Bataan
| Bataan | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Q24746 | |||
| Province of Bataan | |||
|
Bataan Provincial Capitol in Balanga | |||
| |||
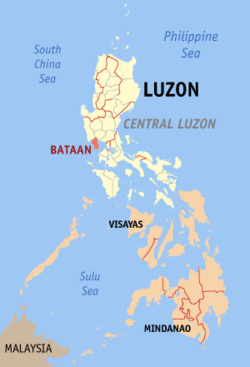 Location in the Philippines | |||
| Coordinates: 15°N 120°E / 15°N 120°ECoordinates: 15°N 120°E / 15°N 120°E | |||
| Country | Philippines | ||
| Region | Central Luzon (Region III) | ||
| Founded | 1754 | ||
| Capital | Balanga | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Albert Garcia (NUP) | ||
| • Vice Governor | Ma. Cristina Garcia (NUP) | ||
| Area[1] | |||
| • Total | 1,372.98 km2 (530.11 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 71st out of 81 | ||
| Highest elevation (Mount Mariveles) | 1,388 m (4,554 ft) | ||
| Population (2015 census)[2] | |||
| • Total | 760,650 | ||
| • Rank | 39th out of 81 | ||
| • Density | 550/km2 (1,400/sq mi) | ||
| • Density rank | 8th out of 81 | ||
| Divisions | |||
| • Independent cities | 0 | ||
| • Component cities |
1
| ||
| • Municipalities | |||
| • Barangays | 237 | ||
| • Districts | 1st and 2nd districts of Bataan | ||
| Demographics | |||
| • Ethnic groups |
| ||
| • Languages | |||
| Time zone | PHT (UTC+8) | ||
| ZIP Code | 2100–2114 | ||
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)47 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | PH | ||
| Website |
bataan | ||
Bataan (/bɑːtɑːˈɑːn/ Filipino: Lalawigan ng Bataan; Kapampangan: Lalawigan ning Bataan) is a province situated in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. Its capital is the City of Balanga. Occupying the entire Bataan Peninsula on Luzon, Bataan is bordered by the provinces of Zambales and Pampanga to the north. The peninsula faces the South China Sea to the west and Subic Bay to the north-west, and encloses Manila Bay to the east.
The Battle of Bataan is famous in history as one of the last stands of American and Filipino soldiers before they were overwhelmed by the Japanese forces in World War II. The Bataan Death March was named after the province, where the infamous march started.
History
In 1647, Dutch naval forces landed in country in an attempt to seize the islands from Spain. The Dutch massacred the people of Abucay in Bataan.
Historian Cornelio Bascara documents that the province of Bataan was established in January 11, 1757 by Governor-General Pedro Manuel Arandia out of territories belonging to Pampanga and the corregimiento of Mariveles which, at the time, included Maragondon, Cavite across the Manila Bay.[3][4]
World War II
Bataan featured prominently during World War II. Prior to the 1941 Japanese invasion, the US Army stored nearly 1,000,000 US gallons (3,800 m3) of gasoline there.

Shortly after the Japanese Army invaded the country in December 1941, the combined US and Filipino forces were being gradually overrun and General Douglas MacArthur moved his troops to the Bataan Peninsula in an attempt to hold out until a relief force could be sent from the US. Japanese forces started a siege of the peninsula on January 7, 1942, and launched an all-out assault on April 3, a few months after the Battle of the Points.
The majority of the American and Filipino forces surrendered on April 9 and were forced to march more than a 100 kilometres (62 mi) from Bataan to Capas, Tarlac, which became known as the Bataan Death March.
Geography
The province has an area of 1,372.98 square kilometres (530.11 sq mi),[5] and covers the entire Bataan Peninsula, a rocky extension of the Zambales Mountains jutting out into the South China Sea, enclosing the Manila Bay. At the northern portion of the peninsula is Mount Natib (elevation 1,253 metres (4,111 ft)) and its surrounding mountains, separated from Mount Samat and the Mariveles Mountains in the south by a pass.[4]
A narrow coastline plain characterizes the eastern portion of the province, while the western coast features many ridges, cliffs and headlands.[4]
Administrative divisions
Bataan is politically subdivided into 11 municipalities and one component city.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demographics
| Population census of Bataan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: National Statistics Office[2][6][7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The population of Bataan in the 2015 census was 760,650 people,[2] with a density of 550 inhabitants per square kilometre or 1,400 inhabitants per square mile.
Religion
Various religious groups are subscribed to by the people but Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion, comprising 85% of the Bataan population. Aglipayan as well as several Christian faiths are the minority.
Education
Schools, colleges and universities
- Acuña Welding School — Hermosa
- AMA Computer Learning Center — Balanga
- Antonio G. Llamas Elementary School — Mariveles
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced Studies
- Bataan Aces Foundation- Balanga
- Bataan Christian School — Pilar
- Bataan Heroes Memorial College — Balanga
- Bataan Maritime Institute — Balanga
- Bataan Montessori School, Inc. — Balanga
- Bataan National High School (formerly Arellano Memorial (Bataan) High School) — Balanga
- Bataan Peninsula State University — Balanga, Dinalupihan, Orani
- Bataan School of Fisheries — Orion
- BEPZ Multinational School (formerly Jose Abad Santos Memorial School) — Mariveles
- BLC International School (formerly Bataan Learning Center)
- Bonifacio Camacho National High School — Abucay
- Cabcaben Elementary School — Mariveles
- Colegio de San Juan de Letran — Abucay
- College of Subic Montessori — Dinalupihan
- DSOB — Blessed Regina Protmann Catholic School — Mariveles
- DSOB — Holy Rosary Parochial Institute — Orani
- DSOB — St. Catherine of Siena Academy — Samal
- DSOB — St. James Catholic School of Morong — Morong
- DSOB — St. John Academy — Dinalupihan
- DSOB — St. Michael the Archangel Academy — Orion
- DSOB — St. Nicholas Catholic School — Mariveles
- DSOB — St. Peter of Verona Academy — Hermosa
- Eastwoods College of Science and Technology — Dinalupihan
- EastWoods Professional College of Science and Technology (formerly SOFTNET College of Science and Technology)
- Jose Rizal Institute — Orion and Orani
- Limay National High School — Limay
- Limay Polytechnic College — Limay
- Llamas Memorial Institute — Mariveles
- Manuel L. Quezon University — Balanga (under construction)
- Maritime Academy of Asia and the Pacific — Mariveles
- Mariveles National High School — Cabcaben — Mariveles
- Mariveles National High School — Poblacion — Mariveles
- Microcity Computer College
- Mountain View Village School — Mariveles
- Northridge Montessori School — Pilar
- Orion National High School — Orion
- The Peninsula School, Incorporated — Limay
- Philippine Women's University — CDCEC Bataan
- Polytechnic University of the Philippines — Mariveles
- St. Joseph College's of Balanga
- Saint Michael the Archangel Academy — Orion
- St. Nicholas Catechetical Center — Mariveles
- Softnet Information Technology Center — Mariveles
- TESDA Provincial and Regional Training Center — Orion and Mariveles
- Thy Word International Bible College Extension — Mariveles
- Tomas del Rosario College — Balanga
- TWI, Bethel Bible College Extension — Balanga
- University of Nueva Caceres — Dinalupihan
- Wellcare Institute of Science & Technology — Pilar
Tourist attractions
Historical places
- Bataan Death March Marker (Orani)
- Bataan First Line of Defense (Layac, Dinalupihan)
- Filipino-Japanese Friendship Tower (Bagac)
- Limbagang Pinpin (Abucay)
- Mount Samat — Shrine of Valor (Pilar)
- World War II Museum (Balanga)
- Zero Kilometer Death March Marker (Mariveles and Bagac)
Churches
- Nuestra Señora del Pilar Church — Morong
- Nuestra Señora del Pilar Church — Pilar
- Nuestra Señora, Virgen Milagrosa del Rosario Church — Orani, declared as a diocesan-shrine by the Diocese of Balanga. It is home to the miraculous image of the Our Lady of the Holy Rosary which was canonically crowned 18 April 1959.
- San Francisco de Asis Church — Limay
- San Jose Cathedral — Balanga City, was declared as a diocesan-shrine and is the seat of the Diocese of Balanga
- San Juan Bautista Church — Dinalupihan
- San Miguel Arcangel Church — Orion
- San Nicolas de Tolentino Church — Mariveles
- San Pedro Martir de Verona Church — Hermosa
- Santa Catalina de Alexandria Church — Bagac
- Santa Catalina de Siena Church — Samal
- Santo Domingo de Guzman Church — Abucay, the oldest church in Bataan
Other places of interest
- Bataan Tourism Center — Balanga
- Las Casas Filipinas de Acuzar — Bagac
- Philippine Refugee Processing Center — Morong
- Ocean Adventure — Mabayo, Morong (SBMA)
- Zoobic Safari — Mabayo, Morong (SBMA)
Natural places of interest
- Ambon-ambon (Lumutan) Falls (Binukawan, Bagac)
- Anvaya Cove (Morong)
- Balong Anito (Mariveles)
- Bataan National Park
- Camaya Coast (Mariveles)
- Claubel Beach Resort (Mariveles)
- Dunsulan Falls
- Emerald Resort (Mariveles)
- Mariveles Five Fingers (Mariveles)
- Mount Mariveles
- Mount Natib (Orani)
- Panoypoy Cove (Mariveles)
- Pasukulan Falls (Abucay)
- Playa La Caleta (Morong)
- Roosevelt Protected Landscape
- San Miguel Mountain Peak (Mariveles)
- Sibul Spring (Abucay)
- Sinagtala & Vista Tala (Orani)
- Talain Cove (Mariveles)
- Tarak Ridge (Mariveles)
- Tortugas Bay Park (Balanga)
Infrastructure
Power
Generation
Bataan is a location of bulk power generation, whose most of the power produced are sent to the Luzon Grid. Most power plants in Bataan rely on fossil fuels, like oil and coal, but renewable energy sources, primarily solar power, forms part of the generation. The total output of existing power plants equals to 2068.1 MW, and new power plants to start operation will increase the output to 4224.1 MW.
Fossil fuel-fired plants form most of the bulk power generation from Bataan, with a total capacity of 2020 MW, and mostly concentrated in Limay and Mariveles. Existing power plants include the GN Power Mariveles Coal Power Plant, with 660 (2x330) MW, SMC Limay Greenfield Power Plant (4x150 MW), Petron Cogeneration Power Plant (4x35 MW), and Panasia Bataan Combined Cycle Power Plant (620 MW). Two plants under construction, the Dinginin Power Station (1,336 MW) and SMC Mariveles Coal Power Plant (4x150) will increase the capacity by 1936 MW.
Renewable energy, primarily solar power, forms a small portion of power generation in Bataan, with a total capacity of 48.1 MW, and are concentrated on the northern part of the province. Existing renewable energy power plants include the Bataan 2020 Cogen Power Plant (12.5 MW), YH Green Energy Solar Power Plant (12.6 MW), Citicore Solar Power Plant (18 MW), and Morong Solar Power Plant (5 MW). Three renewable energy power plants, namely the Solana Solar Alpha Inc. (20 MW), Bataan Solar Power Project (150 MW), and Santa Rita Wind Power Project (50 MW), are awarded to increase the capacity by 220 MW.
The Bataan Nuclear Power Plant in Morong, with 600 MW capacity, is supposed to be the first nuclear power plant in the Philippines and is built during the Marcos era. It was supposed to commence operation in 1986, but abandoned amidst critical opposition to the Marcos regime and concerns on nuclear power.
Distribution
Power distribution in the province are served by the Peninsula Electric Cooperative (PENELCO), but some large customers have their power supply sourced from the transmission grid, operated by National Grid Corporation of the Philippines (NGCP), whose network of 69,000 volt lines supply substations owned by PENELCO.
Sea ports / terminals
- Mariveles Grain Terminal — Mariveles
- Seasia-Nectar Mariveles Dry Bulk Terminal — Mariveles
- Port of Lucanin — Mariveles
- Port of Lamao — Mariveles
- Port Capinpin — Orion
Airport
- Subic Bay International Airport — Morong
Highways / expressways / national roads
Bataan is served by a network of national highways and one expressway. Roman Superhighway, part of highway N301, and Jose Abad Santos Avenue, or highway N3, forms the backbone of the national highway network. Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway, a toll expressway, links the province with the Pampanga and Tarlac. National Road and Governor J.J. Linao National Road forms the secondary network, which connects the smaller municipalities with the main highway network.
Notable people from Bataan
- Persida Acosta (Mariveles) — Chief Public Attorney, Public Attorney's Office
- Bradwyn Guinto (Orani) — basketball player
- Raymond Almazan (Orion) — basketball player
- Cayetano Arellano (Orion) — first Supreme Court Chief Justice of the Republic of the Philippines
- Francisco Baltazar (Orion) — one of the greatest Filipino literary laureates, born in Bigaa (Balagtas), Bulacan but spent his adult life in Orion, Bataan
- Luz Banzon (Balanga) — wife of Philippine President Ramon Magsaysay; seventh First Lady of the Philippines
- David Consunji (Dinalupihan) — chairman of publicly listed holding firm, DMCI Holdings, Incorporated
- Gary David (Dinalupihan) — basketball player and television actor/comedian
- Romi Garduce (Balanga) — mountain climber who reached the peak of Mount Everest
- Merceditas Gutierrez (Samal) — ombudsman, first female to head the post
- Manuel C. Herrera (Pilar) — Ombudsman, justice of the Court of Appeals and chair of the National Unification Commission
- Rodel Naval (Orion) — Filipino singer, songwriter and actor.
- Evangeline Pascual (Orani) — actress and First Runner-Up Miss World 1973
- Felicito Payumo (Dinalupihan) — Chairman of the Subic Bay Metropolitan Authority from 1998-2004
- Chad Peralta (Limay) — Top 6 scholars of the first sequel ABS-CBN Pinoy Dream Academy searched and competed worldwide.
- Tomas Pinpin (Abucay) — printer, writer and publisher
- Kerby Raymundo (Orion) — basketball player
- Jackie Rice (Dinalupihan) — actress
- Eric Rodriguez (Orion) — basketball player
- Geraldine Roman (Orani) — journalist and politician; first transgender woman elected to Congress of the Philippines
- Tomas del Rosario (Orani) — judge, statesman and first governor of the province of Bataan from 1903 to 1905
- Mel Tiangco (Pilar) — popular television newscaster and television host; head of GMA Kapuso foundation.
- Pedro Tuazon (Balanga) — Solicitor General of the Philippines, 1921
- Janine Tugonon (Orion) — model, TV host and beauty pageant titleholder
- Manuel Bamba Villar Jr. (Orani) — Senator, Republic of the Philippines
See also
- Bataan Provincial Expressway
- Petron Corporation (formerly known as Bataan Refining Corporation)
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Balanga
References
- ↑ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on 21 January 2013. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Census of Population (2015). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ Cornelio R. Bascara. 2010. A History of Bataan (1587-1900). UST Publishing
- 1 2 3 Lancion, Jr., Conrado M.; cartography by de Guzman, Rey (1995). "The Provinces; Bataan". Fast Facts about Philippine Provinces (The 2000 Millenium ed.). Makati, Metro Manila, Philippines: Tahanan Books. p. 32. ISBN 971-630-037-9. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Province: Bataan". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- 1 2 Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ "Philippines Census Of Population of all LGUs 1903-2007". archive.org. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
External links
-
 Media related to Bataan at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bataan at Wikimedia Commons -
 Geographic data related to Bataan at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Bataan at OpenStreetMap - Bataan official website
| Adjacent places of Bataan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Zambales | Pampanga |  | |
| South China Sea | |
Manila Bay / Metro Manila | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Manila Bay Cavite |
||||




