Autódromo José Carlos Pace
 | |
| Location | São Paulo, Brazil |
|---|---|
| Time zone | UTC−03:00 |
| Coordinates | 23°42′4″S 46°41′50″W / 23.70111°S 46.69722°WCoordinates: 23°42′4″S 46°41′50″W / 23.70111°S 46.69722°W |
| Capacity | 60,000 |
| Broke ground | 1938 |
| Opened | 1940 |
| Former names | Autódromo de Interlagos (1940–1985) |
| Major events |
FIA Formula One Brazilian Grand Prix (1972-1977, 1979-1980 and 1990-present) FIA World Endurance Championship 6 Hours of São Paulo Mil Milhas Brasil, Stock Car Brasil, Fórmula Truck, TC 2000, Formula 3 Sudamericana (till 2013), Brazilian Formula Three Championship (2014-present) |
| Current Circuit (1990–present) | |
| Length | 4.309 km (2.677 mi) |
| Turns | 15 |
| Lap record |
1:11.473 ( |
| Original Circuit (1940–1989) | |
| Length | 7.960 km (4.975 mi) |
| Turns | 26 |
| Lap record |
2:21.40 ( |
| Website |
www |
Autódromo José Carlos Pace, also known by its former name Interlagos, is a motorsport circuit located in the city of São Paulo, in the neighborhood of Interlagos, renamed after Carlos Pace, a Brazilian Formula One driver who had died in a 1977 plane crash. It is well known for being the venue of the Formula One Brazilian Grand Prix.
The Brazilian Grand Prix has always been more of a promoter event than a profit-raiser in itself. The contract was prolonged until 2022, although tobacco advertising has been banned since 2006.
History

The land on which the circuit is located was originally bought in 1926 by property developers who wanted to build accommodations.[1] Following difficulties partly due to the 1929 stock market crash, it was decided to build a racing circuit instead, construction started in 1938 and the track was inaugurated in May 1940.[1] The design was based on New York's Roosevelt Field Raceway (1937 layout).[2]
The traditional name of the circuit (literally, "between lakes") comes from its location on the neighborhood of Interlagos, a region between two large artificial lakes, Guarapiranga and Billings, which were built in the early 20th century to supply the city with water and electric power. It was renamed in 1985 from "Autódromo de Interlagos" to its current name to honor the Brazilian Formula One driver José Carlos Pace, who died in a plane crash in 1977.[3]
Formula One started racing there in 1972, the first year being a non-championship race, won by Argentinean Carlos Reutemann. The first World Championship Brazilian Grand Prix was held at Interlagos in 1973, the race won by defending Formula One World Champion and São Paulo local Emerson Fittipaldi. Fittipaldi won the race again the following year in bad weather and Brazilian driver José Carlos Pace won his only race at Interlagos in 1975.
Due to safety concerns with the 4.9 mile circuit, including the bumpy track surface and the inadequate barriers, deep ditches, and embankments, the last Formula One race held on the original Interlagos was in 1980, the race was nearly cancelled after protests by many Formula One drivers including defending world champion Jody Scheckter. The safety concerns were somewhat directed towards the track surface, which BBC commentator Murray Walker described as "appallingly bumpy". Most of the ground-effect cars of 1980 were designed in such a way that bumpy surfaces were barely tolerable for the drivers. These factors meant that Formula One would move back to the Jacarepaguá circuit in Rio de Janeiro, hometown of established star Nelson Piquet and where the Brazilian Grand Prix was held in 1978. After Formula One moved away, the only major race being held at Interlagos was the Mil Milhas Brasil, and the last major race on the original circuit was the 1989 Mil Milhas Brasil, and Formula One returned to the circuit the following year after it had been shortened and modified at a cost of $15 million. The track layout, aside from the pit exit being extended along the Curva do Sol over the years has remained the same since 1990. After the ascendancy of another São Paulo local, Ayrton Senna, negotiations were made to return to Interlagos that year, and it has stayed there ever since. The facilities include a kart circuit named after Ayrton Senna. The circuit now also hosts the Brazilian Formula Three Championship.
The circuit is often witness to dramatic results when it hosts the Formula One Brazilian Grand Prix. Felipe Massa almost won the 2008 Driver's World Championship when he finished the 2008 Brazilian Grand Prix as winner, but after he finished, Lewis Hamilton overtook Timo Glock and was crowned World Champion. Despite Rubens Barrichello's pole position in 2009, Mark Webber won the race and Jenson Button won the championship for Brawn after starting 14th. Williams got their first pole since 2006 here at the 2010 Brazilian Grand Prix with Nico Hülkenberg. The race was won by Sebastian Vettel, and with Mark Webber coming second, Red Bull secured the constructors title; however the driver's title was not confirmed until the last race.
Characteristics
The circuit is one of a minority of non-oval racing circuits to go in an anti-clockwise direction (Circuit of the Americas, Imola, Istanbul Park, Yas Marina Circuit, Laguna Seca, Singapore, Korea International Circuit and Circuit Ricardo Tormo in Valencia, being notable others). In 1979 upgrading work was done and the pit lane was extended past the first left-hand turn (Curva 1), making the corner more narrow, and the pit lane ended right in the middle of Curva 1 and 2. The present design of the track dates back from 1990, when the original circuit was shortened from 7,829 m to only 4,397 m (so that it could fit the new FIA restrictions on track length). As a consequence of the reduction, the track lost three long straight sections and nine fast curves (5 were lost forever, 4 were made slower and are still there). The original track was full of fast corners and it allowed cars to keep maximum speed for up to twenty seconds and was considered very dangerous (although no one ever died there whilst racing Formula One) and in 1990 the old layout was majorly revised. The new track still had a very long top-speed section that contained bumps, high-speed turns and little run-off area (though the track is very wide at this point).
Another reason why many drivers consider Interlagos interesting is that it was not built on flat terrain, but follows the ups and downs of hilly ground, which makes it harder to drive and demands more power from the car's engines. The hilly course is also a good feature for road cycling races usually held in the circuit.
The circuit is known for its many inclines and formerly bumpy surface, which could take its toll on F1 cars because they have a very low ride height and little suspension travel. The races are therefore very tough on the car, and also physically tough on the drivers, especially since the circuit is anti-clockwise, where the centrifugal forces in the many hard left turns push the drivers' necks to the right, instead of left as in the majority of circuits on the F1 calendar.
 Interlagos 1973 layout
Interlagos 1973 layout Interlagos 1979 layout
Interlagos 1979 layout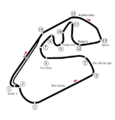 The track as it was redesigned in 1990
The track as it was redesigned in 1990 The latest version of the track
The latest version of the track Overlay showing the differences between present day and 1973 layouts
Overlay showing the differences between present day and 1973 layouts
Improvement in 2007
For the 2007 Brazilian Grand Prix, the largest-scale repairs in the last 35 years were carried out at the circuit, to fundamentally solve problems with the track surface.[4][5] The existing asphalt was entirely replaced,[6] resulting in a much smoother track surface. At the same time, the pit lane entrance was enhanced to improve safety and to add a new fixed grand stand.[7] To facilitate the work, the circuit was closed and no events were held in the five months immediately preceding the race.[8]
On 17 October 2007, Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos (CPTM) began to operate the new station of the Line C (currently called Line 9), Autódromo, near the circuit.[9][10][11][12] The Line C had been extended to improve the access between the center of São Paulo and southern region of the Greater São Paulo including the circuit,[13][14][15] improving circuit accessibility.
Planned 2012 redevelopment
Shortly before the 2011 Brazilian Grand Prix, FIA race director Charlie Whiting detailed several planned upgrades of the circuit, including a new pit entrance and expanded run-off at the final corner, as a response to several fatal accidents at the circuit in 2011.[16] In June 2012, further details of the proposed plans emerged, calling for the construction of a brand new pit building and the relocation of the start line from its current position between Arquibancadas and the Senna 'S' to Reta Oposta.[17] However, later it was decided to keep start/finish straight at its current location along with the new pit building.[18]
Track layout

Race start is in the "Tribunas" section and features a pretty long straight section, then comes "S do Senna" ("Senna's S") [Turns 1 & 2], a series of turns (left then right) that are considered extremely difficult because both of them have a different angle, a different radius, a different length, a different inclination (inward or outward) and a different shape (besides the terrain goes down and then up again).
"Senna's S" connects with "Curva do Sol" ("Sun Turn") [3], a round-shaped large-radius left-turn that leads to "Reta Oposta" ("Opposite Straight", a reference to the disused longer back straight of the pre-1990 circuit, to which it runs parallel), the track's longest (but not the fastest) straight. Reta Oposta is succeeded by a pair of downhill left turns that are called "Descida do Lago" ("Lake Descent") [4 & 5] into a short straight sector that climbs up towards the back of the pit buildings.
This is followed by a slow and difficult section, with small, kart-like turns and elevation changes. These turns are "Ferradura" ("Horseshoe") [6] downhill and right into "Laranjinha" ("Little Orange") [7], another right (the slowest point of the circuit); then the right-hand Turn 8 leads into "Pinheirinho" ("Small Pine Tree") [9], left on a plain field; "Bico de Pato" ("Duck Bill") [10] a right-hand turn complex (first, an easy right kink into the tighter-radius near-hairpin give the distinctive turn its shape and name); and then "Mergulho" ("Dive") [11], a constant-radius left-hand turn that slings the driver straight into a harder left at "Junção" ("Junction") [12].
Turn 13, a left up-hill kink, marks the start of the long, thrilling and dangerous top-speed section. Rising up through "Subida dos Boxes" ("Up to the Pits") [14], the driver encounters a long left turn that sometimes seems straight and sometimes bends in more clearly. As the name implies, Subida dos Boxes is uphill (quite steep, indeed) and demands a lot of power from the cars. At the end of it, Arquibancadas ("Bleachers") [15] forms the end of what was once called "Cotovelo" ("Elbow"). At this point the track seems inclined inwards (or somewhat crooked) as the cars approach top speed back through the "Tribunas" straight. The series of left turns from the exit of Junção all the way to Turn 1 into Senna's S is typically taken at full throttle and treated as a long straight. (This section is known as one of the longest full-throttle stretches on the Formula 1 calendar, and thus demanding of the engine's reliability at sustained high RPM and torque. Other notable stretches of this nature are the "Rettifilo Tribune" straight at Autodromo Nazionale di Monza and the Kemmel Straight at Circuit de Spa-Francorchamps.)
Pit lane
Interlagos has one of the longest pit-lanes ever used in Formula One, starting just before the start-finish straight and rejoining the main course after Curva do Sol. Entering the pits was originally not a trivial task, as the high speed and the left turning may force the car rightwards, out of the pits. The pit lane entrance received some changes to become safer for the 2007 Formula One Brazilian Grand Prix, and later for the 2014 Formula One Brazilian Grand Prix, when a chicane was added.
Lap records
The lap records at the Autódromo José Carlos Pace.
References
- 1 2 Interlagos circuit history Archived 30 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine. - Official Brazilian Grand Prix website
- ↑ Wolfe, Joel (2010), Autos and Progress: The Brazilian search for Modernity, New York City: Oxford UP, p. 234 (footnote 66), ISBN 978-0-19-517456-4
- ↑ "History - The Interlagos Race Track - Autódromo José Carlos Pace". www.autodromodeinterlagos.com.br. Retrieved 22 November 2015.
- ↑ "Interlagos será fechado para reforma" (in Portuguese). www.folhadaregiao.com.br/. 14 June 2007. Retrieved 5 August 2007.
- ↑ "As obras em Interlagos" (in Portuguese). www.autodromointerlagos.com/. 4 September 2007. Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 8 September 2007.
- ↑ "FIA tem uma justificada preocupação com o GP Brasil de Fórmula 1" (in Portuguese). www.gpbrasil.com.br/. Archived from the original on 7 August 2007. Retrieved 5 August 2007.
- ↑ "Alargamento da entrada dos boxes, para maior segurança dos pilotos" (in Portuguese). www.autodromointerlagos.com/. Archived from the original on 7 August 2007. Retrieved 5 August 2007.
- ↑ "Reforma deve acabar com problemas no asfalto de Interlagos" (in Portuguese). www.clicabrasilia.com.br/. 13 June 2007. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 5 August 2007.
- ↑ "ESTAÇÃO AUTÓDROMO É INAUGURADA NESTA QUARTA-FEIRA" (in Portuguese). CET - Companhia de Engenharia de Tráfego. 16 October 2007. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ↑ "INAUGURAÇÃO DA ESTAÇÃO AUTÓDROMO DÁ LARGADA PARA O METRÔ DE SUPERFÍCIE EM SP" (in Portuguese). CET - Companhia de Engenharia de Tráfego. 18 October 2007. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ↑ "CIRCULAÇÃO DE TRENS GANHA ESQUEMA ESPECIAL PARA GP BRASIL DE F1" (in Portuguese). CET - Companhia de Engenharia de Tráfego. 18 October 2007. Archived from the original on 23 October 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ↑ "INAUGURAÇÃO DA ESTAÇÃO AUTÓDROMO MARCA INÍCIO DO METRÔ DE SUPERFÍCIE, NA CAPITAL" (in Portuguese). CET - Companhia de Engenharia de Tráfego. 22 October 2007. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ↑ "CET Operação Interlagos 2007" (in Portuguese). CET - Companhia de Engenharia de Tráfego. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2007.
- ↑ "GOVERNADOR GERALDO ALCKMIN DÁ INÍCIO ÀS OBRAS DE EXTENSÃO DA LINHA C" (in Portuguese). CPTM - Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos. 21 November 2005. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 17 October 2007.
- ↑ "COMPANHIA INICIA OBRAS PARA BENEFICIAR POPULAÇÃO DA GRANDE SÃO PAULO" (in Portuguese). CPTM - Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos. 27 December 2005. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 17 October 2007.
- ↑ Collantine, Keith (22 November 2011). "Single DRS zone in Brazil and track changes for 2012". F1 Fanatic. Keith Collantine. Retrieved 23 November 2011.
- ↑ "F1: Ecclestone Approves Plan To Move Interlagos Pits". SPEED. News Corporation. 15 June 2012. Archived from the original on 17 June 2012. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ "Brazilian Grand Prix F1 venue Interlagos begins major revamp". Edd Straw. Autosport. 5 August 2014. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- ↑ http://www.automobilsport.com/mil-milhas-interlagos-qualifying-result-team-peugeot-creation-pescarolo-barazi-epsilon-embassy-racing-bruneau-alphand-jmb---29992.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Official website
- Info from the Official Formula 1 Website
- Official Brazilian Grand Prix website (English site)
- SaoPauloEsportes.com
- Info from BBC's circuit guide
- Autodromo Jose Carlos Pace History and Statistics
- Autódromo José Carlos Pace on Google Maps (Current Formula 1 Tracks)
- Ciro Pabón's Racetracks 3D views and virtual laps of all F1 circuits, including this one, via Google Earth