Battery "E", 1st Regiment Illinois Volunteer Light Artillery
| Battery "E", 1st Regiment Illinois Volunteer Light Artillery | |
|---|---|
|
Illinois flag | |
| Active | December 19, 1861 to July 15, 1865 |
| Country | United States |
| Allegiance | Union |
| Branch | Artillery |
| Engagements |
Battle of Shiloh 1st Battle of Corinth Vicksburg Campaign Expedition to Oxford, MS Battle of Jackson, Mississippi Siege of Vicksburg Jackson Expedition Battle of Mechanicsville, MS Expedition to Canton, MS Battle of Wyatt, TN Battle of Brice's Crossroads Battle of Pontotoc, MS Battle of Tupelo Price's Missouri Raid Franklin-Nashville Campaign Battle of Nashville |

Battery "E", 1st Regiment Illinois Volunteer Light Artillery was an artillery battery that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It played a minor but noteworthy role in the Battle of Shiloh—being mentioned specifically in General William T. Sherman's After-Action report on the battle—and also served in several other battles in the Western Theater of the war.
Recruitment
Battery "E" was mustered into service at Camp Douglas, in Chicago, Illinois, on December 19, 1861. Its members came primarily from Cook County. On February 13, 1862, they moved to Cairo, where they were issued with horses, artillery and other necessary equipment.[1]
A photo of the original Battery E flag may be seen here.
Battle of Shiloh
Initial deployment
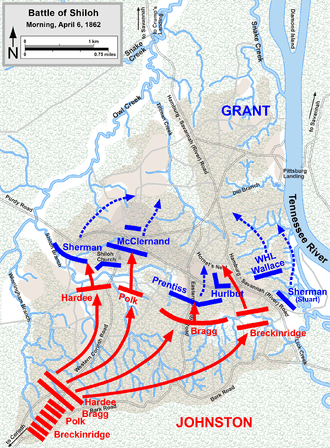
On March 27, 1862, Battery E travelled by boat to Pittsburg Landing, Tennessee, arriving on the 30th.[2] Joining Brig. General William T. Sherman's Fifth Division in Ulysses S. Grant's Army of the Tennessee (together with its sister unit, Battery "B"), the battery was not assigned to a specific brigade during the upcoming Battle of Shiloh, on April 6–7, 1862.[3][4]
During this engagement, Battery E fielded four James Rifles, a rifled bronze artillery piece that proved popular during the early stages of the war, but later fell out of favor due to the excessive wear that combat service imposed upon rifled bronze cannon. According to one history of this engagement, Battery E was entirely inexperienced, having received its horses only ten days before the battle, and having drilled with them only three times.[5]

According to General Sherman's After-action report, he placed Battery E on a ridge to the left of Shiloh Church, covering a section of open ground between the 57th Ohio Infantry and the 53rd Ohio, near a house called the Rea Cabin.[7][8] It was the 53rd Ohio's colonel, Jesse J. Appler, who had earlier tried to warn Sherman of large Confederate forces to his front, only to be told: "Take your damned regiment back to Ohio. There is no enemy nearer than Corinth!"[9] The next morning would prove Sherman fatally wrong, as his division and the rest of the Union Army were attacked during breakfast by a large Confederate force under General Albert Sidney Johnston.
During the coming battle, Battery E would be engaged in turn by elements of Patrick Cleburne's Second Brigade of Johnston's Third Corps, which was under the command of General William Hardee,[10] and by elements of S.A.M. Wood's Third Brigade of the same corps, and later by elements of Patton Anderson's Second Brigade of the First Division of Braxton Bragg's Second Corps. Later, still, the battery would be engaged by two brigades from Leonidas Polk's First Corps, commanded by Bushrod Johnson and Robert M. Russell.[11] Thus, Battery E would face units from all three of Johnston's main Army Corps, during the course of the engagement.
The battle begins
When the battle began, one section (two guns) of Battery E deployed just to the right of the 53rd, which had abandoned its camp and moved into the edge of a treeline facing an open field. The other section remained to the left of the 53rd, as originally deployed. Across this field, Confederates of the 6th Mississippi Infantry and the 23rd Tennessee advanced rapidly toward them.[12] Twelve Confederate guns from Shoup's Arkansas Battery opened up on the Federals,[13] and after firing two rounds in reply, the section that had originally moved to the right was ordered by Sherman's chief of artillery, Major Ezra Taylor, to rejoin the rest of Battery E, on high ground to the left of the 53rd on the other side of Rea Springs and the east fork of Shiloh Branch.[14]
Sherman, who was on the scene as this attack unfolded, ordered Appler to hold his portion of the line, telling him that he had "a good battery" (E Battery) to protect him; he also sent for three additional regiments to protect "Waterhouse's Battery" (Battery E) and the left flank of his line.[15] Sherman later reported that Battery E and a companion battery further off to the right opened up "promptly" on the advancing Confederates along with the assembled infantry, and in Sherman's words: "the battle became general".[16] Battery E, together with Battery B of the 1st Illinois, fired into the Confederates advancing up the ridge toward Sherman's line, as well as on reinforcements crossing Rea Field to their front to aid in the assault.[17]
The following is from Major Ezra Taylor's after-action report:
Although inflicting severe losses on the attacking Southerners,[19] Appler's regiment ultimately broke and ran when its colonel lost his nerve, leaving Battery E unprotected and facing imminent annihilation by the Confederates.[20] Wood's Confederates obliqued to the right to avoid Battery E's fire; they were quickly replaced in turn by Cleburne's and Anderson's brigades,[21] which took horrendous losses at the hands of three Illinois regiments, including the 43rd Illinois, which immediately advanced to assist the artillerists[22]—until they too ultimately broke under the ferocity of the Southern assault led now by elements from Cleburne, Anderson, Russell and Johnson's brigades,[23] including the 13th Tennessee.[24]
Retreat and regroup
Viewing the imminent disintegration of his command, Sherman ordered the remnants of his division, including Battery E, to pull back and regroup on the Hamburg-Purdy Road, about 600 yards behind their then-current position.[25] However, the battery had hardly made 100 yards before Major Taylor rode up and ordered it to unlimber and resume firing, insisting that every inch of ground had to be contested:
Captain Waterhouse's attempt to comply with Major Taylor's order cost him three of his four guns, and resulted in both he and his First Lieutenant being wounded.[27][28] According to David Reed's history of the Battle, Battery E was engaged on its front by several different Rebel regiments, while the 13th Tennessee flanked it on the left side and came up on it from the rear, capturing the guns as the battery members beat a hasty retreat.[29] Colonel (later General) Alfred Vaughan, commanding the 13th Tennessee, reported that when his regiment took possession of Battery E's guns, they found "a dead Union officer [lying] near them, with a pointer dog that refused to allow the Confederates to approach the body."[30]
The remainder of Sherman's division (including the members of Battery E, minus their three lost guns) finally stabilized their lines in conjunction with General John A. McClernand's First Division. The following morning the Federals counterattacked and the Southern army was forced to retreat to Corinth, leaving the exhausted Northerners victors in the bloodiest battle that America had seen up to that time.[31]
After the fight
Sherman reported that during the battle, his division had managed to capture seven guns to replace those lost to the enemy (three by Battery E, and four from other units) earlier in the engagement; thus Battery E was able to be re-equipped with this captured ordinance.[32] All told, the battery lost one man killed and sixteen wounded, plus one missing, during the two-day engagement.[33]
Historians Mark Grimsley and Steven Woodsworth reported that Battery E had performed "magnificently" during the battle, making "an important contribution to prolonging Sherman's stand here." "This is all the more remarkable," they go on to say, "considering the complete lack of experience of Watherhouse's men."[34] Lieutenant J.A. Fitch, who took command of the Battery after Captain Waterhouse was wounded, filed the following after-action report with Major Taylor:
A series of aerial photographs depicting the exact location of "Waterhouse's Battery" and other adjacent units may be seen at Hike Report: The Battle For Shiloh Church. Ground-level photos may be seen here.
Corinth to White Station
Corinth and subsequent movements
Following the Battle of Shiloh, the battery moved with the rest of Sherman's division toward Corinth, Mississippi, which was occupied on May 29, 1862. Following this, they made their way down the Memphis and Charleston Railroad, skirmishing with Confederates along the way, until they reached Memphis, where they went into camp at Fort Pickering. Here they spent their time drilling with their artillery pieces and horses, seeking to improve their efficiency.[36] During this time, the regiment received new recruits, one of whom was Private James Bolton Rice, whose letters to his wife paint a vivid picture of the battery's activities from the time he joined it to late in 1863.[37]
On November 26, Battery E accompanied Sherman's expedition to Oxford, Mississippi, part of a larger operation undertaken by Grant against Confederate General John C. Pemberton's forces entrenched along the Tallahatchie River near Holly Springs.[38][39] Rice reports that the Federal force made twelve miles per day on average, until it encountered Confederate obstructions near College Hill, near Oxford on December 7. These included trees felled across the road, and "every bridge burned."[40]
Private Rice offers a description of a typical day in Battery E during this campaign:


Pemberton's army fell back to Grenada without a fight, so Battery E continued with the rest of its division to Corinth. It entered the town of Holly Springs, Mississippi, sometime prior to January 4, 1863, where Rice describes a scene of devastation left behind by Confederate General Earl van Dorn's raid on the town on December 20, 1862: "broken guns, dead horses, several unburned men, pieces of shells, lights out of every window, government wagons and ambulances half burnt up. The great depot all gone, a train of cars burned upon the track. The air filled [with] the smoke and smell of burning cotton. Large brick buildings blown to atoms, pillaged houses and sick men laying beside the streets."[42]
White Station
Battery E moved through Holly Springs and on to White Station, Tennessee, where it arrived on January 31, 1863 and encamped. In an effort to fight the cold conditions while wintering there in a Sibley tent, Private Rice describes heating two cast-iron wheels weighing forty pounds each in a fire until they became red-hot, then taking them into his tent, where according to him: "...they make it comfortable."[43] During this time of relative quiet, Rice reports one muster where the battery commander asked all of the "weak-kneed ones" to step forward, as "we would be in a fight in only three hours."[44] Four men answered this call—but another trooper who had been ordered to stay behind begged to change places with one of those being sent into battle, even offering "his last dollar" as an incentive, before being refused by every man in the battery.[45] Apparently the battle did not materialize, as Rice makes no further mention of it.
On February 19 and 20, the members of Battery E were witnesses to the burning of Hopefield, Arkansas, a small town across the river whose citizens had taken the Unionist Loyalty oath, but were secretly assisting local Confederate guerrillas. After several Federal soldiers had been murdered in or near the town, four companies of Northern troops attacked Hopefield and burnt the entire city to the ground. Though Battery E did not actively participate in this event, Rice described it as a "long-merited punishment."[46] Returning to Memphis on March 14 of that same year, they took steamboats to Duckport, Louisiana, a (now vanished) landing on the Mississippi River a few miles northwest of Vicksburg, Mississippi.[47] Here, they rejoined the rest of Sherman's XV Corps, one of five corps assigned to Ulysses S. Grant's Army of the Tennessee that was then preparing to embark on the famed Vicksburg Campaign.[48]
Sometime during the winter, according to Private Rice, Battery E was reduced from a six-gun battery to a four-gun battery, numbering 128 effectives.[49] During its time at Vicksburg (see below) the battery was brought back up to its usual six-gun size once again.[50]
Vicksburg campaign
Battle of Jackson
On May 2 the battery went to Grand Gulf, Mississippi; from thence they advanced toward Jackson, Mississippi, the capital of the state. Private James Rice reports that the heat during this time was so intense that even "strong men" fell out of the march and "were left with some comrade to die or come on, as the case might be."[51] Dead horses and mules lay everywhere along the line of march, and Rice reports that Battery E lost six of its own horses to "sunstroke, and drinking poisoned water."[52] Reaching Jackson on May 10, Battery E and the rest of their corps were appalled to discover that the Confederates had disemboweled numerous mules and hogs, then thrown their carcasses into every pond and well to contaminate the water.[53] The air, said he, was filled with the stench of dead animals and members of Battery E and others were detailed over the next two days to bury all the carcasses in the area.[54]
Starting on May 10, Battery E commenced bombardment of the Confederate works at Jackson, beginning at 7am on that Sunday morning. Private Rice reported a bright sunny day, and said that fire and counter-battery fire continued for three hours "as if the heavens were at war with one another, and about to part."[55] Rice himself was nicked by an enemy shell, and others in the battery had what he referred to as "close calls," though no one was seriously hurt.[56]
On May 14, Battery E supported Sherman's final attack on Jackson. Advancing during a driving rainstorm across Lynch Creek—a rain-swollen stream that ran only two miles from the Mississippi State Capitol—the XV Corps quickly ran into the Third Kentucky Mounted Infantry, the First Georgia Sharpshooter Battalion and Captain Martin's Georgia Battery. The Federal advance was temporarily halted by these troops and by enemy artillery fire, before Battery E and a companion battery from the 2nd Iowa responded in kind.[57] One Illinois soldier briefly described Battery E's role in this battle in these terms:
The "accurate fire" from Battery E and the Iowa artillery, coupled with the overwhelming Federal advantage in manpower, quickly forced the Confederates to retreat into their defensive works; within a matter of a few hours, Sherman's XV Corps had entered Jackson.[59]
.

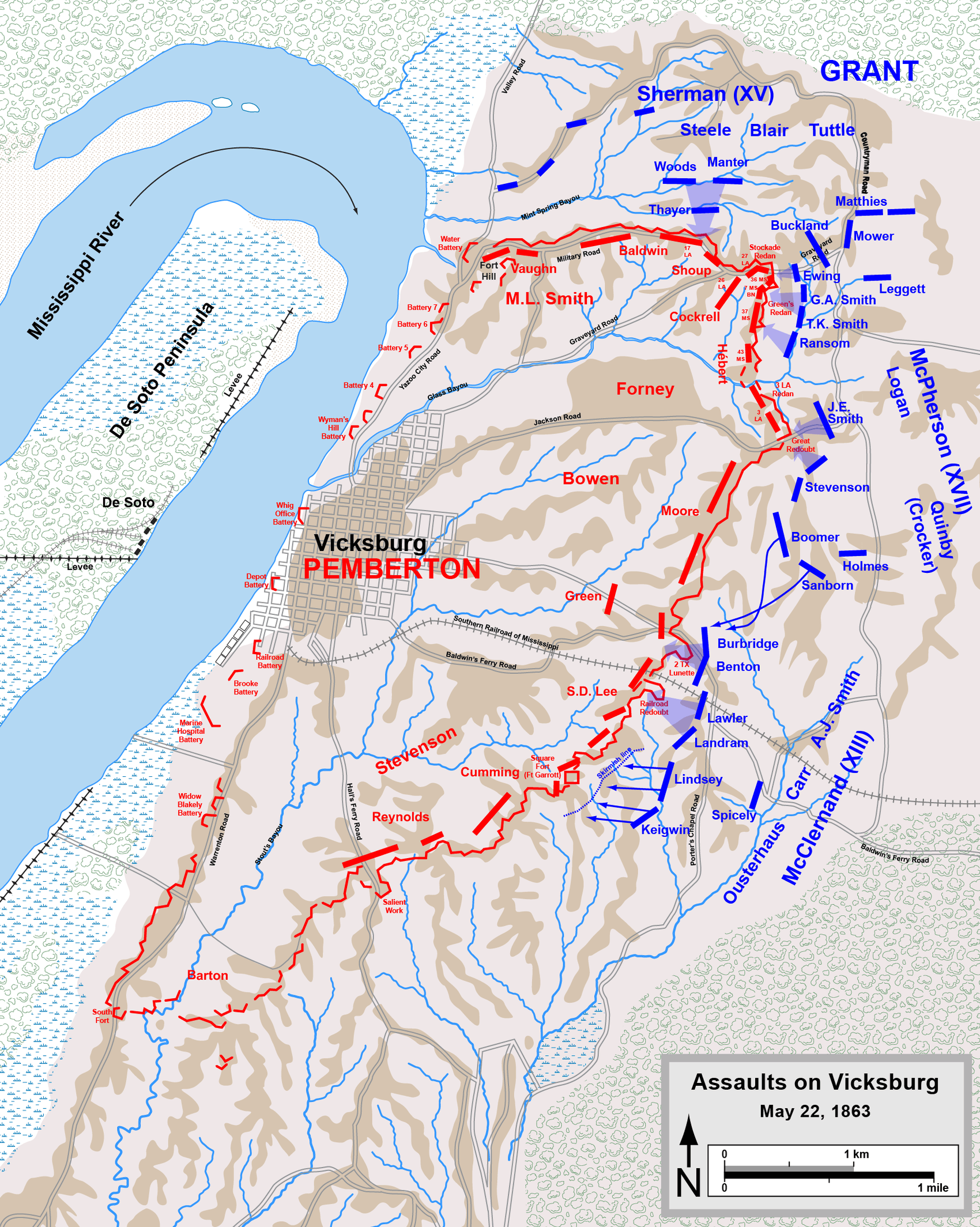
Action at Vicksburg
On May 16, Battery E moved on Vicksburg, the South's "Gibraltar of the West", arriving on the 18th, where it took an active part in the siege as part of the Third Division of Sherman's XV Corps. Together with the 2nd Battery of Iowa Light Artillery, it was assigned as the division's artillery force.[60] During this time, the battery fielded four James Rifles and three captured 6-pound guns in a spot near the northeast corner of the Confederate defensive line (currently located along Old Graveyard Road, between Union Ave. and Confederate Ave.).[61] The battery supported the abortive Federal assault upon the "Stockade Redan" on May 22, which resulted in more than a thousand Federal casualties, and led to the awarding of 78 Medals of Honor to attacking soldiers.[62] A photo of the exact location of Battery E's position at Vicksburg may be seen here. The larger page from which this photo was taken may be viewed here.
On May 30, the battery was given a 30-pount Parrott rifle, which it retained until 3 June, when the Parrott gun was moved to a more advanced position at "Battery Jenny."[63]
On 5 June, Battery E was ordered to trade its old artillery pieces in for six new 12-pound guns.[64] The battery was divided into three two-gun sections; two, under Lieutenants John Fitch and Orrin Cram, remained on the line. The third was moved up to an advanced battery.[65] By 7 June, Private Rice reported to his wife that the battery had been split between five different places, and only counted 96 men as fit for duty.[66]
In contrast to the starving Confederates inside Vicksburg—whose lack of food ultimately doomed their defense of the city, rather than the unsuccessful Federal assaults on their defenses[67]—Battery E and the rest of the Union Army fared well with regard to victuals during the siege. Rice reported that he had to eat here: "flour, tea, coffee, sugar, hardtack, pork, dried apples, rice, beans and fresh beef every other day."[68] He said that his favorite food was "flour and water mixed together as you would make batter, fry it in grease with meat, a cup of coffee, a hardtack and sugar; I make out a hearty meal."[69]
Artillerists as infantry
Members of Battery E sometimes played the role of sharpshooters and even infantry during the siege, as Private Rice relates:
On 22 June Battery E relocated with two brigades of infantry from its 3rd Division to Bear Creek on the exterior line, where it remained until Vicksburg was surrendered by General Pemberton on July 4, 1863.[71] Throughout the siege, the Battery lost two killed and six wounded.
Later operations in Mississippi
Expedition to Brandon, Mississippi
On July 5, 1863, the day after Vicksburg's surrender, a detachment from Battery E was ordered with elements from the 72nd Ohio Infantry, the 114th Illinois, the 8th Iowa and the 9th Iowa under the command of General Frederick Steele to proceed to Brandon, Mississippi, where they were to locate and burn Confederate military stores and destroy the local railroad. The battery lost one of its three guns while crossing a pontoon bridge over the Pearl River, but the gun was recovered the next day.[72] Encountering Southern cavalry about six miles past the bridge, the battery's "war dogs" (to quote Private Rice) quickly drove them back.[73]
Upon receiving reports from scouts that an enemy battery was on a nearby hill, Battery E was ordered to shell the hillside in an effort to discern the enemy's position. Private Rice describes what happened next:
Riding into Brandon, Battery E fired on Confederate scouts in a house there, "knocking out every window in the house."[75] They set fire to a storehouse and burned down an entire block of the town, then turned their attention to the railroad depot and nearby trackage, which they equally destroyed.[76]
Return to Jackson

Following this event, Battery E returned to Jackson (which had been reoccupied by Confederate forces). Though harassed during their march by Southern units, Private Rice reported that they "kept out of range of our brass band. For... when we play 'Dixie' on it, it makes them more than dance."[77] Upon arriving at Jackson, it assisted in a nine-day siege, after which Confederate General Joseph E. Johnson evacuated the city.[78] Private Rice describes Jackson as a "doomed city" in the battle's aftermath, affirming that he and his comrades tore up and burned tracks and ties from five different railroads extending twenty miles out from the city in all directions; he equally describes the devastation wrought by the Federal inside the city itself.[79]
Ordered to return to Vicksburg, Battery E and other units crossed the battlefield at Champion Hill, scene of a Federal victory about two months earlier. Rice describes how rain had washed away the soil used to cover the corpses of Confederate dead (who, says he, had simply been tossed into ditches on the battlefield by Federal troops, and covered with a layer of dirt); he describes men seeing and even kicking at skulls, bones and clothing protruding from the half-opened graves.[80]
Bear Creek
On July 23 Battery E went into camp on Bear Creek, in rear of Vicksburg on Oak Ridge, where Private Rice reports that they were exceptionally troubled by chiggers and flies, not to mention the oppressive summer heat.[81] This became their summer camp, and expeditions were made to Mechanicsburg, Miss., Canton, and other places. On November 5 they went to Vicksburg, and took boat for Memphis, arriving there the 12th. During that winter they went to Lagrange, Tenn.; also, Corinth, Jack Creek, then back again to Corinth, and back to Memphis via Lagrange.[82]
Meridian expedition
On February 6, 1864, Battery E was ordered to cooperate with a 7000-man cavalry column led by General William Sooy Smith moving south from Memphis to link up with General Sherman's forces engaged in the Meridian Expedition; by this point, it had been equipped with six 12-pound Napoleon guns.[83] On the 10th of February 1864, it fought in a skirmish at Wyatt, Tennessee, on the Tallahatchie River. On February 15 the Battery was ordered back to Memphis, and took no further role in the campaign.[84] In Memphis, they camped at the head of Main Street, near the city's Navy Yard. In April 1864 the Battery went to Bolivar, Mississippi, and Ripley in search of General Nathan Bedford Forrest; but their supplies soon ran out, and they were forced to return to Memphis to refit.[85]
Brice's Crossroads and aftermath
June 1, 1864, the battery marched to Guntown, Mississippi, where it took part in the disastrous Battle of Brice's Crossroads on June 10. Here, the battery together with the 9th Minnesota Infantry formed a reserve force deployed near the crossroads itself.[86] Attacked by Confederates under General Forrest on both flanks at once, Colonel William McMillian, commanding the infantry on that portion of the field, ordered Battery E to sweep the Guntown Road with grapeshot and canister.[87] Despite heroic efforts by the 9th Minnesota and other Federal units, the Northern army was pushed back, with Col. McMillian ordering Battery E and Battery B of the Second Illinois Light Artillery to hold off the advancing Rebels until the infantry could escape.[88]
The fleeing Federals became bottled up on a bridge just north of the crossroads, with Confederate artillery raking them as they struggled to cross the narrow structure, upon which the retreat became a rout, and Forrest won one of the greatest victories in his career.[89] Battery E, which had been ordered to hold the crossroads itself at all costs, found itself stranded amidst the advancing Southern attack, deserted by all infantry support—but still firing without letup.[90] Captain John Fitch, commanding the battery in this battle, describes the scene amid the tangled underbrush and forest: "I could not see the enemy, but judged from their firing that they were very near. I immediately gave them canister with both pieces, as fast as I could load and fire."[91] Fitch and the rest of Battery E managed to hold their ground until the last of the Federal regiments had passed, though by this time they were being fired on from front, left and rear—including the garden of a plantation house only seventy-five feet away.[92] Incredibly, Battery E managed to limber its two guns and escape to the nearby creek, where they simply stormed through the water to the safety of a road on the other side.[93]
In his after-action report, Colonel Alexander Wilkin, commanding the 9th Minnesota, commended Captain Fitch of Battery E for the "judicious and gallant manner" in which he and his battery had conducted themselves during the battle.[94] Total losses for this battle were one killed, three wounded and four missing. The battery returned to Memphis after the defeat, "every man for himself", with the men listed as "very much demoralized".[95]
The battery next marched on Tupelo, and July 12 it fought at Pontotoc, Mississippi.[96] On July 13, they were ambushed, and lost one wounded.[97] On the 14th, the battery participated in the Battle of Tupelo, which resulted in a defeat for Forrest.[98]
Actions in Missouri
On July 15, 1864, Battery E returned to Memphis. On September 3, 1864, they took steamboats down the Mississippi to White River Gap and from thence to Duvall's Bluff, Arkansas. Marching through Arkansas swamps to Cape Girardeau under General J. A. Mower, they next travelled up the Missouri River to Jefferson City, Missouri, where they joined in the ongoing Federal pursuit of Confederate General Sterling Price (then engaged in a campaign that became known as Price's Missouri Raid) to the western boundary of the State.[99]
After Price's defeat at the Battle of Westport, the Battery returned to St. Louis, arriving there on November 15, 1864.[100]
Service in Tennessee
After drawing a new complement of horses, Battery E took boats for Nashville, Tennessee, and were with General Thomas during the siege of Nashville and annihilation of Hood's Army.[101]
Muster out
The battery's enlistments expired December 19, 1864, but the battery was not mustered out of service until December 24, 1864, at Louisville, Kentucky.[102] New recruits were brought into replace those who had been discharged; these continued to serve until July 15, 1865, when they were discharged near Chattanooga, Tennessee.[103][104]
Total strength and casualties
The battery lost 5 enlisted men who were killed in action or who died of their wounds and 25 enlisted men who died of disease, for a total of 30 fatalities.[105]
Anecdotes
Camp followers
Private James Bolton Rice, whose letters home to his wife provide a vivid description of life and action in Battery E from 1862 to 1865, gives a picture of the seedier side of life in a Federal army camp during mid-1862:
Rice followed this statement up with his own assurance of loyalty to his wife, telling her that this sight "disgust[s] me more than anything I see in the Army."[107]
On the march
In a letter dated January 22, 1863, Rice describes what it was like to be on the march, on half-rations, in the Federal army:
Needless to say, conditions in the Confederate forces were even worse, as their logistics system was not nearly as well-supplied or developed as its Federal counterpart.[109]
Dissention in the ranks
In another letter, Rice describes the antipathy many Federal soldiers felt following the issuance of Abraham Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation in January 1863:
In subsequent paragraphs, Rice voraciously attacks Northern "Copperheads", referring to them as "damning traitors" and saying they should be "choked down and served as we serve them down here." He goes on to say that four men in his own regiment are Copperheads (in his estimation), describing them as "weak-kneed, weak-backed ones who were scared into the Service through fear of the draft." He ends, however on a note of guarded optimism that the government will overcome the "arch-traitors" and "rise like the morning mist, and show the world that America still stands with its government and institutions stronger better dearer than ever."[111]
Grant and Sherman
During the Siege of Vicksburg, Rice wrote down his impressions of Ulysses S. Grant's generalship, together with his opinion of the rampant rumors of his drunkenness earlier in the war:
Rice later recorded his opinion of William T. Sherman's generalship, speaking of the "invincible Wm Sherman," and reporting that "wherever he goes, the soldiers greet him with cheer on cheers, shouting what the heroes of Vicksburg think of him ... suffice it that we are all willing to follow him to victory or death."[114]
Rice does not indicate how much this glowing opinion of his leaders was shared by his comrades in Battery E, or what their views might have been. His assessment of Grant's talent certainly proved well-founded, as Grant would be elevated to General-in-Chief of all Federal armies the following year, and go on to lead the North to victory two years later. Sherman would equally go on to success and fame in Georgia, South Carolina and North Carolina.
The dark side
Looting has been a pastime for soldiers of every century, and the Civil War was certainly no exception. Not all Union troopers fit the popular image of a citizen-soldier fighting for a noble cause; some were simply criminals in uniform. Several such men seem to have found their way into Battery E and its sister units during the winter of 1863-64, as Private Rice relates in a letter to his wife:
Rice further elaborates on gangs of muggers in the Union Army, whom he claimed would waylay anyone they met, high or low:
Rice reported that few of these men were ever punished, mostly due to lack of evidence or the reluctance of fellow soldiers to testify against them (often from fear of reprisal).[118]
Commanders
- Captain Allen C. Waterhouse - promoted to major.
- Captain John A. Fitch - promoted to major.
- Captain Orrin W. Cram - Mustered out with the battery.[119]
Assignments and service
Organizational assignments
- Organized at Chicago, Ill., and mustered in December 19, 1861.
- Moved to Cairo, Ill., February 13, 1862.
- Attached to District of Cairo, Ill., to March, 1862.
- Artillery, 5th Division, District of Memphis, Tenn., to November, 1862.
- Artillery, 5th Division, District [1037] of Memphis, Tenn., Right Wing 13th Army Corps (Old), Dept. of the Tennessee, November, 1862.
- Artillery, 1st Division, District of Memphis, Tenn., 13th Army Corps, to December, 1862.
- Artillery, 8th Division, 16th Army Corps, to March, 1863.
- Artillery, 3rd Division, 15th Army Corps, to December, 1863.
- Artillery, 1st Division, 16th Army Corps, to June, 1864.
- Artillery, 1st Division, Sturgis' Expedition, June, 1864.
- 1st Brigade, 1st Division, 16th Army Corps, to December, 1864.
- Artillery, 1st Division, Detachment Army of the Tennessee, Dept. of the Cumberland, to February, 1865.
- Artillery Reserve, Dept. of the Cumberland, Chattanooga, Tenn., to July, 1865.[120]
Engagements and service
- Duty at Paducah, Ky., till March, 1862.
- Expedition from Paducah to Tennessee River and operations about Crump's Landing, Tenn., March 8–14.
- Expedition to Yellow Creek, Miss., and occupation of Pittsburg Landing, Tenn., March 14–17.
- Battle of Shiloh, Tenn., April 6–7.
- Advance on and siege of Corinth, Miss., April 29-May 30.
- March to Memphis, Tenn., via Lagrange, Grand Junction and Holly Springs, June 1-July 21.
- Duty at Memphis, Tenn., till November.
- Grant's Central Mississippi Campaign, November 2, 1862, to January 10, 1863.
- Guard R. R. till March, 1863.
- Moved to Memphis, thence to Duckport, La., March 12-April 1.
- Demonstrations on Haines' and Snyder's Bluffs April 25-May 2.
- Movement to join army in rear of Vicksburg, via Richmond and Grand Gulf, May 2–14.
- Jackson, Miss., May 14.
- Siege of Vicksburg May 18-July 4.
- Assaults on Vicksburg May 19 and 22.
- Expedition to Mechanicsburg May 26-June 4.
- Advance on Jackson, Miss., July 4–10.
- Siege of Jackson July 10–17.
- Brandon Station July 19.
- Camp at Big Black till November.
- Expedition to Canton October 14–20.
- Bogue Chitto Creek October 17.
- Ordered to Memphis, Tenn., November 12, and duty guarding Railroad till January, 1864.
- Expedition to Tallahatchie River February 5–19.
- Coldwater Ferry February 8.
- Near Senatobia February 8–9.
- Wyatt's February 14.
- At Memphis till April.
- Sturgis' Expedition from Memphis to Ripley, Miss., April 30-May 9.
- Sturgis' Expedition from Memphis into Mississippi June 1–13.
- Brice's, or Tishamingo Creek, near Guntown, June 10.
- Smith's Expedition to Tupelo July 5–21.
- Camargo's Cross Roads, Harrisburg, July 13.
- Tupelo July 14–15.
- Old Town, or Tishamingo Creek, July 15.
- Smith's Expedition to Oxford, Miss., August 1–30.
- Tallahatchie River August 7–9.
- Oxford August 9.
- Abbeville August 23.
- Moved to Duvall's Bluff, Ark., September 1; thence march through Arkansas and Missouri.
- Light Artillery Reserve, Dept. of the Cumberland, to July, 1865.
- Mustered out July 15, 1865.[121]
See also
Notes
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Official Records, Series I, Volume X, Part 1, pages 100-108
- ↑ Official Records, Series I, Volume X, Part 1, pages 93-98
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 88.
- ↑ "Civil War Landscapes Association". Civilwarlandscapes.org. Retrieved 2012-08-28.
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 74-75.
- ↑ Sherman's Folly At Shiloh
- ↑ The Battle of Shiloh, and the Organizations Engaged, by David W. Reed, pg. 13.
- ↑ The Battle of Shiloh, and the Organizations Engaged, by David W. Reed, pg. 13.
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 74-75.
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 87.
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 77.
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 87.
- ↑ Official Record of the War of the Rebellion: Shiloh, Part 1, pg. 273.
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pg. 78. The 6th Mississippi lost 300 out of 425 men assigned to that regiment in this attack.
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ The Battle of Shiloh, and the Organizations Engaged, by David W. Reed, pg. 14.
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ The Battle of Shiloh, and the Organizations Engaged, by David W. Reed, pg. 14.
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 87.
- ↑ Official Record of the War of the Rebellion: Shiloh, Part 1, pg. 273.
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pp. 87.
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ The Battle of Shiloh, and the Organizations Engaged, by David W. Reed, pg. 14.
- ↑ The Battle of Shiloh, and the Organizations Engaged, by David W. Reed, pg. 14.
- ↑ Four Things You May Not Know About the Battle of Shiloh from History.com
- ↑ Sherman's Official Report of the Battle of Shiloh
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Shiloh, A Battlefield Guide, pg. 88.
- ↑ Official Record of the War of the Rebellion: Shiloh, Part 1, pp. 277-78.
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 1: 1860-62 Typewritten transcripts of privately held collection.
- ↑ Memoirs of General William T. Sherman, ch. 12.
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 1: 1860-62 Letter of December 8, 1862.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 1: 1860-62 Letter of December 8, 1862. Spelling and all else as in the original.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of January 4, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of February 6, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of February 18, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of February 18, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of February 18, 1863.
- ↑ Duck Port Map
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 30, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Triumph and Defeat: the Vicksburg Campaign, Vol. 2, by Terrence J. Winchell, pg. 38.
- ↑ Triumph and Defeat: the Vicksburg Campaign, Vol. 2, by Terrence J. Winchell, pg. 38.
- ↑ Triumph and Defeat: the Vicksburg Campaign, Vol. 2, by Terrence J. Winchell, pg. 38.
- ↑ National Park Service: Vicksburg National Military Park (Siege of Vicksburg: Union order of battle).
- ↑ Historical Marker Transcription: Battery E, 1st Illinois Light Artillery, includes map and photo of marker.
- ↑ Battle of Vicksburg
- ↑ Historical Marker Transcription: Battery E, 1st Illinois Light Artillery
- ↑ Historical Marker Transcription: Battery E, 1st Illinois Light Artillery
- ↑ Historical Marker Transcription: Battery E, 1st Illinois Light Artillery
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of June 7, 1863.
- ↑ Start of the Siege—and Starving—of Vicksburg
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of June 7, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of June 7, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of June 7, 1863.
- ↑ Historical Marker Transcription: Battery E, 1st Illinois Light Artillery
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of July 29, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of August 10, 1863.
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Artillery types during Sherman's Meridian Expedition, Feb. 1864
- ↑ The War of the Rebellion.
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ Expedition From Memphis, Tenn into Mississippi, official after-action report of Col. William E. McMillian, commander 95th Ohio Infantry.
- ↑ Expedition From Memphis, Tenn into Mississippi, official after-action report of Col. William E. McMillian, commander 95th Ohio Infantry.
- ↑ Expedition From Memphis, Tenn into Mississippi, official after-action report of Col. William E. McMillian, commander 95th Ohio Infantry.
- ↑ The Battle of Brice's Crossroads, by Stewart Bennett, pg. 103.
- ↑ The Battle of Brice's Crossroads, by Stewart Bennett, pg. 103.
- ↑ The Battle of Brice's Crossroads, by Stewart Bennett, pg. 103.
- ↑ The Battle of Brice's Crossroads, by Stewart Bennett, pg. 103.
- ↑ The Battle of Brice's Crossroads, by Stewart Bennett, pg. 103.
- ↑ Report of Col. Alexander Wilkin, Commanding 9th Minnesota Infantry
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E The Order of Battle for the Battle of Westport does not list this Battery, so it appears doubtful that they took part in this, the decisive battle of Price's doomed campaign.
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ History of 1st Illinois Light Artillery, Co. E
- ↑ http://www.civilwararchive.com/Unreghst/unilart1.htm#bate The Civil War Archive website after Dyer, Frederick Henry. A Compendium of the War of the Rebellion. 3 vols. New York: Thomas Yoseloff, 1959.
- ↑ Dyer, 1959.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 1: 1860-62 Letter of September 28, 1862. Some punctuation added.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 1: 1860-62 Letter of September 28, 1862.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of January 22, 1863.
- ↑ What Did Civil War Soldiers Eat?
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of January 30, 1863. Punctuation added for clarity.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of January 30, 1863. Punctuation added for clarity.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of June 3–4, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 2: 1863 Letter of June 11, 1863.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 3: 1864 Letter of 25 January 1864.
- ↑ According to Dave Manuel's "Inflation Calculator" website , $500 in 1864 equals nearly $7,700 today. The monthly pay for a private in the Federal Army during this time was $13 ($200 in 2016 dollars); it would rise to $16 ($246 in 2016) in June 1864.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 3: 1864 Letter of 15 January 1864.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 3: 1864 Letter of 25 April 1864.
- ↑ Letters of James Bolton Rice to his wife, Vol 3: 1864 Letter of 15 January 1864.
- ↑ http://www.rootsweb.com/~ilcivilw/acm/art-1e.htm Illinois in the Cvil war website after Illinois Adjutant General's muster rolls
- ↑ Compendium of the War of the Rebellion by Frederick Dyer.
- ↑ Compendium of the War of the Rebellion by Frederick Dyer.
References
- The Civil War Archive
- Roster of personnel assigned to Battery E, 1st Illinois Light Artillery (Note: not all ranks listed are correct as of the end of the war)

