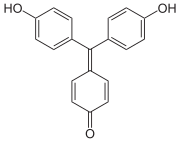
Aurin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-[Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)methylene]-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-one | |
| Other names
Aurin, corallin, p-rosolic acid, C.I. 43800 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 2055205 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.129 |
| EC Number | 210-041-8 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 290.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | see text |
| Density | 1.283 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 308 °C (586 °F; 581 K) (decomposes) |
| Insoluble | |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 482 nm[1] |
| -161.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  [1] [1] |
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H315, H319, H335[1] | |
| P261, P305+351+338[1] | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Aurin (C.I. 43800), sometimes named rosolic acid or corallin is an organic compound, forming yellowish or deep-red crystals with greenish metallic luster. It is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. It is soluble in strong acids to form yellow solution, or in aqueous alkalis to form carmine red solutions.
| Aurin (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 5.0 | above pH 6.8 | |
| 5.0 | ⇌ | 6.8 |
Due to this behaviour it can be used as pH indicator with pH transition range 5.0 - 6.8. It used as intermediate in manufacturing of dyes.
Synthesis
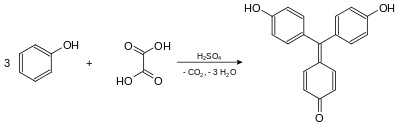
Aurin is formed by heating of phenol and oxalic acid in concentrated sulfuric acid.
Safety
Causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Avoid ingestion and/ or inhalation.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Sigma-Aldrich Co., p-Rosolic acid. Retrieved on 2014-05-06.
External links
- MSDS at Oxford University
- History of aurin in Heinrich Caro and the creation of modern chemical industry
 "Aurin". New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
"Aurin". New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.