Androgen ester
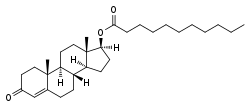
Testosterone undecanoate, one of the most widely used estrogen esters.
An androgen or anabolic steroid ester is an ester of an androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) such as the natural testosterone or dihydrotestosterone (DHT) or the synthetic nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). Esterification renders AAS into metabolically-resistant prohormones of themselves, improving oral bioavailability, increasing lipophilicity, and extending half-life (which necessitates less frequent administration). In addition, with intramuscular injection, AAS esters are absorbed more slowly into the body, further improving half-life. Aside from differences in pharmacokinetics (e.g., duration), these esters essentially have the same effects as the parent drugs.[1] They are used in androgen replacement therapy (ART), among other indications.
See also
- List of androgen esters
- List of androgens/anabolic steroids
- Steroid ester
- Estrogen ester
- Progestogen ester
References
- ↑ Richard Lawrence Miller (2002). The Encyclopedia of Addictive Drugs. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 416–. ISBN 978-0-313-31807-8.
| AR |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.