Aonidiella orientalis
| Aonidiella orientalis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hemiptera |
| Suborder: | Sternorrhyncha |
| Superfamily: | Coccoidea |
| Family: | Diaspididae |
| Subfamily: | Aspidiotinae |
| Tribe: | Aspidiotini |
| Genus: | Aonidiella |
| Species: | A. orientalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Aonidiella orientalis (Newstead, 1894) | |
Aonidiella orientalis is a species of insect in the family Diaspididae, the armored scale insects. It is known commonly as the Oriental yellow scale.[1] It is an agricultural pest on a wide variety of crop plants.[1]
Description
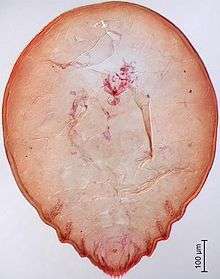
This is a scale insect, a tiny insect which is most easily identified by the female, which attaches itself to a host plant, loses its legs, and remains stationary covered by a somewhat rounded scale-like shield of wax. In this species, the female forms a flat, circular scale which is white, brown, or yellow in color.[1] It is up to 2.6 millimeters long.[2] The insect within is no more than 1.4 millimeters long.[1] The winged male of this species also produces a scale.[2]
Distribution
This species is likely native to Asia. It can be found nearly worldwide today because it has been introduced to many areas with shipments of plants and then began a slow spread. It is common in many tropical and subtropical areas, and it can survive in greenhouses in cooler regions. It is not known from Europe.[2] Some ports check for this and other scales in quarantined plant shipments.[1]
Biology
The female attaches to the surface of a plant, forms a waxy shield, and lays eggs beneath it.[1] They are often viviparous, producing live young instead of laying eggs.[2] The larvae emerge and leave the shield; at this point they are called "crawlers". They roam the plant, feeding on sap by inserting their stylets. Males reach the adult stage at about 19 days. Females reach adulthood and yield the next generation of larvae at about 44 days.[1] Males have wings but no mouthparts, and they do not feed.[1] There are about three to five generations per year, depending on conditions.[2]
Impact
This species is highly polyphagous: it can feed on a wide variety of plant taxa. It has been found on most every kind of plant except conifers. It is problematic in many kinds of plant crops, including fruits, vegetables, herbs, medicinal plants, fiber plants, oil plants, and ornamental plants.[1] Crops affected include sisal hemp, tea, cotton, mastic, oil palms, neem, and many foods and flowers.[1]
The insect damages the plant by sucking sap, weakening it. The physical damage includes discoloration and deformation of leaves. Flowers and fruits fail to develop. When the insects feed on the fruits they are discolored and warped, reducing their value on the market. Infestations can kill plants, even established trees.[1]
Severe impacts can occur in places where the insect is newly introduced. It was first seen in papaya crops in Queensland in 1988, and it rapidly became the most serious pest in the local industry.[1] It was first found on mangoes in Israel in 1980; now it is established in mango groves throughout the surrounding region and is spreading to other local crops, such as olive and guava.[3] Some groves are doubly infested, also harboring populations of the related red scale (Aonidiella aurantii).[3] It was first found on neem in Cameroon in 1985 and had spread over one million kilometers by 1998, infesting many economically important trees.[4]
Control
Infested twigs, branches, and shoots can be removed from trees, slowing the spread of the scale. Pesticides have been used, but are less popular now as attention turns to biological pest control. There are many natural enemies of the scale which can be reared and released in infested orchards, reducing scale populations.[1]
Natural enemies have been trialed in Queensland's papaya groves. Good results were observed with the parasitoid wasps Comperiella lemniscata and Encarsia citrina.[5] Other insects, such as the larva of the coconut moth (Batrachedra arenosella) and the lady beetles Lindores lophanthae, Chilocorus circumdatus, and C. baileyi have been helpful in severe infestations.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Aonidiella orientalis (Oriental yellow scale). Invasive Species Compendium. CABI.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Aonidiella orientalis (Oriental scale). Arthropods of Economic Importance. World Biodiversity Database. ETI Bioinformatics.
- 1 2 Ofek, G., et al. (1997). The control of the oriental red scale, Aonidiella orientalis Newstead and the California red scale, A. aurantii (Maskell) (Homoptera: Diaspididae) in mango orchards in Hevel Habsor (Israel). Alon Hanotea, 51(5), 212-218.
- ↑ Lale, N. (1998). Neem in the Conventional Lake Chad Basin area and the threat of Oriental yellow scale insect (Aonidiella orientalis Newstead) (Homoptera: Diaspididae). Journal of Arid Environments 40(2) 191–197.
- ↑ Elder, R. J., Smith, D., and Bell, K. L. (1998). Successful parasitoid control of Aonidiella orientalis (Newstead) (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) on Carica papaya L. Australian Journal of Entomology, 37(1), 74-79.
- ↑ Oriental Scale. Department of Agriculture and Fisheries, Queensland.