Atlanto-axial joint
| Atlantoaxial joint | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Articulatio atlantoaxialis mediana, articulatio atlantoaxialis lateralis |
| MeSH | A02.835.583.097 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | 12160952 |
| TA |
A03.2.04.001 A03.2.05.001 |
| FMA | 25524 |
The atlantoaxial joint is a joint in the upper part of the neck between the first and second cervical vertebrae; the atlas and axis. It is a pivot joint.
The atlantoaxial joint is of a complicated nature. It consists of no fewer than four distinct joints.
There is a pivot articulation between the odontoid process of the axis and the ring formed by the anterior arch and the transverse ligament of the atlas.
Lateral and median joints
There are three atlantoaxial joints: median, lateral and posterior:[1]
- The median atlantoaxial joint is sometimes considered a triple joint:[2]
- one between the posterior surface of the anterior arch of atlas and the front of the odontoid process
- one between the anterior surface of the ligament and the back of the odontoid process
- The lateral atlantoaxial joint involves the lateral mass of atlas and axis.[3] Between the articular processes of the two bones there is on either side an arthrodial or gliding joint.
Ligaments
The ligaments connecting these bones are:
- Articular capsules
- Anterior atlantoaxial ligament
- Posterior atlantoaxial ligament
- Transverse ligament of the atlas
The atlantoaxial joint in common terminology is actually a composition of three: two lateral and one median atlantoaxial joints. Because of its proximity to the brain stem and importance in stabilization, fracture or injury at this level can be catastrophic. Common trauma and pathologies include (but are not limited to):
The Dens: significant depression on the skull can push the dens into the brainstem, causing death. The dens itself is vulnerable to fracture due to trauma or ossification.
Transverse ligament: Should the transverse ligament of the atlas fail due to trauma or disease, the dens is no longer anchored and can travel up the cervical spine, causing paralysis. If it reaches the medulla death can result. Alar ligaments: stress or trauma can stretch the weaker alar ligaments, causing an increase in range of motion of approximately 30%.
Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane: genetic traits can sometimes result in ossification, turning the groove into a foramen.
Capsule
The atlantoaxial articular capsules are thick and loose, and connect the margins of the lateral masses of the atlas with those of the posterior articular surfaces of the axis.
Each is strengthened at its posterior and medial part by an accessory ligament, which is attached below to the body of the axis near the base of the odontoid process, and above to the lateral mass of the atlas near the transverse ligament.
Abnormal widening
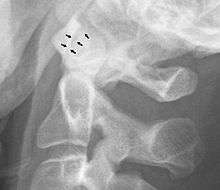
A widening of the atlanto-axial joint, as measured between the posterior surface of the anterior arch of atlas and the front of the odontoid process, indicates an injury to the transverse atlantal ligament.[4] Normally, this atlanto-dental distance is less than 2 mm, sometimes a maximum of 3 mm is accepted in men and 2.5 mm in women.[4]
References
- ↑ Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (1998). Terminologia anatomica: international anatomical terminology. Thieme. pp. 27–. ISBN 978-3-13-114361-7. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Carmine D. Clemente (2010). Clemente's Anatomy Dissector. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-1-60831-384-6. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ "Lateral atlantoaxial joint". Medcyclopaedia. GE.
- 1 2 Rojas, C.A.; Bertozzi, J.C.; Martinez, C.R.; Whitlow, J. (2007). "Reassessment of the Craniocervical Junction: Normal Values on CT". American Journal of Neuroradiology. 28 (9): 1819–1823. ISSN 0195-6108. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0660.
Bibliography
- Dalley, Arthur F; Moore, Keith L. Clinically Oriented Anatomy Fourth Edition. Baltimore. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1992.
- Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy &Physiology: the Unity of Form and Function. New York. McGraw Hill, 2007.
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.