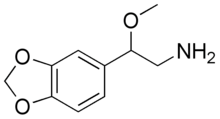
BOH (drug)
BOH, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-β-methoxyphenethylamine, is a drug of the phenethylamine class.[1] It is the β-methoxy analog of methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA) and is also more distantly related to methylone. On account of its similarity to norepinephrine, the effects of BOH may be of a purely adrenergic nature.[1]
BOH was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.[1] In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 80–120 mg, and the duration listed as 6–8 hours. Shulgin reports that BOH causes slight warmth, mydriasis, anorexia, mild nausea, and cold feet, with no psychedelic, entactogen, or euphoriant effects.[1] He gives it a ++ on the Shulgin Rating Scale.[1] Very little is known about the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, effects, and toxicity of BOH.
See also
References
|
|---|
| Adamantanes | |
|---|
| Adenosine antagonists | |
|---|
| Alkylamines | |
|---|
| Ampakines | |
|---|
| Arylcyclohexylamines | |
|---|
| Benzazepines | |
|---|
| Cholinergics | |
|---|
| Convulsants | |
|---|
| Eugeroics | |
|---|
| Oxazolines | |
|---|
| Phenethylamines |
- 1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-aminobutane
- 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane
- 2-Fuoroamphetamine
- 2-Fuoromethamphetamine
- 2-OH-PEA
- 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane
- 2,3-MDA
- 3-Fuoroamphetamine
- 3-Fluoroethamphetamine
- 3-Fluoromethcathinone
- 3-Methoxyamphetamine
- 3-Methylamphetamine
- 3,4-DMMC
- 4-BMC
- 4-CMC
- 4-Ethylamphetamine
- 4-Fluoroamphetamine
- 4-Fluoromethamphetamine
- 4-MA
- 4-Methylbuphedrone
- 4-Methylcathinone
- 4-MMA
- 4-Methylpentedrone
- 4-MTA
- 6-FNE
- AL-1095
- Alfetamine
- a-Ethylphenethylamine
- Amfecloral
- Amfepentorex
- Amfepramone
- Amidephrine
- 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene
- 2-Aminoindane
- 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole
- 2-Aminotetralin
- Acridorex
- Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine)
- Amphetaminil
- Arbutamine
- β-Methylphenethylamine
- β-Phenylmethamphetamine
- Benfluorex
- Benzedrone
- Benzphetamine
- BDB
- BOH
- 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine
- BPAP
- Buphedrone
- Bupropion
- Butylone
- Camfetamine
- Cathine
- Cathinone
- Chlorphentermine
- Cilobamine
- Cinnamedrine
- Clenbuterol
- Clobenzorex
- Cloforex
- Clortermine
- Cypenamine
- D-Deprenyl
- Denopamine
- Dimethoxyamphetamine
- Dimethylamphetamine
- Dimethylcathinone
- Dobutamine
- DOPA (Dextrodopa, Levodopa)
- Dopamine
- Dopexamine
- Droxidopa
- EBDB
- Ephedrine
- Epinephrine
- Epinine
- Etafedrine
- Ethcathinone
- Ethylnorepinephrine
- Ethylone
- Etilamfetamine
- Etilefrine
- Famprofazone
- Fencamfamin
- Fencamine
- Fenethylline
- Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine, Levofenfluramine)
- Fenproporex
- Feprosidnine
- Flephedrone
- Fludorex
- Formetorex
- Furfenorex
- Gepefrine
- Hexapradol
- Hexedrone
- HMMA
- Hordenine
- 4-Hydroxyamphetamine
- 5-Iodo-2-aminoindane
- Ibopamine
- IMP
- Indanylamphetamine
- Iofetamine
- Isoetarine
- Isoethcathinone
- Isoprenaline
- L-Deprenyl (Selegiline)
- Lefetamine
- Lisdexamfetamine
- Lophophine
- MBDB
- MDA
- MDBU
- MDEA
- MDMA
- MDMPEA
- MDOH
- MDPR
- MDPEA
- Mefenorex
- Mephedrone
- Mephentermine
- Metanephrine
- Metaraminol
- Mesocarb
- Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine)
- Methoxamine
- Methoxyphenamine
- MMA
- Methcathinone
- Methedrone
- Methoxyphenamine
- Methylenedioxycathinone
- Methylone
- Mexedrone
- MMDA
- MMDMA
- MMMA
- Morforex
- N,alpha-Diethylphenylethylamine
- N-Ethylbuphedrone
- N-Ethylhexedrone
- N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine
- Naphthylamphetamine
- Nisoxetine
- Norepinephrine
- Norfenefrine
- Norfenfluramine
- Normetanephrine
- L-Norpseudoephedrine
- Octopamine (drug)
- Orciprenaline
- Ortetamine
- Oxifentorex
- Oxilofrine
- PBA
- PCA
- PCMA
- PHA
- Pentorex
- Pentedrone
- Pentylone
- Phenatine
- Phenpromethamine
- Phentermine
- Phenylalanine
- Phenylephrine
- Phenylpropanolamine
- Pholedrine
- PIA
- PMA
- PMEA
- PMMA
- PPAP
- Phthalimidopropiophenone
- Prenylamine
- Propylamphetamine
- Pseudoephedrine
- Ropinirole
- Salbutamol (Levosalbutamol)
- Sibutramine
- Synephrine
- Theodrenaline
- Tiflorex
- Tranylcypromine
- Tyramine
- Tyrosine
- Xylopropamine
- Zylofuramine
|
|---|
| Phenylmorpholines | |
|---|
| Piperazines | |
|---|
| Piperidines | |
|---|
| Pyrrolidines | |
|---|
| Racetams | |
|---|
| Tropanes | |
|---|
| Tryptamines | |
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| DRAs | |
|---|
| NRAs | |
|---|
| SRAs | |
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins |