Yosemite toad
| Yosemite toad | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult female in Kings Canyon | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Bufonidae |
| Genus: | Anaxyrus |
| Species: | A. canorus |
| Binomial name | |
| Anaxyrus canorus (Camp, 1916) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Bufo canorus Camp, 1916 | |
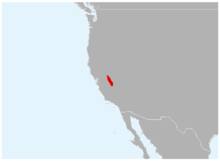
The Yosemite toad (Anaxyrus canorus, formerly Bufo canorus) is a species of true toad in the family Bufonidae. Endemic to the Sierra Nevada of California, the species ranges from the Alpine County to Fresno County. Yosemite toads show an elevational range of 1,950–3,445 m (6,398–11,302 ft) asl.[1][2]
Description
They are the most sexually dichromatic anuran in North America, with males and females displaying strikingly divergent patterns and coloration at maturity.[3] Adult toads are long-lived with upper age limit at least 15 years,[3][4] likely an adaptation to their seasonal, high-elevation environment.
Ecology
The Yosemite toad utilizes montane meadows, sub-alpine meadows, riparian areas, and the surrounding forest matrix. They have been found to move up to 1.26 kilometers from their breeding groun[5]ds. They are explosive breeders, migrating to breeding pools and flooded areas in late spring while snowbanks still veil the frozen meadows. Males intermittently give an advertisement call from pool margins, under logs, or inside willows to attract females. Their specific name, canorus (meaning "melodious"), reflects the tuneful and pleasant sound produced by this species.[6] When females arrive, they are immediately grasped in amplexus by one or multiple males as the males fight for a limited number of mating opportunities. Breeding sex ratios can be very skewed toward males[3][4] since females may not breed every years.[6] While in amplexus, females will lay one or more clutches of 1,500 to 2,000 eggs. Females remain for few days, males for few weeks.[4][6]
Conservation
Yosemite toads have declined substantially in distribution and abundance across their restricted range. They are assesses as "Endangered" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN),[1] are protected by the Endangered Species Act (ESA),[7] and are a California species of special concern.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 Geoffrey Hammerson, Rob Grasso, Carlos Davidson (2004). "Anaxyrus canorus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2004: e.T3180A9659674. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ Frost, Darrel R. (2015). "Anaxyrus canorus (Camp, 1916)". Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Anaxyrus canorus Yosemite Toad". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Anaxyrus canorus Yosemite Toad". AmphibiaWeb: Information on amphibian biology and conservation. [web application]. Berkeley, California: AmphibiaWeb. 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ Liang, C.T. 2010. Habitat modeling and movements of the Yosemite toad (Anaxyrus (=Bufo) canorus) in the Sierra Nevada, California. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California, Davis. (September) 126 pp.
- 1 2 3 4 Nafis, Gary (2000–2015). "Yosemite Toad - Anaxyrus canorus". A Guide to the Amphibians and Reptiles of California (http://www.californiaherps.com/). Retrieved 19 December 2015. External link in
|work=(help) - ↑ "Three California Amphibians to Get Federal Protections under the Endangered Species Act". U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 25 April 2014. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
