Architectural model

An architectural model is a type of scale model - a physical representation of a structure - built to study aspects of an architectural design or to communicate design ideas.
Depending on the purpose, models can be made from a variety of materials, including blocks, paper, and wood, and at a variety of scales.
Purpose

Architectural models are used by architects for a range of purposes:
- Ad hoc models, or sketch models, are sometimes made to study the interaction of volumes, different viewpoints, or concepts during the design process. They may also be useful in explaining a complicated or unusual design to builders, or as a focus for discussion between designers and consultants such as architects, engineers and town planners.
- Presentation models can be used to exhibit, visualise or sell a final design. A model are also used as show pieces, for instance as a feature in the reception of a building, or as part of a museum exhibition such as scale replicas of historical buildings.
Types of models include:
- Exterior models are models of buildings which usually include some landscaping or civic spaces around the building.
- Interior models are models showing interior space planning, finishes, colors, furniture and beautification.
- Landscaping design models are models of landscape design and development representing features such as walkways, small bridges, pergolas, vegetation patterns and beautification. Landscaping design models usually represent public spaces and may, in some cases, include buildings as well.
- Urban models are models typically built at a much smaller scale (starting from 1:500 and less, 1:700, 1:1000, 1:1200, 1:2000, 1:20 000), representing several city blocks, even a whole town or village, large resort, campus, industrial facility, military base and so on. Urban models are a vital tool for town/city planning and development. Urban models of large urban areas are displayed at museums such as the Shanghai Urban Planning Exhibition Center, Queens Museum in New York, the Beijing Planning Exhibition Hall, and the Singapore City Gallery.
- Engineering and construction models show isolated building/structure elements and components and their interaction.
 A model by architect Lorenzo Winslow which he used to explore the structure of the Grand Staircase at the White House for his redesign of the East Wing.
A model by architect Lorenzo Winslow which he used to explore the structure of the Grand Staircase at the White House for his redesign of the East Wing. Model of a museum building.
Model of a museum building. Model of a building interior.
Model of a building interior. A scale replica model of the demolished Capitol Theatre in Causeway Bay, Hong Kong
A scale replica model of the demolished Capitol Theatre in Causeway Bay, Hong Kong- A model used for urban planning in the Buenos Aires Province
Virtual modeling
Buildings are increasingly designed in software with CAD (computer-aided design) systems. Early virtual modelling involved the fixing of arbitrary lines and points in virtual space, mainly to produce technical drawings. Modern packages include advanced features such as databases of components, automated engineering calculations, visual fly-throughs, dynamic reflections, and accurate textures and colours.[1][2]
Materials
Rough study models can be made quickly using cardboard, wooden blocks, polystyrene, foam, foam boards and other materials. Such models are an efficient design tool for three-dimensional understanding of a structure, space or form, used by architects, interior designers and exhibit designers.
Common materials used for centuries in architectural model building were card stock, balsa wood, basswood and other woods. Modern professional architectural model builders are taking advantage of twenty-first century materials, such as Taskboard (a flexible and lightweight wood/fiber board), plastics, wooden and wooden-plastic composites, foams, foam board and urethane compounds.
A number of companies produce ready-made pieces for structural components (e.g. girders, beams), siding, furniture, figures (people), vehicles, trees, bushes and other features which are found in the models. Features such as vehicles, people figurines, trees, street lights and other are called "scenery elements" and serve not only to beautify the model, but also to help the observer to obtain a correct feel of scale and proportions represented by the model.
Increasingly, rapid prototyping techniques such as 3D printing and CNC routing are used to automatically construct models straight from CAD plans.[3]
- A model of two residential towers, made of earthenware during the Han Dynasty in China.
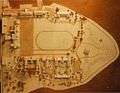 A wooden exterior model of the Royal Military College of Canada grounds
A wooden exterior model of the Royal Military College of Canada grounds
Scales
Architectural models are being constructed at much smaller scale than their 1:1 counterpart.
The scales and their architectural use is broadly as follows:
- 1:1 Full (or real) size for details
- 1:2 Details
- 1:5 Details
- 1:10 Interior spaces/furniture
- 1:20 Interior spaces/furniture
- 1:50 Interior spaces/detailed floor plans/different floor levels
- 1:100 Building plans/layouts
- 1:500 Building layouts/site plans
- 1:1000 Urban scale for site or location plans
- 1:1250 Site plans
- 1:2500 Site plans/city maps
Sometimes model railroad scales such as 1:160 and 1:87 are used due to ready availability of commercial figures, vehicles and trees in those scales, and models of large buildings are most often built in approximately that range of scales due to size considerations.
See also
- Architectural rendering
- Building model (non-architectural)
- Maquette
- Origamic architecture (OA)
- Scale model
- Superquick
References
- ↑ "What is Architectural Visualisation?". Flying 3D. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- ↑ "What is Accurate Visual Representation?". Flying 3D. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- ↑ Ian Gibson, Thomas Kvan, Ling Wai Ming (2002). "Rapid prototyping for architectural models". Rapid Prototyping Journal. 8 (2): 91–95. doi:10.1108/13552540210420961.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Architectural models. |