998). New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-282425-2
- Tony Jacques: Dictionary of Battles And Sieges: A Guide to 8,500 Battles from Antiquity Through the Twenty-first Century. F-O Greenwood Publishing Group 2007, ISBN 0-313-33536-2, p. 428 (Auszug, p. 428, at Google Books)
