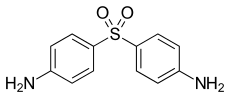
Dapsone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aczone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682128 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 70 to 80% |
| Protein binding | 70 to 90% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (mostly CYP2E1-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 20 to 30 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.136 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H12N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 248.302 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 175 to 176 °C (347 to 349 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dapsone, also known as diaminodiphenyl sulfone (DDS),[1] is an antibiotic commonly used in combination with rifampicin and clofazimine for the treatment of leprosy.[2] It is a second-line medication for the treatment and prevention of pneumocystis pneumonia and for the prevention of toxoplasmosis in those who have poor immune function.[2] Additionally, it has been used for acne, dermatitis herpetiformis, and various other skin conditions.[3] Dapsone is available both topically and by mouth.[4]
Severe side effects may include: a decrease in blood cells, red blood cell breakdown especially in those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G-6-PD), or hypersensitivity.[2] Common side effects include nausea and loss of appetite.[4] Other side effects include liver inflammation and a number of types of skin rashes.[2] While it is not entirely clear the safety of use during pregnancy some physicians recommend that it be continued in those with leprosy.[2] It is of the sulfone class.[2]
Dapsone was first studied as an antibiotic in 1937.[3] Its use for leprosy began in 1945.[3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[5] The oral form is available as a generic drug and not very expensive.[2][6]
Medical uses
Infections
Dapsone is commonly used in combination with rifampicin and clofazimine for the treatment of leprosy.[2] It is also used to both treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP).[2][7] It is also used for toxoplasmosis in people unable to tolerate trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole.[7]
Dapsone by mouth was one of the first medications used to treat moderate to severe acne vulgaris, and is still occasionally prescribed for the treatment of severe cases.[8][9] A topical form of dapsone is also effective with potentially less side effects.[10]
It is unclear if the combination with pyrimethamine is useful in the prevention of malaria.[11]
Other
Dermatitis herpetiformis, often in combination with a gluten-free diet.[2]
Dapsone may be used to treat brown recluse spider bites that become necrotic.[12]
Dapsone is the recommended treatment for erythema elevatum diutinum, as a review found that using oral dapsone alone was effective in 80% of early cases of the disease. However, dapsone can potentially cause severe side effects, meaning that sometimes steroids or other antibiotics should be used instead, although these alternative treatments are much less effective.[13]
An August 2015 review notes that dapsone is reported to be effective against generalized granuloma annulare.[14]
Adverse effects
The dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome develops in 0.5–3.6% of persons treated with the drug, and is associated with a mortality of 9.9%.[15]
Blood
The most prominent side-effects of this drug are dose-related hemolysis (which may lead to hemolytic anemia) and methemoglobinemia.[16] About 20% of patients treated with dapsone suffer hemolysis[17] and the side-effect is more common and severe in those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, leading to the dapsone-containing antimalarial combination Lapdap being withdrawn from clinical use.[18][19] A case of hemolysis in a neonate from dapsone in breast milk has been reported.[20] Agranulocytosis occurs rarely when dapsone is used alone but more frequently in combination regimens for malaria prophylaxis.[21] Abnormalities in white blood cell formation, including aplastic anemia, are rare, yet are the cause of the majority of deaths attributable to dapsone therapy.[22][23][24]
Liver
Toxic hepatitis and cholestatic jaundice have been reported by the manufacturer. Jaundice may also occur as part of the dapsone reaction or dapsone syndrome (see below). Dapsone is metabolized by the Cytochrome P450 system, specifically isozymes CYP2D6, CYP2B6, CYP3A4, and CYP2C19.[25] Dapsone metabolites produced by the cytochrome P450 2C19 isozyme are associated with the methemoglobinemia side effect of the drug.
Skin
When used topically, dapsone can cause mild skin irritation, redness, dry skin, burning and itching. When used together with benzoyl peroxide products, temporary yellow or orange skin discolorations can occur.[26][27]
Other adverse effects
Other adverse effects include nausea, headache, and rash (which are common), and insomnia, psychosis, and peripheral neuropathy. Effects on the lung occur rarely and may be serious, though are generally reversible.[28]
Dapsone reaction
Hypersensitivity reactions occur in some patients. This reaction may be more frequent in patients receiving multiple-drug therapy.[29][30][31]
The reaction always involves a rash and may also include fever, jaundice, and eosinophilia.[32][33][34][35][36] In general, these symptoms will occur within the first six weeks of therapy or not at all, and may be ameliorated by corticosteroid therapy.[7]
Mechanism of action
As an antibacterial, dapsone inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid, via competition with para-aminobenzoate for the active site of dihydropteroate synthase.[37] Though structurally distinct from dapsone, the sulfonamide group of antibacterial drugs also work in this way.
As an anti-inflammatory, dapsone inhibits the enzyme myeloperoxidase. As part of the respiratory burst that neutrophils use to kill bacteria, myeloperoxidase converts hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) into hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl is the most potent oxidant generated by neutrophils, and can cause significant tissue damage during inflammation. Dapsone arrests myeloperoxidase in an inactive intermediate form, reversibly inhibiting the enzyme. This prevents accumulation of hypochlorous acid, and reduces tissue damage during inflammation.[38][39][40][41][42] Myeloperoxidase inhibition has also been suggested as a neuron-sparing mechanism for reducing inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and stroke.[43]
When used for the treatment of skin conditions in which bacteria do not have a role, the mechanism or action of dapsone is not well understood. Dapsone has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects,[44] which are thought to come from the drug's blockade of myeloperoxidase. This is thought to be its mechanism of action in treating dermatitis herpetiformis.[45]
Dapsone is an odorless white to creamy-white crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste.
Specific considerations
Certain patients are at higher risks of adverse effects when using dapsone. Some specific issues that should be considered are:[7]
- Related to the blood (a full blood count should be obtained prior to initiating therapy):
- Related to the liver (obtain liver function tests before starting therapy):
- Liver impairment
- Related to allergy:
- Sulfonamide allergy is associated with dapsone allergy
HbA1c may be an unreliable measure of glycemic control in people with diabetes mellitus taking dapsone due to increased red cell turnover.
History
Discovery
In the early 20th century, the German chemist Paul Ehrlich was developing theories of selective toxicity based largely on the ability of certain dyes to kill microbes. Gerhard Domagk, who would later win a Nobel Prize for his efforts, made a major breakthrough in 1932 with the discovery of the antibacterial prontosil red (sulfonamidochrysoidine). Further investigation into the involved chemicals opened the way to sulfa drug and sulfone therapy, first with the discovery of sulfanilamide, the active agent of prontosil, by Daniel Bovet and his team at Pasteur Institute (1935),[46] then with of dapsone independently by Ernest Fourneau[47] in France and Gladwin Buttle[48] in United-Kingdom.[49]

Fromm & Wittman, 1908
Proposed use in antimalarial drugs
The spread of drug-resistant malaria in Africa has encouraged the development of new, low-cost antimalarial drugs. Plasmodium falciparum, one of the Plasmodium species that causes malaria, has developed resistance both to chloroquine and sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine, two of the most common treatments for malaria. Artemisinin, another antimalarial drug, had been developed in the 1980s but was too expensive for large-scale use. This led GlaxoSmithKline to develop Lapdap, a combination drug consisting of chlorproguanil and dapsone. Lapdap was licensed in the United Kingdom starting in October 2003.[19]
One advantage of Lapdap had was that chlorproguanil and dapsone are both low-cost drugs. Another was that by virtue of being of a combination drug, it was less likely to cause drug resistance. However, because dapsone causes hemolytic anemia in patients with G6PD deficiency, and because G6PD deficiency affects 10-25% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa, it was discovered that Lapdap is not safe for use in Africa. It was available in many African countries for four years before GlaxoSmithKline took it off the market in February 2008.[19]
Dapsone gel
Dapsone had been reported in a few cases to effectively treat acne, but the risk of hemolytic anemia kept it from being widely used for this purpose. For many years scientists attempted to develop a topical formulation of dapsone that would be as effective against acne as oral dapsone, but without the hemolysis side effect. This was difficult to accomplish because dapsone is highly insoluble in aqueous solvents. In the early 2000s QLT USA developed Aczone, a 5% dapsone gel that was shown to be effective against acne without causing clinically significant declines in hemoglobin levels, even in subjects with G6PD deficiency.[50] In February 2016, the FDA approved a 7.5% dapsone gel. This higher strength has the advantage of a once-daily application, versus twice-daily application of the 5% formulation.[51]
References
- ↑ Thomas L. Lemke (2008). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1142. ISBN 9780781768795.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Dapsone". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved Jan 12, 2015.
- 1 2 3 Zhu, YI; Stiller, MJ; et al. (2001). "Dapsone and sulfones in dermatology: overview and update". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 45 (3): 420–34. PMID 11511841. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114733.
- 1 2 Joel E. Gallant (2008). Johns Hopkins HIV Guide 2012. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 193. ISBN 9781449619794.
- ↑ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ Greenwood, David (2008). Antimicrobial Drugs: Chronicle of a Twentieth Century Medical Triumph. Oxford University Press. p. 197. ISBN 9780199534845.
- 1 2 3 4 Rossi S, ed. (2006). Australian Medicines Handbook. Adelaide. ISBN 0-9757919-2-3.
- ↑ Ross, CM (1961). "The treatment of acne vulgaris with dapsone". Br J Dermatol. 73 (10): 367–70. PMID 14494150. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1961.tb14398.x.
- ↑ "Dapsone and Acne Vulgaris". ScienceOfAcne.com. 2012-10-10. Retrieved 2012-08-17.
- ↑ Pickert, A; Raimer, S (June 2009). "An evaluation of dapsone gel 5% in the treatment of acne vulgaris". Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy. 10 (9): 1515–21. PMID 19505219. doi:10.1517/14656560903002097.
- ↑ Croft, AM (29 November 2007). "Malaria: prevention in travellers.". Clinical evidence. 2007. PMC 2943798
 . PMID 19450348.
. PMID 19450348. - ↑ Forks, TP (2000). "Brown recluse spider bites.". J Am Board Fam Pract. 13 (6): 415–23. PMID 11117338. doi:10.3122/15572625-13-6-415.
- ↑ Momen, S.E.; Jorizzo, J.; Al-Niaimi, F. (December 2014). "Erythema elevatum diutinum: a review of presentation and treatment". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. John Wiley & Sons. 28 (12): 1594–1602. doi:10.1111/jdv.12566.
- ↑ Lukács, J.; Schliemann, S.; Elsner, P. (August 2015). "Treatment of generalized granuloma annulare – a systematic review". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. John Wiley & Sons. 29 (8): 1467–1480. doi:10.1111/jdv.12976.
- ↑ Zhang FR, Liu H, Irwanto A, et al. (October 2013). "HLA-B*13:01 and the dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome.". N Engl J Med. 369 (17): 1620–8. PMID 24152261. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213096.
- ↑ Jopling WH (1983). "Side-effects of antileprosy drugs in common use". Lepr Rev. 54 (4): 261–70. PMID 6199637.
- ↑ Puavilai S, Chutha S, Polnikorn N, et al. (July 1984). "Incidence of anemia in leprosy patients treated with dapsone". J Med Assoc Thai. 67 (7): 404–7. PMID 6512448.
- ↑ "Antimalarial chlorproguanil-dapsone (LapDap™) withdrawn following demonstration of post-treatment haemolytic anaemia in G6PD deficient patients in a Phase III trial of chlorproguanil-dapsone-artesunate (Dacart™) versus artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem®) and confirmation of findings in a comparative trial of LapDap™ versus Dacart ™" (PDF). World Health Organization. 4 March 2008. QSM/MC/IEA.1.
- 1 2 3 Luzzatto L (August 2010). "The rise and fall of the antimalarial Lapdap: a lesson in pharmacogenetics". Lancet. 376 (9742): 739–41. PMID 20599264. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60396-0.
- ↑ Sanders SW, Zone JJ, Foltz RL, Tolman KG, Rollins DE (April 1982). "Hemolytic anemia induced by dapsone transmitted through breast milk.". Ann Intern Med. 96 (4): 465–6. PMID 7065565. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-465.
- ↑ Firkin FC, Mariani AF (1977). "Agranulocytosis due to dapsone". Med. J. Aust. 2 (8): 247–51. PMID 909500.
- ↑ Foucauld J, Uphouse W, Berenberg J (1985). "Dapsone and aplastic anemia". Ann. Intern. Med. 102 (1): 139. PMID 3966740. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-102-1-139_2.
- ↑ Meyerson MA, Cohen PR (1994). "Dapsone-induced aplastic anemia in a woman with bullous systemic lupus erythematosus". Mayo Clin. Proc. 69 (12): 1159–62. PMID 7967777. doi:10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65768-1.
- ↑ Björkman A, Phillips-Howard PA (1991). "Adverse reactions to sulfa drugs: implications for malaria chemotherapy". Bull. World Health Organ. 69 (3): 297–304. PMC 2393107
 . PMID 1893504.
. PMID 1893504. - ↑ Ganesan, S; Sahu, R; Walker, LA; Tekwani, BL (April 2010). "Cytochrome P450-dependent toxicity of dapsone in human erythrocytes". J Appl Toxicol. 30 (3): 271–5. PMID 19998329. doi:10.1002/jat.1493.
- ↑ Aczone(Dapsone) Package insert. Irvine CA: Allergan Inc.; September 2008
- ↑ "Dapsone (Aczone)". Medications For Acne. PharmacistAnswers.
- ↑ Jaffuel D, Lebel B, Hillaire-Buys D, Pene J, Godard P, Michel FB, Blayac JP, Bousquet J, Demolyi P (1998). "Eosinophilic pneumonia induced by dapsone". BMJ. 317 (7152): 181. PMC 28611
 . PMID 9665900. doi:10.1136/bmj.317.7152.181.
. PMID 9665900. doi:10.1136/bmj.317.7152.181. - ↑ Richardus JH, Smith TC (1989). "Increased incidence in leprosy of hypersensitivity reactions to dapsone after introduction of multidrug therapy". Lepr Rev. 60 (4): 267–73. PMID 2491425.
- ↑ Kumar RH, Kumar MV, Thappa DM (1998). "Dapsone syndrome—a five year retrospective analysis". Indian J Lepr. 70 (3): 271–6. PMID 9801899.
- ↑ Rao PN, Lakshmi TS (2001). "Increase in the incidence of dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome—an appraisal". Lepr Rev. 72 (1): 57–62. PMID 11355519.
- ↑ Joseph MS (1985). "Hypersensitivity reaction to dapsone. Four case reports". Lepr Rev. 56 (4): 315–20. PMID 4079634.
- ↑ Jamrozik K (1986). "Dapsone syndrome occurring in two brothers". Lepr Rev. 57 (1): 57–62. PMID 3702581.
- ↑ Hortaleza AR, Salta-Ramos NG, Barcelona-Tan J, Abad-Venida L (1995). "Dapsone syndrome in a Filipino man". Lepr Rev. 66 (4): 307–13. PMID 8637384.
- ↑ Tomecki KJ, Catalano CJ (1981). "Dapsone hypersensitivity. The sulfone syndrome revisited". Arch Dermatol. 117 (1): 38–9. PMID 6450569. doi:10.1001/archderm.1981.01650010044023.
- ↑ Kromann NP, Vilhelmsen R, Stahl D (1982). "The dapsone syndrome". Arch Dermatol. 118 (7): 531–2. PMID 7092282. doi:10.1001/archderm.1982.01650190085028.
- ↑ "Mechanisms of Action of Dapsone in Dermatological Diseases". Dapsone: Clinical Uses in Various Cutaneous Diseases. Medscape Today. Archived from the original on May 17, 2011.
- ↑ Bozeman PM, Learn DB, Thomas EL (1990). "Assay of the human leukocyte enzymes myeloperoxidase and eosinophil peroxidase". J. Immunol. Methods. 126 (1): 125–33. PMID 2154520. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(90)90020-v.
- ↑ Bozeman PM, Learn DB, Thomas EL (1992). "Inhibition of the human leukocyte enzymes myeloperoxidase and eosinophil peroxidase by dapsone". Biochem. Pharmacol. 44 (3): 553–63. PMID 1324677. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(92)90449-s.
- ↑ Stendahl O, Molin L, Lindroth M (1983). "Granulocyte-mediated release of histamine from mast cells. Effect of myeloperoxidase and its inhibition by antiinflammatory sulfone compounds". Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 70 (3): 277–84. PMID 6186607. doi:10.1159/000233335.
- ↑ Kettle AJ, Gedye CA, Winterbourn CC (1993). "Superoxide is an antagonist of antiinflammatory drugs that inhibit hypochlorous acid production by myeloperoxidase". Biochem. Pharmacol. 45 (10): 2003–10. PMID 8390258. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(93)90010-t.
- ↑ Kettle AJ, Winterbourn CC (1991). "Mechanism of inhibition of myeloperoxidase by anti-inflammatory drugs". Biochem. Pharmacol. 41 (10): 1485–92. PMID 1850278. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(91)90565-m.
- ↑ Diaz-Ruiz A, Zavala C, Montes S, et al. (November 2008). "Antioxidant, antiinflammatory and antiapoptotic effects of dapsone in a model of brain ischemia/reperfusion in rats". J. Neurosci. Res. 86 (15): 3410–9. PMID 18615706. doi:10.1002/jnr.21775.
- ↑ Begon E, Chosidow O, Wolkenstein P (December 2004). "[Disulone]". Ann Dermatol Venereol (in French). 131 (12): 1062–73. PMID 15692440. doi:10.1016/S0151-9638(04)93842-2.
- ↑ Uetrecht JP (1995). "Myeloperoxidase as a generator of drug free radicals". Biochem. Soc. Symp. 61: 163–70. PMID 8660393.
- ↑ Tréfouël, J. et T.; Nitti, F.; Bovet, D. (23 November 1935). "Activité du p.aminophénylsulfamide sur l’infection streptococcique expérimentale de la souris et du lapin". Comptes rendus des séances de la Société de biologie et de ses filiales (in French). 120: 756.
- ↑ Fourneau, E.; Tréfouël, Th. et J.; Nitti, F.; Bovet, D. (1937). "Action antistreptococcique des dérivés sulfurés organiques". Comptes rendus de l'Académie des sciences (in French). 204: 1763.
- ↑ Buttle, G.A.H.; Stephenson, D.; Smith, S.; Dewing, T.; Foster, G.E. (June 1937). "Treatment of streptococcal infections in mice with 4:4'diamino-dipheni-sulphone". Lancet. 229 (5936): 1331–4. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)75868-5.
- ↑ "Leprosy | 14 History of dapsone and dyes". Archived from the original on 2009-02-12. Retrieved 2009-02-24. (1937)
- ↑ Stotland, Mira; Shalita, Alan R.; Kissling, Robert F. (April 2009). "Dapsone 5% Gel: A Review of its Efficacy and Safety in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. John Wiley & Sons. 10 (4): 1594–1602. doi:10.2165/00128071-200910040-00002.
- ↑ "Aczone (dapsone) 7.5% Gel Prescribing Information" (PDF). Allergan. February 2016. Retrieved 23 June 2016.