Arylcyclohexylamine
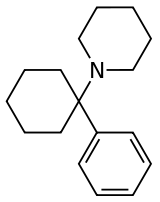
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.
History
Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo in 1954, with the latter compound described as a potent sedative.[1] Arylcyclohexylamines anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine.[1] The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since, the class has been expanded by scientific research into stimulant, analgesic, and neuroprotective agents, and also by clandestine chemists in search of novel recreational drugs.
Structure
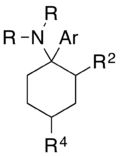
An arylcyclohexylamine is composed of a cyclohexylamine unit with an aryl moiety attachment. The aryl group is positioned geminal to the amine. In the simplest cases, the aryl moiety is typically a phenyl ring, sometimes with additional substitution. The amine is usually not primary, secondary amines such as methylamino or ethylamino, or tertiary cycloalkylamines such as piperidino and pyrrolidino, are the most commonly encountered N-substituents.
Pharmacology
Arylcyclohexylamines varyingly possess NMDA receptor antagonistic,[2][3] dopamine reuptake inhibitory,[4] and μ-opioid receptor agonistic[5] properties. Additionally, σ receptor agonistic,[6] nACh receptor antagonistic,[7] and D2 receptor agonistic[8] actions have been reported for some of these agents. Antagonism of the NMDA receptor confers anesthetic, anticonvulsant, neuroprotective, and dissociative effects; blockade of the dopamine transporter mediates stimulant and euphoriant effects as well as psychosis in high amounts; and activation of the μ-opioid receptor causes analgesic and euphoriant effects. Stimulation of the σ and D2 receptors may also contribute to hallucinogenic and psychomimetic effects.[8]
Versatile agents with a wide range of possible pharmacological activities depending on the extent and range to which chemical modifications are implemented. The various choice of substitutions that are made allows for "fine-tuning" of the pharmacological profile that results. As examples, BTCP is a selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor,[4] PCP is primarily an NMDA antagonist,[2] and BDPC is a superpotent μ-opioid agonist,[9] while PRE-084 is a selective sigma receptor agonist.[10] Thus, radically different pharmacology is possible through different structural combinations.
List of arylcyclohexylamines
| Compound | Aryl Substituent | N Group | Cyclohexyl ring |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCA[11] | Phenyl | NH2 | - |
| PCM[11] | Phenyl | Methylamino | - |
| Eticyclidine | Phenyl | Ethylamino | - |
| PCPr[12] | Phenyl | n-Propylamino | - |
| PCiP | Phenyl | Isopropylamino | - |
| PCBu | Phenyl | n-Butylamino | - |
| PCEOH | Phenyl | Hydroxyethylamino | - |
| PCMEA[13] | Phenyl | Methoxyethylamino | - |
| PCEEA | Phenyl | Ethoxyethylamino | - |
| PCMPA | Phenyl | Methoxypropylamino | - |
| PCDM[11] | Phenyl | Dimethylamino | - |
| Dieticyclidine | Phenyl | Diethylamino | - |
| 2-HO-PCP[2] | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Hydroxy |
| 2-Me-PCP[14] | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Methyl |
| 2-MeO-PCP[15] | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Methoxy |
| 2-Keto-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Keto |
| 2-Keto-PCE | Phenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto |
| 4-Methyl-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 4-Methyl |
| 4-Keto-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 4-Keto |
| 2'-Cl-PCP | o-Chlorophenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 2'-MeO-PCP | o-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 3'-F-PCP[16] | m-Fluorophenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 3'-Me-PCP[17] | m-Methylphenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 3'-NH2-PCP | m-Aminophenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 3'-HO-PCP | m-Hydroxyphenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 3'-MeO-PCP | m-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 3'-MeO-PCE | m-Methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | - |
| 3'-MeO-PCPr | m-Methoxyphenyl | n-Propylamino | - |
| 3'-MeO-PCPy[17] | m-Methoxyphenyl | Pyrrolidine | - |
| 3'-MeO-2-Keto-PCPr | m-Methoxyphenyl | n-Propylamino | 2-Keto |
| 3'-MeO-2-Keto-PCPy | m-Methoxyphenyl | Pyrrolidine | 2-Keto |
| 2'-Cl-2-Keto-PCPy | o-Chlorophenyl | Pyrrolidine | 2-Keto |
| 4'-HO-PCP | p-Hydroxyphenyl | Piperidine | - |
| Methoxydine (4'-MeO-PCP) | p-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | - |
| 4'-F-PCP[16] | p-Fluorophenyl | Piperidine | - |
| Arketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| Deschloroketamine | Phenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| Esketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| Ethketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto |
| Ketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| Methoxyketamine | o-Methoxyphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| MDCK | o-Tolyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine | o-Fluorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| Bromoketamine | o-Bromophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| TFMDCK | o-Trifluoromethylphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| SN 35210 [18] | o-Chlorophenyl | Carbomethoxybutylamino | 2-Keto |
| Methoxetamine | m-Methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto |
| Methoxmetamine | m-Methoxyphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto |
| Phencyclidine (PCP) | Phenyl | Piperidine | - |
| PC3MP | Phenyl | 3-Methylpiperidine | - |
| PC4MP | Phenyl | 4-Methylpiperidine | - |
| Rolicyclidine (PCPy) | Phenyl | Pyrrolidine | - |
| PCDMPy | Phenyl | 3,3-Dimethylpyrrolidine | - |
| PCMo | Phenyl | Morpholine | - |
| Methoxy-PCM[3] (2-MeO-PCMo) | o-Methoxyphenyl | Morpholine | - |
| 3'-MeO-PCMo | m-Methoxyphenyl | Morpholine | - |
| 4'-MeO-PCMo | p-Methoxyphenyl | Morpholine | - |
| Methyl-PCM[19] (4-Me-PCMo) | p-Methylphenyl | Morpholine | - |
| Hydroxy-methyl-PCM | 2-Methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl | Morpholine | - |
| TCM | 2-Thienyl | Methylamino | - |
| TCE | 2-Thienyl | Ethylamino | - |
| Tenocyclidine (TCP) | 2-Thienyl | Piperidine | - |
| TCPy | 2-Thienyl | Pyrrolidine | - |
| Tiletamine | 2-Thienyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto |
| Gacyclidine | 2-Thienyl | Piperidine | 2-Methyl |
| BDPC | p-Bromophenyl | Dimethylamino | 4-Phenethyl-4-hydroxy |
| Dimetamine | p-Methylphenyl | Dimethylamino | 4-Keto |
| BTCP[20] | Benzothiophen-2-yl | Piperidine | - |
| PRE-084 | Phenyl | Morpholinylethylcarboxylate | - |
- Other cycloalkane ring sizes have been experimented with than just purely thinking in terms of the cyclohexylamine. The requisite cycloalkylketone is reacted with PhMgBr; 3° alcohol is then reacted with NaN3; azide then reduced with LAH. Then in the final step the piperidine ring is constructed with 1-5-dibromo-pentane.[21]
In the p- and m-fluoro pcp analog paper, pyrrolidino ring sizes were also experimented with.
Arylcyclohexylamines by Ahmadi and Kalir
| Ketamine Ahmadi (2012).[22] | Ahmadi (2009).[23] | Ahmadi (2014).[24] | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | |
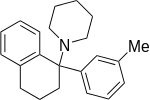
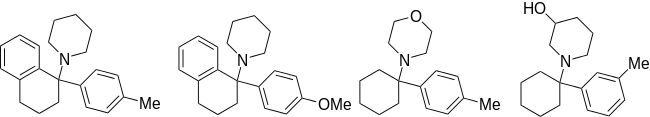
| Ahmadi (2011).[25] | Ahmadi 1-tetralone (2010).[26] | Ahmadi (2010).[27] | Ahmadi PCP (2010).[28] |
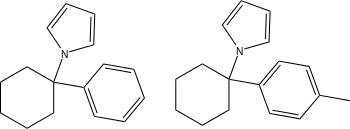 |  |  |  |
| Ahmadi PCP Maze (2012).[29] F, L, B, P. | Kalir PCP analgesic analog (1981).[30] | ||
 |  | ||
Rigid
Conformationally constrained analogs have also been prepared and researched by Morieti et al.[31]
References
- 1 2 Morris, H.; Wallach, J. (2014). "From PCP to MXE: a comprehensive review of the non-medical use of dissociative drugs". Drug Testing and Analysis. 6 (7–8): 614–32. PMID 24678061. doi:10.1002/dta.1620.
- 1 2 3 Ahmadi, A.; Mahmoudi, A. (2005). "Synthesis and biological properties of 2-hydroxy-1-(1-phenyltetralyl)piperidine and some of its intermediates as derivatives of phencyclidine". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 55 (9): 528–532. PMID 16229117. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296900.
- 1 2 Ahmadi, A.; Khalili, M.; Hajikhani, R.; Naserbakht, M. (2011). "New morpholine analogues of phencyclidine: Chemical synthesis and pain perception in rats". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 98 (2): 227–233. PMID 21215770. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2010.12.019.
- 1 2 Chaudieu, I.; Vignon; Chicheportiche; Kamenka; Trouiller; Chicheportiche (1989). "Role of the aromatic group in the inhibition of phencyclidine binding and dopamine uptake by PCP analogs". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 32 (3): 699–705. PMID 2544905. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(89)90020-8.
- ↑ Itzhak, Y.; Simon (1984). "A novel phencyclidine analog interacts selectively with mu opioid receptors". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 230 (2): 383–386. PMID 6086884.
- ↑ He, X. S.; Raymon, L. P.; Mattson, M. V.; Eldefrawi, M. E.; De Costa, B. R. (1993). "Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-1-(2-benzobthienyl)cyclohexylpiperidine homologues at dopamine-uptake and phencyclidine- and sigma-binding sites". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 36 (9): 1188–1193. PMID 8098066. doi:10.1021/jm00061a009.
- ↑ Eterović, V. A.; Lu, R.; Eakin, A. E.; Rodríguez, A. D.; Ferchmin, P. A. (1999). "Determinants of phencyclidine potency on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors from muscle and electric organ". Cellular and molecular neurobiology. 19 (6): 745–757. PMID 10456235.
- 1 2 Seeman, P.; Ko, F.; Tallerico, T. (2005). "Dopamine receptor contribution to the action of PCP, LSD and ketamine psychotomimetics". Molecular Psychiatry. 10 (9): 877–883. PMID 15852061. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001682.
- ↑ Lednicer, D.; Vonvoigtlander, P. F. (1979). "4-(p-Bromophenyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-phenethylcyclohexanol, an extremely potent representative of a new analgesic series". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 22 (10): 1157–1158. PMID 513062. doi:10.1021/jm00196a001.
- ↑ Maurice, T.; Su, T. P.; Parish, D. W.; Nabeshima, T.; Privat, A. (1994). "PRE-084, a sigma selective PCP derivative, attenuates MK-801-induced impairment of learning in mice". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 49 (4): 859–869. PMID 7886099. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(94)90235-6.
- 1 2 3 Thurkauf, A.; De Costa, B.; Yamaguchi, S.; Mattson, M. V.; Jacobson, A. E.; Rice, K. C.; Rogawski, M. A. (1990). "Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of 1-phenylcyclohexylamine analogs". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 33 (5): 1452–8. PMID 2329567. doi:10.1021/jm00167a027.
- ↑ Sauer, C.; Peters, F.; Staack, R.; Fritschi, G.; Maurer, H. (2008). "Metabolism and toxicological detection of a new designer drug, N-(1-phenylcyclohexyl)propanamine, in rat urine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry". Journal of Chromatography A. 1186 (1–2): 380–390. PMID 18035363. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.002.
- ↑ Sauer, C.; Peters, F.; Schwaninger, A.; Meyer, M.; Maurer, H. (2009). "Investigations on the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes involved in the metabolism of the designer drugs N-(1-phenyl cyclohexyl)-2-ethoxyethanamine and N-(1-phenylcyclohexyl)-2-methoxyethanamine". Biochemical Pharmacology. 77 (3): 444–450. PMID 19022226. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.10.024.
- ↑ Iorio, M. A.; Tomassini, L.; Mattson, M. V.; George, C.; Jacobson, A. E. (1991). "Synthesis, stereochemistry, and biological activity of the 1-(1-phenyl-2-methylcyclohexyl)piperidines and the 1-(1-phenyl-4-methylcyclohexyl)piperidines. Absolute configuration of the potent trans-(-)-1-(1-phenyl-2-methylcyclohexyl)piperidine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 34 (8): 2615–2623. PMID 1875352. doi:10.1021/jm00112a041.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A.; Mahmoudi, A. (2006). "Synthesis with improved yield and study on the analgesic effect of 2-methoxyphencyclidine". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 56 (5): 346–350. PMID 16821645. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296732.
- 1 2 Ogunbadeniyi, A. M.; Adejare, A. (2002). "Syntheses of fluorinated phencyclidine analogs". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 114: 39–42. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(01)00565-6.
- 1 2 Wallach, J.; Paoli, G. D.; Adejare, A.; Brandt, S. D. (2013). "Preparation and analytical characterization of 1-(1-phenylcyclohexyl)piperidine (PCP) and 1-(1-phenylcyclohexyl)pyrrolidine (PCPy) analogues". Drug Testing and Analysis. 6 (7–8): 633–50. PMID 23554350. doi:10.1002/dta.1468.
- ↑ Harvey, M; Sleigh, J; Voss, L; Pruijn, F; Jose, J; Gamage, S; Denny, W (2015). "Determination of the Hypnotic Potency in Rats of the Novel Ketamine Ester Analogue SN 35210". Pharmacology. 96 (5–6): 226–32. PMID 26352278. doi:10.1159/000439598.
- ↑ Ahmadi A, Khalili M, Hajikhani R, Naserbakht M (2011). "Synthesis and determination of acute and chronic pain activities of 1-[1-(4-methylphenyl) (cyclohexyl)] morpholine as a new phencyclidine derivative in rats". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 61 (2): 92–7. PMID 21428243. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296173.
- ↑ Vignon, J.; Pinet, V.; Cerruti, C.; Kamenka, J. M.; Chicheportiche, R. (1988). "3HN-1-(2-benzo(b)thiophenyl)cyclohexylpiperidine (3HBTCP): A new phencyclidine analog selective for the dopamine uptake complex". European Journal of Pharmacology. 148 (3): 427–436. PMID 3384005. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(88)90122-7.
- ↑ McQuinn, Roy L. (1981). "Structure-activity relationships of the cycloalkyl ring of phencyclidine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 24 (12): 1429–1432. PMID 7310819. doi:10.1021/jm00144a011.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A; Khalili, M; Hajikhani, R; Hosseini, H; Afshin, N; Nahri-Niknafs, B (2012). "Synthesis and study the analgesic effects of new analogues of ketamine on female wistar rats". Medicinal chemistry (Shariqah (United Arab Emirates)). 8 (2): 246–51. PMID 22385170. doi:10.2174/157340612800493683.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A; Khalili, M; Abbassi, S; Javadi, M; Mahmoudi, A; Hajikhani, R (2009). "Synthesis and study on analgesic effects of 1-1-(4-methylphenyl) (cyclohexyl) 4-piperidinol and 1-1-(4-methoxyphenyl) (cyclohexyl) 4-piperidinol as two new phencyclidine derivatives". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 59 (4): 202–6. PMID 19517897. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296386.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A; Khalili, M; Marami, S; Ghadiri, A; Nahri-Niknafs, B (2014). "Synthesis and pain perception of new analogues of phencyclidine in NMRI male mice". Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry. 14 (1): 64–71. PMID 24251803. doi:10.2174/1389557513666131119203551.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A; Solati, J; Hajikhani, R; Pakzad, S (2011). "Synthesis and analgesic effects of new pyrrole derivatives of phencyclidine in mice". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 61 (5): 296–300. PMID 21755813. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296202.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A; Khalili; Hajikhani; Barghi; Mihandoust (2010). "Synthesis and determination of chronic and acute thermal and chemical pain activities of a new derivative of phencyclidine in rats". Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research : IJPR. 9 (4): 379–85. PMC 3870061
 . PMID 24381602.
. PMID 24381602. - ↑ Ahmadi, A; Khalili, M; Mihandoust, F; Barghi, L (2010). "Synthesis and determination of acute and chronic pain activities of 1-1-(3-methylphenyl) (tetralyl)piperidine as a new derivative of phencyclidine via tail immersion and formalin tests". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 60 (1): 30–5. PMID 20184224. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296245.
- ↑ Ahmadi, A; Solati, J; Hajikhani, R; Onagh, M; Javadi, M (2010). "Synthesis and analgesic effects of 1-1-(2-methylphenyl)(cyclohexyl)-3-piperidinol as a new derivative of phencyclidine in mice". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 60 (8): 492–6. PMID 20863005. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296317.
- ↑ Hajikhani, R; Ahmadi, A; Naderi, N; Yaghoobi, K; Shirazizand, Z; Rezaee, N. M.; Niknafs, B. N. (2012). "Effect of phencyclidine derivatives on anxiety-like behavior using an elevated-plus maze test in mice". Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 21 (3): 307–12. PMID 23214193.
- ↑ Itzhak, Y. (1981). "New analgesic drugs derived from phencyclidine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 24 (5): 496–9. PMID 7241506. doi:10.1021/jm00137a004.
- ↑ Moriarty, R.; Enache, L.; Zhao, L.; Gilardi, R.; Mattson, M.; Prakash, O. (1998). "Rigid phencyclidine analogues. Binding to the phencyclidine and sigma 1 receptors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 41 (4): 468–477. PMID 9484497. doi:10.1021/jm970059p.
External links
- Morris, H; Wallach, J. "From PCP to MXE: a comprehensive review of the non-medical use of dissociative drugs". Drug Test Anal. 6: 614–32. PMID 24678061. doi:10.1002/dta.1620.
- Synthesis and Effects of PCP Analogs
- Interview with a Ketamine Chemist
- PCP analogs (Cumulative)