Azinphos-ethyl
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
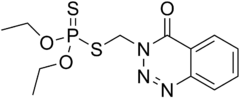
| IUPAC name
3-(Diethoxyphosphinothioylsulfanylmethyl)-1,2,3-benzotriazin-4-one | |
| Other names
Gusathion; Ethyl azinphos | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.316 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | TD8400000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16N3O3PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 345.37 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 53 °C (127 °F; 326 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
17.5 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Azinphos-ethyl (also spelled azinophos-ethyl) is a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide.
Regulation
It is very toxic to mammals with a World Health Organization hazard classification as class IB, highly hazardous.[2] It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 Azinphos-Ethyl, Chemical Sampling Information, Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- ↑ Azinphos-ethyl Pesticide Data Sheet Archived June 8, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., International Programme on Chemical Safety
- ↑ "40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities" (PDF) (July 1, 2008 ed.). Government Printing Office. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.