Great Locomotive Chase

The Great Locomotive Chase or Andrews' Raid was a military raid that occurred on April 12, 1862, in northern Georgia during the American Civil War. Volunteers from the Union Army, led by civilian scout James J. Andrews, commandeered a train and took it northward toward Chattanooga, Tennessee, doing as much damage as possible to the vital Western and Atlantic Railroad (W&A) line from Atlanta to Chattanooga as they went. They were pursued by Confederate forces at first on foot, and later on a succession of locomotives for 87 miles.
Because the Union men had cut the telegraph wires, the Confederates could not send warnings ahead to forces along the railway. Confederates eventually captured the raiders and executed some quickly as spies, including Andrews; some others were able to flee. Some of the raiders were the first to be awarded the Medal of Honor by the US Congress for their actions. As a civilian, Andrews was not eligible.
Background

Major General Ormsby M. Mitchel, commanding Federal troops in middle Tennessee, sought a way to contract or shrink the extent of the northern and western borders of the Confederacy; by pushing them permanently away from; and, out of, contact with the Ohio and Mississippi valleys. This could be done; by first, a southward, and then an eastward penetration from the Union base at Nashville, which would seize and sever the Memphis & Charleston Railroad between Memphis and Chattanooga (at the time there were no other railway links between the Mississippi river and the east) and then capture the water and railway junction of Chattanooga, Tennessee, thereby severing the Western Confederacy's contact with both the Ohio and Mississippi river valleys.
At the time, the standard means of capturing a city was by encirclement to cut it off from supplies and reinforcements, then would follow artillery bombardment and direct assault by massed infantry. However, Chattanooga's natural water and mountain barriers to its east and south made this nearly impossible with the forces that Mitchel had available. But if he could somehow block railroad reinforcement of the city from Atlanta to the southeast, he could take Chattanooga. The Union Army would then have rail reinforcement and supply lines to its rear, leading west to the Union-held stronghold and supply depot of Nashville, Tennessee.

James J. Andrews, a civilian scout and part-time spy, proposed a daring raid to Mitchell that would destroy the Western and Atlantic Railroad as a useful reinforcement and supply link to Chattanooga from Atlanta and the rest of Georgia. He recruited the men known later as "Andrews' Raiders". These were the civilian William Hunter Campbell and 22 volunteer Union soldiers from three Ohio regiments: the 2nd, 21st, and 33rd Ohio Infantry. Andrews instructed the men to arrive in Marietta, Georgia, by midnight of April 10, but heavy rain caused a one-day delay. They traveled in small parties in civilian attire to avoid arousing suspicion. All but two (Samuel Llewellyn and James Smith) reached the designated rendezvous point at the appointed time. Llewellyn and Smith joined a Confederate artillery unit, as they had been instructed to do in such circumstances. Andrews' proposal was a combined operation; General Mitchel and his forces would first move on Chattanooga; then, the Andrews’ Raid would promptly destroy the rail line between Chattanooga and Atlanta. These essentially simultaneous actions would bring about the capture of Chattanooga. Andrews' Raid was intended to deprive the Confederates of the integrated use of the railways to respond to a Union advance, using their interior lines of communication.
When the Union Army threatened Chattanooga, the Confederate States Army would (from its naturally protected rear) first reinforce Chattanooga's garrison from Atlanta. When sufficient forces had been deployed to Chattanooga to stabilize the situation and hold the line, the Confederates would then launch a counterattack from Chattanooga with the advantage of a local superiority of men and materiel. It was this process that the Andrews raid sought to disrupt.
The chase
Because railway dining cars were not yet in common use, railroad timetables included water, rest, and meal stops. In addition, as the locomotives of the time needed to frequently replenish fuel and water, stops for passenger and crew meals were combined with the stops to replenish the locomotive's needs.
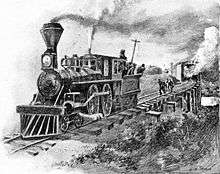
The raid began on April 12, 1862, when the regular morning northbound passenger train from Atlanta, with the locomotive General made its fuel, water, and meal stop at Big Shanty, Georgia (now Kennesaw), on its regular run to Chattanooga. The locomotive would be fully serviced to prepare for the steep graded further north. This time allowed for the passengers and crew to have breakfast at the Lacy Hotel. There Andrews and his raiders hijacked the General and the train's first car. Their plan was to take the train north towards Chattanooga, stopping to damage or destroy track, bridges, telegraph wires, and track switches behind them, so as to prevent the Confederate Army from being able to move troops and supplies from Atlanta to Chattanooga. The Raiders planned to cross through the Federal siege lines on the outskirts of Chattanooga and rejoin Mitchel's army. They chose to capture the train at Big Shanty station because it had no telegraph office. They steamed out of Big Shanty, leaving behind startled passengers, crew members, and onlookers, which included a number of Confederate soldiers from Camp McDonald, directly opposite the Lacy Hotel.
The train's conductor, William Allen Fuller, and two other men, chased the stolen train, first on foot, then by handcar. Locomotives of the time normally averaged 15 miles per hour (24 km/h), with short bursts of an average speed of 20 miles per hour (32 km/h). In addition, the terrain north of Atlanta is very hilly, and the ruling grades are steep. Even today, average speeds are usually never greater than 40 miles per hour (64 km/h) between Chattanooga and Atlanta. Since Andrews intended to stop periodically to perform acts of sabotage, a determined pursuer, even on foot, could conceivably have caught up with the train before it reached Chattanooga.
In his footrace north, Fuller spotted the locomotive Yonah at Etowah and commandeered it, chasing the raiders north all the way to Kingston. There, Fuller switched to the locomotive William R. Smith and continued north towards Adairsville. Two miles south of Adairsville, however, the raiders had destroyed the tracks, and Fuller was forced to continue the pursuit on foot. Beyond the damaged section, he took command of the southbound locomotive Texas at Adairsville, running it backwards, tender-first, northward.[1]
The raiders never got far ahead of Fuller. Destroying the railway behind the hijacked train was a slow process. The raiders were too few in number and were too poorly equipped with the proper railway track tools and demolition equipment, or with suitable igniters and explosives to effectively close the line. Also, the raiders had stolen a regularly scheduled train on its route, and they needed to keep to that train's timetable. If they reached a siding ahead of schedule, they had to wait there until scheduled southbound trains passed them before they could continue north. As well, railway officials in Chattanooga had sufficient time to evacuate engines and rolling stock to the south, hauling critical railroad supplies away from the Union threat, so as to prevent their either being captured by General Mitchel or trapped uselessly inside Chattanooga during a Union siege of the city.
Andrews’ claimed to the station masters he encountered that his train was a special northbound ammunition movement ordered by General Beauregard in support of his operations against the Union forces threatening Chattanooga. This story was sufficient for the isolated station masters Andrews encountered (as he had cut the telegraph wires to the south), but it had no impact upon the train dispatchers and station masters north of him, whose telegraph lines to Chattanooga were working. These dispatchers were following their orders to dispatch and control the special train movements southward at the highest priority.
As the first of the southbound freight evacuation trains approached, Andrews inquired of that train's conductor why his train was carrying a red marker flag on its rear car. Andrews was told that Confederate Railway officials in Chattanooga had been notified by Confederate Army officials that Mitchel was approaching Chattanooga from Stevens, Alabama, intending to either capture or lay siege to the city, and as a result of this warning, the Confederate Military Railways had ordered the Special Freight movements. The red train marker flag on the southbound train meant that there was at least one additional train behind the one which Andrews had just encountered, and that Andrews had no "authority for movement" until the last train of that sectional movement had passed him. This gave Fuller all the time he needed to close the distance.
The raiders considered stopping to attack and overwhelm the first work party they encountered, who were operating a locomotive, the Yonah, at Etowah. If the Yonah had been seized, it could possibly have been run at high speed and derailed, demolished, and/or its boiler deliberately exploded in a tunnel or covered bridge. This would have not only stopped Fuller's pursuit, but it would also have achieved the raiders' mission of closing the line between Marietta and Chattanooga. However, given the size of the Yonah's work party (even though unarmed) relative to the size of the raiding party, Andrews judged that any firefight would be too long and too involved, and would alert nearby troops and civilians.
The Texas train crew had been bluffed by Andrews into taking the station siding, thereby allowing the General to continue northward along the single-track main line. Fuller, when he met the Texas, took command of her, picked up eleven Confederate troops at Calhoun, and continued his pursuit.
With the Texas still chasing the General tender-first, the two trains steamed through Dalton and Tunnel Hill. The raiders continued to sever the telegraph wires, but they were unable to burn bridges or damage Tunnel Hill. The wood they had hoped to burn was soaked by rain.

Finally, at milepost 116.3, north of Ringgold, Georgia, just 18 miles from Chattanooga, with the locomotive out of fuel, Andrews' men abandoned the General and scattered. Andrews and all of his men were caught within two weeks, including the two who had missed the hijacking.
Aftermath

Confederate forces charged all the raiders with "acts of unlawful belligerency"; the civilians were charged as unlawful combatants and spies. All the prisoners were tried in military courts, or courts-martial. Tried in Chattanooga, Andrews was found guilty. He was executed by hanging on June 7 in Atlanta. On June 18, seven others who had been transported to Knoxville and convicted as spies were returned to Atlanta and also hanged; their bodies were buried unceremoniously in an unmarked grave (they were later reburied in Chattanooga National Cemetery).
Writing about the exploit, Corporal William Pittenger said that the remaining raiders worried about also being executed. They attempted to escape and eight succeeded. Traveling for hundreds of miles in pairs, they all made it back safely to Union lines, including two who were aided by slaves and Union sympathizers and two who floated down the Chattahoochee River until they were rescued by the Union blockade vessel USS Somerset. The remaining six were held as prisoners of war and exchanged for Confederate prisoners on March 17, 1863.
Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton awarded some of the raiders with the first Medal of Honor. Private Jacob Wilson Parrott, who had been physically abused as a prisoner, was awarded the first. Later, all but two of the other soldiers who had participated in the raid also received the medal, with posthumous awards to families for those who had been executed. As civilians, Andrews and Campbell were not eligible.
Raiders
| Image | Rank | Name | Unit | Date of Medal of Honor award | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
James J. Andrews (c. 1829 – 1862) | No award | Hanged in Atlanta; ineligible as a civilian for the Medal of Honor | ||
 |
Private | William Bensinger (1840–1918) | 21st Ohio | March 25, 1863 | Exchanged; later promoted to captain |
 |
Private | Wilson W. Brown (1837–1916) | 21st Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Escaped; later promoted to 2nd lieutenant |
 |
Private | Robert Buffum (1828–1871) | 21st Ohio | March 25, 1863 | Exchanged; later promoted to 2nd lieutenant |
 |
William Hunter Campbell (1839–1862) | No award | Hanged; ineligible as a civilian for the Medal of Honor | ||
 |
Corporal | Daniel Allen Dorsey (1838–1918) | 33rd Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Escaped; later promoted to 1st lieutenant |
 |
Corporal | Martin Jones Hawkins (1830–1886) | 33rd Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Overslept and did not participate; escaped; later promoted to sergeant |
 |
Private | William James Knight (1837–1916) | 21st Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Escaped |
| Corporal | Samuel Llewellyn (1841–1915) | 33rd Ohio | No award | Did not participate; enlisted in a Confederate unit before reaching Marietta; later promoted to sergeant | |
 |
Sergeant | Elihu H. Mason (1831–1896) | 21st Ohio | March 25, 1863 | Exchanged; later promoted to captain |
 |
Private | Jacob Parrott (1843–1908) | 33rd Ohio | March 25, 1863 | Exchanged; later promoted to 1st lieutenant |
 |
Corporal | William Pittenger (1840–1904) | Company G, 2nd Ohio Infantry Regiment | March 25, 1863 | Exchanged; later promoted to Sergeant. |
 |
Private | John Reed Porter (1838–1923) | 21st Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Overslept and did not participate; escaped; later promoted to 1st lieutenant; last living raider |
 |
Corporal | William H. H. Reddick (1840–1903) | 33rd Ohio | March 25, 1863 | Exchanged; later promoted to 2nd lieutenant |
 |
Private | Samuel Robertson (1843–1862) | 33rd Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Hanged as a spy; received award posthumously |
 |
Sergeant Major | Marion A. Ross (1832–1862) | 2nd Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Hanged as a spy; received award posthumously |
 |
Sergeant | John Morehead Scott (1839–1862) | 21st Ohio | August 4, 1866 | Hanged as a spy; received award posthumously |
 |
Private | Charles Perry Shadrack (1840–1862) | 2nd Ohio | No award | Hanged as a spy; real name was Phillip Gephart Shadrach
MOH authorized under Public Law January 28, 2008 (H.R. 4986; sec 564), however, by omission, this was not awarded. |
 |
Private | Samuel Slavens (1831–1862) | 33rd Ohio | July 28, 1883 | Hanged as a spy; received award posthumously |
| Private | James Smith (1844–1868), born Ovid Wellford Smith | 2nd Ohio | July 6, 1864 | Did not participate; enlisted in a Confederate unit before reaching Marietta, but was held prisoner in Swims Jail during the Raid;[2] later promoted to corporal | |
 |
Private | George Davenport Wilson (1830–1862) | 2nd Ohio | No award | Hanged as a spy
MOH authorized under Public Law January 28, 2008 (H.R. 4986; sec 565) however, by omission, this was not awarded. |
 |
Private | John Alfred Wilson (1832–1904) | 21st Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Escaped |
 |
Private | John Wollam (1840–1890) | 33rd Ohio | July 20, 1864 | Escaped |
 |
Private | Mark Wood (1839–1866) | 21st Ohio | September 17, 1863 | Escaped; later promoted to 2nd lieutenant |
In popular culture
- The pursuit of Andrews' Raiders was featured in the Buster Keaton silent film comedy The General (1926).
- The Walt Disney dramatic film The Great Locomotive Chase (1956), starring Fess Parker as Andrews, was also based on these exploits.
- Robert W. Smith wrote a piece for concert band named for the incident.
- The Great Locomotive Chase Festival, held annually in Adairsville, Georgia, commemorates the event.[3]
Monument and markers
_(14759595895).jpg)

The Ohio Monument dedicated to Andrews' Raiders is located at the Chattanooga National Cemetery. There is a scale model of the General on top of the monument, and a brief history of the Great Locomotive Chase. The General is now in the Southern Museum of Civil War and Locomotive History, Kennesaw, Georgia, while the Texas is on display at the Atlanta Cyclorama.
One marker indicates where the chase began, near the Big Shanty Museum (now known as Southern Museum of Civil War and Locomotive History) in Kennesaw, while another shows where the chase ended at Milepost 116.3, north of Ringgold — not far from the recently restored depot at Milepost 114.5.
Historic sites along the 1862 chase route include:
- marker near Big Shanty Museum
- Big Shanty Village Historic District
- Camp McDonald
- Acworth Downtown Historic District
- Tarleton Moore House
- Grand Theater (Cartersville, Georgia)
- Old Bartow County Courthouse, now the Bartow History Museum, built so close to the railroad that court was interrupted when any train passed, not built until 1869
- Adairsville Historic District
- the Calhoun Depot, built in 1852-53, at Calhoun, 10 miles north of Adairsville.[4]
- Calhoun Downtown Historic District
- William Taylor House (Resaca, Georgia), associated with northern Georgia soldiers who fought for the Union in the Civil War, though house not built until 1913
- Masonic Lodge No. 238, not built until 1915
- Dalton Commercial Historic District
- Western and Atlantic Depot, Dalton, Georgia
- Crown Mill Historic District
- Western and Atlantic Railroad Tunnel at Tunnel Hill
- Ringgold Gap Battlefield, gap between White Oak Mountain and Taylor Ridge through which railway runs, site of November 1863 battle protecting Confederate retreat after Battle of Missionary Ridge at Chattanooga
- Ringgold Depot
- Ringgold Commercial Historic District
- marker at milepost 116.3
Kennesaw House, 21 Depot St. (c.1845), a hotel on the L&N railway in Marietta, Georgia, is a contributing building in the Northwest Marietta Historic District. In 1862 this was the Fletcher House hotel where Andrews' Raiders stayed the night before commandeering The General.[5]
Finally, there is a historic marker in downtown Atlanta, at the corner of 3rd and Juniper streets, at the site where Andrews was hanged.
Bibliography
- Daring and Suffering: A History of the Great Railroad Adventure, Lieut. William Pittenger (J. W. Daughaday, 1863)
- Daring and Suffering: A History of the Andrews Railroad Raid, by William Pittenger, with Introduction by Col. James G. Bogle, (Cumberland House Publishing, August 1, 1999, ISBN 978-1-58182-034-8), a first-hand account of one of the Raiders, with an introduction by one of the foremost experts on the subject.
- Wild Train: The Story of the Andrews Raiders, by Charles O'Neill, (Random House, 1959), long considered one of the most authoritative accounts of the Raid.
- The Case of Private Smith and the Remaining Mysteries of the Andrews Raid, by Parlee C. Gross, (General Publishing Company, 1963) focuses on the fates of the three soldiers who started off with the rest of the company but did not reach Marietta—Ovid Wellford "James" Smith and Samuel Llewellyn, who joined a Confederate unit as directed by Andrews when they were stopped and sharply questioned en route, and an unknown third soldier.
- Stealing the General: The Great Locomotive Chase and the First Medal of Honor, by Russell S. Bonds, (Westholme Publishing, October 15, 2006, ISBN 1-59416-033-3)
- The Great Locomotive Chase – The Andrews Raid 1862 by Gordon L. Rottman; Osprey Raid Series #5 (Osprey Publishing, November 2009, ISBN 978-1-84603-400-8)
See also
References
- ↑ On this Date in Civil War History: The Great Locomotive Chase - April 12, 1862, This Week in the Civil War website
- ↑ James Smith Great Locomotive Chase
- ↑ Cartersville-Bartow County CVB, Adairsville, Georgia Archived 2014-02-07 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Kenneth H. Thomas, Jr. (June 22, 1982). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory/Nomination: Calhoun Depot" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved August 10, 2016. with nine photos from 1981
- ↑ David T. Agnew and Elizabeth Z. Macgregor, (April 7, 1975). "National Register of Historic Places Registration: Northwest Marietta Historic District" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved September 11, 2016. with 18 photos from 1974-75; #16 shows Kennesaw House
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Great Locomotive Chase. |
- The Great Locomotive Chase
- "A Memorable Raid". The Indianapolis News. 15 February 1886. p. 1. Retrieved August 11, 2014 – via Newspapers.com.

- A collection of links on the Great Locomotive Chase
- Official website of Southern Museum of Civil War and Locomotive History in Kennesaw GA
- The Great Locomotive Chase, story of Andrews Raiders Informative page about the raid including photos, a map and links.
- Railfanning.org: The Andrews Raid
- On this Date in Civil War History: The Great Locomotive Chase - April 12, 1862
- 1911 reunion photograph of the 33rd OVI featuring two of the Andrews Raiders {Dorsey and Llewellyn}