Aragonese language
| Aragonese | |
|---|---|
| aragonés | |
| Pronunciation | Aragonese pronunciation: [aɾaɣoˈnes] |
| Native to | Spain |
| Region | Aragon; northern and central Huesca and northern Zaragoza |
Native speakers | 25,500 (2011)[1] including speakers living outside the native area (2011) |
|
Indo-European
| |
Early form | |
| Latin (Aragonese alphabet) | |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Academia d'a Luenga Aragonesa |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 |
an |
| ISO 639-2 |
arg |
| ISO 639-3 |
arg |
| Glottolog |
arag1245[2] |
| Linguasphere |
51-AAA-d |
|
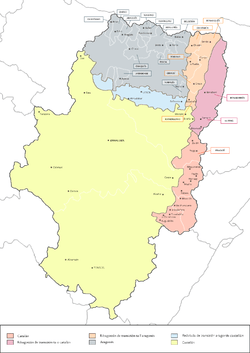
Map of Aragon with the dialects of northern Aragon in gray, blue, and light orange | |
Aragonese (/ˌærəɡɒˈniːz/; aragonés [aɾaɣoˈnes] in Aragonese) is a Romance language spoken in several dialects by 10,000 to 30,000 people in the Pyrenees valleys of Aragon, Spain, primarily in the comarcas of Somontano de Barbastro, Jacetania, Alto Gállego, Sobrarbe, and Ribagorza/Ribagorça. It is the only modern language which survived from medieval Navarro-Aragonese in a form distinctly different from Spanish.
Informally known as fabla ("talk" or "speech"), Aragonese is also commonly referred to by the names of its local dialects such as cheso (from Valle de Hecho) or patués (from the Benasque Valley).
History
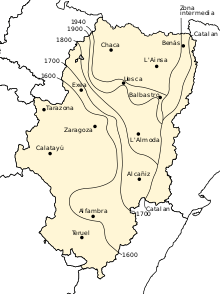
Aragonese, which developed in portions of the Ebro basin, can be traced back to the High Middle Ages. It spread throughout the Pyrenees to areas where languages similar to Basque were previously spoken. The Kingdom of Aragon (formed by the counties of Aragon, Sobrarbe and Ribagorza) expanded southward from the mountains, pushing the Moors farther south in the Reconquista and spreading the Aragonese language.
The union of the Catalan counties and the Kingdom of Aragon which formed the 12th-century Crown of Aragon did not merge the languages of the two territories; Catalan continued to be spoken in the east and Navarro-Aragonese in the west, with boundaries blurred by dialectal continuity. The Aragonese Reconquista in the south ended with the cession of Murcia by James I of Aragon to the Kingdom of Castile as dowry for an Aragonese princess.
The best-known proponent of the Aragonese language was Johan Ferrandez d'Heredia, the Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller in Rhodes at the end of the 14th century. He wrote an extensive catalog of works in Aragonese and translated several works from Greek into Aragonese (the first in medieval Europe).
The spread of Castilian (Spanish), the Castilian origin of the Trastámara dynasty, and the similarity between Castilian and Aragonese facilitated the recession of the latter. A turning point was the 15th-century coronation of the Castilian Ferdinand I of Aragon, also known as Ferdinand of Antequeraa.
In recent times, Aragonese was mostly regarded as a group of rural dialects of Spanish. Compulsory education undermined its already weak position; for example, pupils were punished for using it. However, the 1978 Spanish transition to democracy heralded literary works and studies of the language.
Modern Aragonese
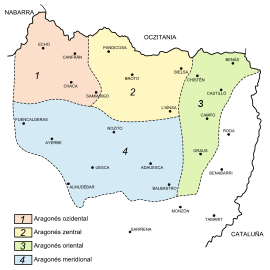
Aragonese is the native language of the Aragonese mountain ranges of the Pyrenees, in the comarcas of Somontano, Jacetania, Sobrarbe, and Ribagorza. Cities and towns in which Aragonese is spoken are Huesca, Graus, Monzón, Barbastro, Bielsa, Chistén, Fonz, Echo, Estadilla, Benasque, Campo, Sabiñánigo, Jaca, Plan, Ansó, Ayerbe, Broto, and El Grado.
It is spoken as a second language by inhabitants of Zaragoza, Huesca, Ejea de los Caballeros, or Teruel. According to recent polls, there are about 25,500 speakers (2011) [3] including speakers living outside the native area.
In 2009, the Languages Act of Aragon recognized the "native language, original and historic" of Aragon. The language received several linguistic rights, including its use in public administration.[4]
Dialects
- Western dialect: Ansó, Valle de Hecho, Chasa, Berdún, Chaca
- Central dialect: Panticosa, Biescas, Torla, Broto, Bielsa, Yebra, Aínsa-Sobrarbe
- Eastern dialect: Benás, Plan, Bisagorri, Campo, Perarrúa, Graus, Estadilla
- Southern dialect: Agüero, Ayerbe, Rasal, Bolea, Lierta, Uesca, Almudévar, Nozito, Labata, Alguezra, Angüés, Pertusa, Balbastro, Nabal[5]
Phonology
Traits

Aragonese has many historical traits in common with Catalan. Some are conservative features that are also shared with the Astur-Leonese languages and Galician-Portuguese, where Spanish innovated in ways that did not spread to nearby languages.
Shared with Catalan
- Romance initial F- is preserved, e.g. FILIUM > fillo ("son", Sp. hijo, Cat. fill, Pt. filho).
- Romance palatal approximant (GE-, GI-, I-) consistently became medieval [dʒ], as in medieval Catalan and Portuguese. This becomes modern ch [tʃ], as a result of the devoicing of sibilants (see below). In Spanish, the medieval result was either [dʒ] (modern [x]), [ʝ] or nothing, depending on the context. E.g. IUVENEM > choven ("young man", Sp. joven /ˈxoβen/, Cat. jove /ˈʒoβǝ/), GELARE > chelar ("to freeze", Sp. helar /eˈlaɾ/, Cat. gelar /ʒǝˈla/).
- Romance groups -LT-, -CT- result in [jt], e.g. FACTUM > feito ("done", Sp. hecho, Cat. fet, Gal./Port. feito), MULTUM > muito ("many"/"much", Sp. mucho, Cat. molt, Gal. moito, Port. muito).
- Romance groups -X-, -PS-, SCj- result in voiceless palatal fricative ix [ʃ], e.g. COXU > coixo ("crippled", Sp. cojo, Cat. coix).
- Romance groups -Lj-, -C'L-, -T'L- result in palatal lateral ll [ʎ], e.g. MULIERE > muller ("woman", Sp. mujer, Cat. muller), ACUT'LA > agulla ("needle", Sp. aguja, Cat. agulla).
Shared with Catalan and Spanish
- Open O, E from Romance result systematically in diphthongs [we], [je], e.g. VET'LA > viella ("old woman", Sp. vieja, Cat. vella). This includes before a palatal approximant, e.g. octō > ueito ("eight", Sp. ocho, Cat. vuit). Spanish diphthongizes except before yod, whereas Catalan only diphthongizes before yod.
- Loss of final unstressed -E but not -O, e.g. GRANDE > gran ("big"), FACTUM > feito ("done"). Catalan loses both -O and -E; Spanish preserves -O and sometimes -E.
Shared with Spanish
- Former voiced sibilants become voiceless ([z] > [s], [dʒ] > [tʃ]).
Shared with neither
- Latin -B- is maintained in past imperfect endings of verbs of the second and third conjugations: teneba, teniba ("he had", Sp. tenía, Cat. tenia), dormiba ("he was sleeping", Sp. dormía, Cat. dormia).
- High Aragonese dialects (alto aragonés) and some dialects of Gascon have preserved the voicelessness of many intervocalic stop consonants, e.g. CLETAM > cleta ("sheep hurdle", Cat. cleda, Fr. claie), CUCULLIATAM > cocullata ("crested lark", Sp. cogujada, Cat. cogullada).
- Several Aragonese dialects maintain Latin -ll- as geminate /ll/.
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Open | a |
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | t͡ʃ | k | |
| voiced | b | d | g | |||
| Fricative | f | θ | s | ʃ | ||
| Approximant | central | j | w | |||
| lateral | l | ʎ | ||||
| Flap | ɾ | |||||
| Trill | r | |||||
Orthography
In 2010, the Academia de l'Aragonés (founded in 2006) established an orthographic standard to modernize medieval orthography and to make it more etymological. The new orthography is used by the Aragonese Wikipedia.[6]
Aragonese had two orthographic standards:
- The grafía de Uesca, codified in 1987 by the Consello d'a Fabla Aragonesa (CFA) at a convention in Huesca, is used by most Aragonese writers. It has a more uniform system of assigning letters to phonemes, with less regard for etymology; words traditionally written with ⟨v⟩ and ⟨b⟩ are uniformly written with ⟨b⟩ in the Uesca system. Similarly, ⟨ch⟩, ⟨j⟩, and ⟨g⟩ before ⟨e⟩ and ⟨i⟩ are all written ⟨ch⟩. It uses letters associated with Spanish, such as ⟨ñ⟩.[7]
- The grafía SLA, devised in 2004 by the Sociedat de Lingüistica Aragonesa (SLA), is used by some Aragonese writers. It uses etymological forms which are closer to Catalan, Occitan, and medieval Aragonese sources. In the SLA system ⟨v⟩, ⟨b⟩,⟨ch⟩, ⟨j⟩, and ⟨g⟩ before ⟨e⟩ and ⟨i⟩ are distinct, and the digraph ⟨ny⟩ replaces ⟨ñ⟩.
During the 16th century, Aragonese Moriscos wrote aljamiado texts (Romance texts in Arabic writing), possibly because of their inability to write in Arabic. The language in these texts has a mixture of Aragonese and Castilian traits, and they are among the last known written examples of the Aragonese formerly spoken in central and southern Aragon.[8]
| Sounds and features | Academia de l'Aragonés | Grafía de Uesca (1987) | Grafía SLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| /a/ | a | a | a |
| /b/ | b, v according to Latin etymology Ex: bien, servicio, val, activo, cantaba, debant |
b Ex: bien, serbizio, bal, autibo, cantaba, debán |
b, v according to Romance etymology, as in Catalan and Occitan Ex: bien, servício, val, activo, cantava, devant |
| /k/ |
|
|
|
| /kw/ | If there is an etymological q, as in Catalan and a bit in Occitan:
|
cu as in Spanish Ex: cuan, cuestión |
If there is an etymological q, as in Catalan and a bit in Occitan:
|
| /tʃ/ | ch Ex: chaminera, minchar, chusticia, cheografía |
ch Ex: chaminera, minchar, chustizia, cheografía |
|
| /d/ | d | d | d |
| /e/ | e | e | e |
| /f/ | f | f | f |
| /ɡ/ |
|
|
|
| /ɡw/ |
|
|
|
| Etymological h (rendered silent after Latin) |
Written according to Latin etymology Ex: historia, hibierno |
Not written Ex: istoria, ibierno |
Written as in Medieval Aragonese and Catalan Ex: história, hivierno |
| /i/ | i | i | i |
| /l/ | l | l | l |
| /ʎ/ | ll | ll | ll |
| /m/ | m | m | m |
| /n/ | n | n | n |
| /ɲ/ | ny as in Medieval Aragonese and Catalan Ex: anyada |
ñ as in Spanish Ex: añada |
ny as in Medieval Aragonese and Catalan Ex: anyada |
| /o/ | o | o | o |
| /p/ | p | p | p |
| /ɾ/ | r | r | r |
| /r/ |
|
|
|
| /s/ | s (also between two vowels, never *ss) | s (also between two vowels, never *ss) | s (also between two vowels, never *ss) |
| /t/ | t | t | t |
| Etymological final -t (silent in Modern Aragonese) |
Written as in Medieval Aragonese, Catalan and Occitan Ex: sociedat, debant, chent |
Not written Ex: soziedá, debán, chen |
Written as in Medieval Aragonese, Catalan and Occitan Ex: sociedat, devant, gent |
| /u, w/ | u | u | u |
| /jʃ/ (Eastern dialects) /ʃ/ (Western dialects) |
ix as unifying grapheme for all dialects Ex: baixo |
x Ex: baxo |
|
| /j/ |
|
|
|
| /θ/ |
|
z Ex: zona, Probenza, fez, zentro, serbizio, realizar, berdaz |
|
| Learned Greco-Roman words | Assimilatory tendencies not written Ex: dialecto, extension, and lexico |
Assimilatory tendencies written Ex: dialeuto, estensión, but lecsico |
Not all assimilatory tendencies written Ex: dialecto, extension, and lexico |
| Accent mark for stress (accented vowel in bold) |
Spanish model, but with the possibility for oxytones to not be accented Ex:
|
Spanish model Ex:
|
Portuguese, Catalan and Occitan model Ex:
|
Grammar
Aragonese grammar is similar to that of other Iberian Romance languages, such as Spanish and Catalan.
Articles
The definite article in Aragonese has undergone dialect-related changes, with definite articles in Old Aragonese similar to their present Spanish equivalents. The most-widespread articles in Aragonese are similar to those in Galician and Portuguese, since they lack the initial l:
| Masculine | Feminine | |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | o | a |
| Plural | os | as |
The second (auxiliary) article, after a vowel, is used with an r (pronounced [ɾ]).
| Masculine | Feminine | |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | ro | ra |
| Plural | ros | ras[10] |
Lexicology
Neighboring Romance languages have influenced Aragonese. Catalan and Occitan influenced Medieval Aragonese, and the Catalan influence continued under the Crown of Aragon in the Ribagorçan dialect. Since the 15th century, Spanish has most influenced Aragonese; it was adopted throughout Aragon as the first language, limiting Aragonese to the northern region surrounding the Pyrenees. French has also influenced Aragonese; Italian loanwords have entered through other languages (such as Catalan), and Portuguese words have entered through Spanish. Germanic words came with the conquest of the region by Germanic peoples during the fifth century, and English has introduced a number of new words into the language.
Gender
Words that were part of the Latin second declension—as well as words that joined it later on—are usually masculine:
- FILIU(M) > fillo (son)
- SCIURU + OLU(M) > esquiruelo (squirrel)
Words that were part of the Latin first declension are usually feminine:
- FILIA(M) > filla (daughter).
Some Latin neuter plural nouns joined the first declension as singular feminine nouns:
- FOLIA > fuella (leaf).
Words ending in -or are feminine:
- a honor, a calor, a color, and (in Medieval Aragonese) la amor
The names of fruit trees usually end in -era (a suffix derived from Latin -ARIA) and are usually feminine:
- a perera, a manzanera, a nuquera, a castanyera, a tellera / o tilero, a olivera, a ciresera, l'almendrera
The genders of river names vary:
- Many ending in -a are feminine: a Cinca/a Cinga, a Cinqueta, a Garona, L'Arba, a Noguera, a Isuela, La Uecha, La Uerva, etc. The latter was known as río de la Uerba during the 16th century.
- Many from the second and the third declension are masculine: L'Ebro, O Galligo, O Flumen, L'Alcanadre.
Pronouns
Unlike most other Ibero-Romance varieties, Aragonese has partitive and locative clitic pronouns derived from the Latin inde and ibi: en/ne and bi/i/ie.
Such pronouns are present in most major Romance languages (Catalan en and hi, Occitan ne and i, French en and y, and Italian ne and ci/vi).
En/ne is used for:
- Partitive objects: No n'he visto como aquello ("I haven't seen anything like that", literally 'Not (of it) I have seen like that').
- Partitive subjects: En fa tanto de mal ("It hurts so much", literally '(of it) it causes so much of pain')
- Ablatives, places from which movements originate: Se'n va ra memoria ("Memory goes away", literally '(away from [the mind]) memory goes')
Bi/i/ie is used for:
- Locatives, where something takes place: N'ibi heba uno ("There was one of them"), literally '(Of them) there was one')
- Allatives, places that movements go towards or end: Vés-be ('Go there (imperative)')
Literature
Aragonese was not written until the 12th and 13th centuries; the history Liber Regum,[11] Razón feita d'amor,[11] Libre dels tres reys d'orient,[11] and Vida de Santa María Egipcíaca date from this period,[11][12] there is also an Aragonese version of the Chronicle of Morea, differing also in its content and written in the late 14th century called Libro de los fechos et conquistas del principado de la Morea.
Early modern period
Since 1500, Spanish was the cultural language of Aragon; many Aragonese wrote in Spanish, and during the 17th century the Argensola brothers went to Castile to teach Spanish.[13] Aragonese became a popular village language.[14] During the 17th century, popular literature in the language began to appear. In a 1650 Huesca literary contest, Aragonese poems were submitted by Matías Pradas, Isabel de Rodas and "Fileno, montañés".
Contemporary literature
The 19th and 20th centuries have seen a renaissance of Aragonese literature in several dialects. In 1844, Braulio Foz' novel Vida de Pedro Saputo was published in the Almudévar (southern) dialect. The 20th century featured Domingo Miral's costumbrist comedies and Veremundo Méndez Coarasa's poetry, both in Hecho (western) Aragonese; Cleto Torrodellas' poetry and Tonón de Baldomera's popular writings in the Graus (eastern) dialect and Arnal Cavero's costumbrist stories and Juana Coscujuela' novel A Lueca, historia d'una moceta d'o Semontano, also in the southern dialect.
See also
- Academia de l'Aragonés
- Arredol – Electronic Aragonese newspaper
References
- ↑ Report about Census of population 2011 of Aragonese Sociolinguistics Seminar and University of Zaragoza
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Aragonese". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Report about Census of population 2011 of Aragonese Sociolinguistics Seminar and University of Zaragoza
- ↑ Languages Act of Aragon Official Bulletin of Aragon
- ↑ Aragonese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ "Propuesta Ortografica de l'Academia de l'Aragonés" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-10-11. Retrieved July 2016. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ "Normas graficas de l'aragonés" (PDF). Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2008-10-14.
- ↑ Aragonese in Aljamiado literature
- ↑ Some orthographic details related to local dialects are not listed.
- ↑ Francho Nagore, Gramica de la Lengua Aragonesa. Mira Editores (1989).
- 1 2 3 4 I Curso sobre lengua y literatura en Aragón: (Edad Media)
- ↑ La vida de Santa Maria Egipciaca: a fourteenth-century translation into Old Castilian from Latin of a work by Paul the Deacon
- ↑ Alazet: revista de filología, Número 5
- ↑ El aragonés de la literatura aljamiado-morisca
Further reading
- Mott, Brian (2007), "Chistabino (Pyrenean Aragonese)" (PDF), Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 37 (1): 103–114, doi:10.1017/S0025100306002842
- Campos Bandrés, Iris Orosia; Martínez Cortés, Juan Pablo; Paricio Martín, Santiago J. (2016). The Aragonese Language in Education in Spain (PDF). Leeuwarden: Mercator.
External links
| Aragonese edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| For a list of words relating to Aragonese language, see the Aragonese language category of words in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aragonese language. |
- Catalogue of Aragonese publications
- Academia de l'Aragonés
- Consello d'a Fabla Aragonesa
- Ligallo de Fablans de l'Aragonés
- A.C. Nogará
- Sociedat de Lingüistica Aragonesa
- Aragonese language