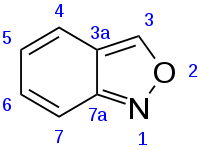
Anthranil
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,1-Benzisoxazole | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.437 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5NO | |
| Molar mass | 119.12 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.183 g/mL[1] |
| Boiling point | 101–102 °C (214–216 °F; 374–375 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  [1] [1] |
| H302[1] | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Anthranil (2,1-benzisoxazole) is an organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, which features a fused benzene-isoxazole bicyclic ring structure. It is an isomer of the more common compounds benzoxazole and benzisoxazole, with the oxygen atom being located in the 3-position. This arrangement disrupts the aromaticity of the molecules by cross-conjugation, making it by far the least stable of the 3 structural isomers.[2]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Sigma-Aldrich Co., Anthranil. Retrieved on 2017-03-02.
- ↑ Domene, Carmen; Jenneskens, Leonardus W.; Fowler, Patrick W. (2005). "Aromaticity of anthranil and its isomers, 1,2-benzisoxazole and benzoxazole". Tetrahedron Letters. 46 (23): 4077–4080. ISSN 0040-4039. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.04.014.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.