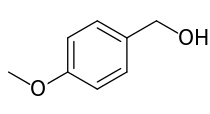
Anisyl alcohol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4-Methoxyphenyl)methanol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(4-Methoxyphenyl)methanol | |
| Other names
4-Methoxybenzyl alcohol; Anise alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.976 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 138.17 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.113 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 22–25 °C (72–77 °F; 295–298 K) |
| Boiling point | 259 °C (498 °F; 532 K) |
| low | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Anisyl alcohol (4-methoxybenzyl alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3OC6H4CH2OH.[1] It is a colorless liquid that is used as a fragrance and flavorant. It occurs naturally but is produced by reduction of anisaldehyde.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.21105859.html
- ↑ Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, , Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe and Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragrances" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2003, Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.