Bafilomycin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
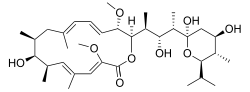
(3Z,5E,7R,8S,9S,11E,13E,15S,16R)-16- [(1S,2R,3S)-3-[(2R,4R,5S,6R)-2,4-dihydroxy-6- isopropyl-5-methyl-2-tetrahydropyranyl]-2- hydroxy-1-methylbutyl]-8-hydroxy-3,15- dimethoxy-5,7,9,11-tetramethyl-1- oxacyclohexadeca-3,5,11,13-tetraen-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.187 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| Properties | |
| C35H58O9 | |
| Molar mass | 622.83 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
The bafilomycins are a family of toxic macrolide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus. These compounds all appear in the same fermentation and have quite similar biological activity. Bafilomycins are specific inhibitors of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase.
The most used bafilomycin is bafilomycin A1. This is a useful tool as it can prevent the re-acidification of synaptic vesicles once they have undergone exocytosis.
Bafilomycin has antibacterial, antifungal, antineoplastic, immunosuppressive activities. In addition, bafilomycin A1 has antimalarial activity [2] It has been shown to decrease multi-drug resistance.
Bafilomycin B1 has been mentioned as a potential antiosteoporotic agent in treating bone lytic diseases.
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.