Azacitidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vidaza, Azadine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607068 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | SubQ, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | possible hepatic metabolism, mostly urinary excretion |
| Biological half-life | 4 hr.[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | 5-azacytidine, Azacytidine, 320-67-2; Ladakamycin, 4-Amino-1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-s-triazin-2(1H)-one, U-18496 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.711 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
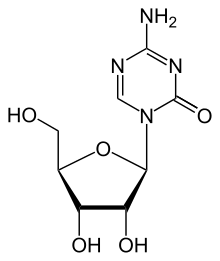
| Formula | C8H12N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 244.205 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Azacitidine (INN; trade name Vidaza) is a chemical analog of cytidine, a nucleoside in DNA and RNA. Azacitidine and its deoxy derivative, decitabine (also known as 5-aza-2′deoxycytidine), are used in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome. Both drugs were first synthesized in Czechoslovakia as potential chemotherapeutic agents for cancer.[2]
Uses
Clinical
Azacitidine, marketed as Vidaza, is used mainly in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome, for which it received approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on May 19, 2004.[3][4] In two randomized controlled trials comparing azacitidine to supportive treatment, 16% of subjects with myelodysplastic syndrome who were randomized to receive azacitidine had a complete or partial normalization of blood cell counts and bone marrow morphology, compared to none who received supportive care, and about two-thirds of patients who required blood transfusions no longer needed them after receiving azacitidine.[5]
It is also sometimes used for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia,[6] as a hypomethylating agent; an oral version called CC-486 is being tested as an easier to administer treatment for AML. [7]
Non-clinical
Azacitidine can be used in vitro to remove methyl groups from DNA. This may weaken the effects of gene silencing mechanisms that occur prior to methylation. Certain methylations are believed to secure DNA in a silenced state, and therefore demethylation may reduce the stability of silencing signals and confer relative gene activation.[8]
Azacitidine induces tumor regression on isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 mutant glioma xenografts in mice.[9]
In research, 5-azacitidine is commonly used for promoting cardiomyocyte differentiation of adult stem cells. However, it has been suggested that this drug has a compromised efficacy as a cardiac differentiation factor because it promotes the transdifferentiation of cardiac cells to skeletal myocytes.[10]
Mechanism of action
Azacitidine is a chemical analogue of the nucleoside cytosine, which is present in DNA and RNA. It is thought to have antineoplastic activity via two mechanisms – at low doses, by inhibiting of DNA methyltransferase, causing hypomethylation of DNA,[11] and at high doses, by its direct cytotoxicity to abnormal hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow through its incorporation into DNA and RNA, resulting in cell death. Azacitidine is a ribonucleoside, so it is incorporated into RNA to a larger extent than into DNA. In contrast, decitabine (5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine) is a deoxyribonucleoside, so it can only incorporate into DNA. Azacitidine's incorporation into RNA leads to the dissembly of polyribosomes, defective methylation and acceptor function of transfer RNA, and inhibition of the production of proteins. Its incorporation into DNA leads to covalent binding with DNA methyltransferases, which prevents DNA synthesis and subsequent leads to cytotoxicity. It has been shown effective against human immunodeficiency virus in vitro[12] and human T-lymphotropic virus.[13]
Inhibition of methylation
After azanucleosides such as azacitidine have been metabolized to 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine-triphosphate (aka, decitabine-triphosphate), they can be incorporated into DNA and azacytosine can be substituted for cytosine. Azacytosine-guanine dinucleotides are recognized as substrate by the DNA methyltransferases, which catalyze the methylation reaction by a nucleophilic attack. This results in a covalent bond between the carbon-6 atom of the cytosine ring and the enzyme. The bond is normally resolved by beta-elimination through the carbon-5 atom, but this latter reaction does not occur with azacytosine because its carbon-5 is substituted by nitrogen, leaving the enzyme remains covalently bound to DNA and blocking its DNA methyltransferase function. In addition, the covalent protein adduction also compromises the functionality of DNA and triggers DNA damage signaling, resulting in the degradation of trapped DNA methyltransferases. As a consequence, methylation marks become lost during DNA replication.[14][15]
Toxicity
Azacitidine causes anemia (low red blood cell counts), neutropenia (low white blood cell counts), and thrombocytopenia (low platelet counts), and patients should have frequent monitoring of their complete blood counts, at least prior to each dosing cycle. The dose may have to be adjusted based on nadir counts and hematologic response.[16]
It can also be hepatotoxic in patients with severe liver impairment, and patients with extensive liver tumors due to metastatic disease have developed progressive hepatic coma and death during azacitidine treatment, especially when their albumin levels are less than 30 g/L. It is contraindicated in patients with advanced malignant hepatic tumors.[16]
Renal toxicity, ranging from elevated serum creatinine to kidney failure and death, have been reported in patients treated with intravenous azacitidine in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents for conditions other than myelodysplastic syndrome. Renal tubular acidosis developed in five patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (an unapproved use) treated with azacitidine and etoposide, and patients with renal impairment may be at increased risk for renal toxicity. Azacitidine and its metabolites are primarily excreted by the kidneys, so patients with renal insufficiency should be closely monitored for other side effects, since their levels of azacitidine may progressively increase.[16]
Based on animal studies and its mechanism of action, azacitidine can cause severe fetal damage. Sexually active women of reproductive potential should use contraception during while receiving azacitidine and for one week after the last dose, and sexually active men with female partners of reproductive potential should use contraception during treatment and for three months following the last dose.[16]
Azacitidine can also nausea, vomiting, fevers, diarrhea, redness at its injection sites, constipation, bruising, petechiae, rigors, weakness, abnormally low potassium levels in the bloodstream, and many other side effects, some of which can be severe or even fatal.[16]
See also
References
- ↑ Deglin, Judith, & Vallerand, April. (2009). Davis's drug guide for nurses. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company, pp. 204-206.
- ↑ Cihák A. (1974). "Biological effects of 5-azacytidine in eukaryotes". Oncology. 30 (5): 405–422. PMID 4142650. doi:10.1159/000224981.
- ↑ Vidaza web site.
- ↑ "Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations". fda.gov. United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ↑ Kaminskas, Edvardas; Farrell, Anne T.; Wang, Yong Cheng; Sridhara, Rageshwari; Pazdur, Richard (2005). "FDA Drug Approval Summary: Azacitidine (5-azacytidine, Vidaza) for Injectable Suspension". The Oncologist. 10 (3): 176–182. PMID 15793220. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.10-3-176.
- ↑ Estey E.H. (September 2013). "Epigenetics in clinical practice: the examples of azacitidine and decitabine in myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia". Leukemia. 27 (9): 1803–1812. PMID 23757301. doi:10.1038/leu.2013.173.
- ↑ CC-486 (Oral Azacitidine) Monotherapy in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
- ↑ Whitelaw E. and Garrick D. (2005), The Epigenome, Chapter 7, In: Mammalian Genomics, Ed: Ruvinsky A. & Marshall Graves J.A., CABI Publishing, Wallingford, U.K., ISBN 0-85199-910-7.
- ↑ Borodovsky, Alexandra; et al. (October 2013). "5-azacytidine reduces methylation, promotes differentiation and induces tumor regression in a patient-derived IDH1 mutant glioma xenograft". Oncotarget. 4 (10): 1737–1747. PMC 3858560
 . PMID 24077805. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1408.
. PMID 24077805. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1408. - ↑ Kaur, Keerat; Yang, Jinpu; Eisenberg, Carol; Eisenberg, Leonard (2014). "5-azacytidine promotes the transdifferentiation of cardiac cells to skeletal myocytes." (PDF). Cellular Reprogramming. 16: 324–30. PMID 25090621. doi:10.1089/cell.2014.0021.
- ↑ Martens, U.M., ed. (2010). "11 5-Azacytidine/Azacitidine". Small molecules in oncology. Recent Results in Cancer Research. 184. Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 159–170. ISBN 978-3-642-01222-8. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-01222-8.
- ↑ Dapp, Michael J.; Clouser, Christine L.; Patterson, Steven; Mansky, Louis M. (2009). "5-Azacytidine can induce lethal mutagenesis in human immunodeficiency virus type 1". Journal of Virology. 83 (22): 11950–11958. PMC 2772699
 . PMID 19726509. doi:10.1128/JVI.01406-09.
. PMID 19726509. doi:10.1128/JVI.01406-09. - ↑ Antiretroviral activity of 5-azacytidine during treatment of a HTLV-1 positive myelodysplastic syndrome with autoimmune manifestations
- ↑ Stresemann, C.; Lyko, F. (2008). "Modes of action of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitors azacytidine and decitabine". International Journal of Cancer. 123 (1): 8–13. PMID 18425818. doi:10.1002/ijc.23607.
- ↑ Navada, Shyamala C.; Steinmann, Juliane; Lübbert, Michael; Silverman, Lewis R. (January 2, 2014). "Clinical development of demethylating agents in hematology". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 124 (1): 4–46. PMC 3871232
 . PMID 24382388. doi:10.1172/JCI69739. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
. PMID 24382388. doi:10.1172/JCI69739. Retrieved 20 May 2016. - 1 2 3 4 5 "Prescribing Information - Azacitidine for Infection" (PDF). fda.gov. United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 20 May 2016.